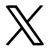Examples demonstrate the selection of compressed air flowmeter
2021-04-21
In our country, the standard status of gas is generally defined as 20℃, 101.325KPa (for coal gas, our standard status is 0℃, 101.325KPa), and the flow of fluid in standard state is defined as the standard condition flow. Compressed air flow meter selection (standard condition unit: Nm3/h, working condition unit: m3/h) must pay attention to the selection of some coefficients, pay attention to conversion.
Conversion according to the equation of state: the standard flow rate and the working condition flow rate are the temperature and pressure of the gas.
Usually, the flow we say is the flow of the standard condition state in order to facilitate a unified unit; The actual flow recorded by the factory operation is basically the flow under the working condition.
Take gas as compressed air for example (example of conversion from standard flow rate to operating flow rate) :
The rated gas production of the air compressor is 2 cubic meters per minute, and the pipeline pressure is 8 kilograms. What is the actual flow rate of the pipeline?
Rough calculation, assuming the compressed air temperature of 20 degrees, then the operating flow rate =2/(0.8+0.101325)*0.101325=0.2248 cubic meters/min =1.3488 m3/h
0.101325 is the absolute pressure of the atmosphere. 0.8 is the pipeline pressure, and the unit is MPa
The calculation formula of standard condition to working condition is: (standard method) gas equation of state: PV=nRT
Conversion formula of working condition and standard condition: P ×V × T =P ×V /T standard
It follows that:
P standard: standard condition pressure, unit Kpa, standard atmospheric pressure value =101.325Kpa
V: standard condition flow, unit m3/h
T scale: standard condition temperature, unit Kelvin K, value 273.15K (0℃)
P: working condition pressure = (gauge pressure Mpa×1000+P now) Kpa. Present: the actual atmospheric pressure on site, approximate standard atmospheric pressure value =101.325Kpa
V worker: operating flow
T worker: operating temperature = (actual temperature ℃+273.15) K. Temperature conversion: K= actual temperature ℃+273.15
Simple calculation formula:
Fast approximate conversion formula: standard flow rate = working condition flow rate × (working pressure kgf/cm2+1)
That is: standard condition flow rate = working condition flow rate × (pressure KG+1)
For example, the flow rate of the air compressor is 30 cubic meters per minute and the pressure is 8kg. Pipe: DN80.
Because the air intake of the compressor is the standard condition (Nm3/h)
So 30 Nm3/min is equal to 1,800 Nm3/h
With 8kg pressure and flow rate of 1800Nm3/h, the approximate calculation is:
Flow rate (m3/h) =1800÷ (8+1) =200 (m3/h)
According to the calculation, the flow rate of compressed air under the standard condition is 1800 Nm3/h. Flow rate: 200m3/h.
According to your design, the pipe diameter is DN80.
Commonly used flowmeters for measuring compressed air are vortex flowmeters, precession vortex flowmeters, and thermal gas mass flowmeters (only show the standard condition).
DN80 LUGB Vortex flowmeter Common flow range: 86-1100 m3/h (working condition)
DN80 ATLQ precession vortex flowmeter Common flow range: 28-400 m3/h (working condition)
DN80 ATFM thermal gas flowmeter Common flow range: 1.8-1800 Nm3/h (standard condition)
According to the flow range of the flow meter: in line with DN80 pipeline, the compressor is 30 cubic meters per minute, the pressure is 8kg, and the flow meter is more suitable for DN80 precession vortex flowmeter. Then choose vortex flowmeter.
Share To:
News
- Why is the thermal gas mass flowmeter not affected by pressure strength and temperature?
- What to do when a thermal gas mass flow meter fails?
- How are thermal gas mass flow meters used? What are the applications?
- Under what circumstances is the gas measurement need to be regulated compensated vortex flowmeter
- Why Is The Aister Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter So Popular ?
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturers explain their main advantages in measurement
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturer Aister instrument field experience summary
- Aister Instrument Empowerment Conference