What are the classifications of radar level gauge antennas
2024-03-19
Radar level gauges use different types of antennas based on the specific application requirements and the characteristics of the measured medium. The choice of antenna influences factors such as beam angle, focusing capability, and the ability to handle various tank conditions. Here are some common classifications of radar level gauge antennas:
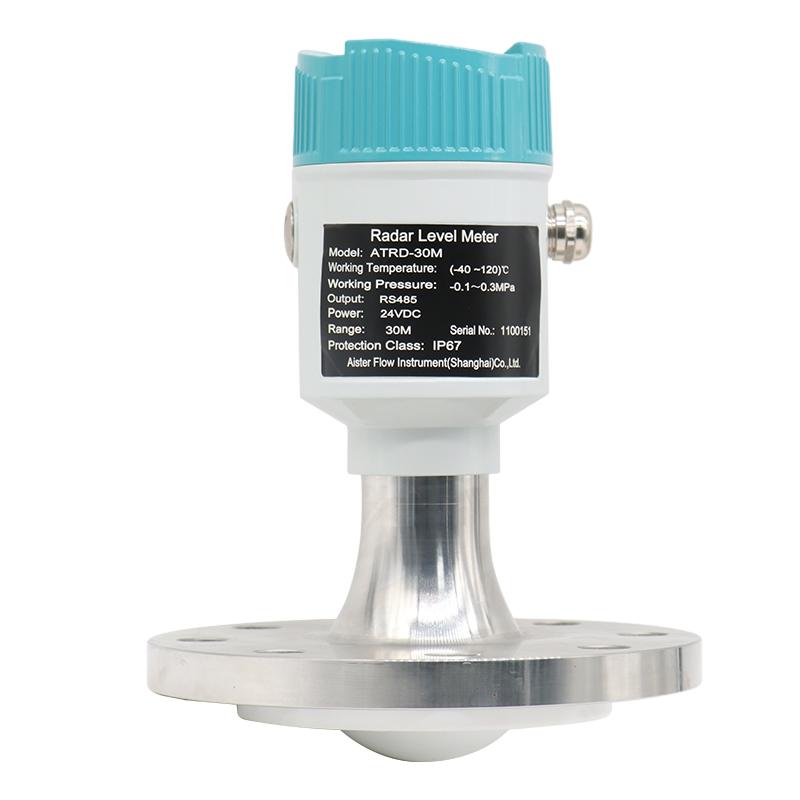

Horn Antenna:
Horn antennas are widely used in radar level gauges. They have a flared, horn-shaped structure and are known for their wide beam angles. Horn antennas are suitable for applications where a broad beam is required to cover a large surface area, or when dealing with materials that may cause signal reflections.
Parabolic Antenna:
Parabolic antennas are characterized by their dish-like shape with a curved reflective surface. These antennas are used when a narrow beam angle and high directivity are essential for accurate and focused level measurements. Parabolic antennas are particularly effective in applications where precision is critical.
Planar Array Antenna:
Planar array antennas consist of multiple radiating elements arranged in a flat or planar structure. They offer flexibility in beam shaping and can be used to create different beam patterns. Planar array antennas are suitable for applications with specific geometric constraints or where a customized beam shape is required.
Slot Antenna:
Slot antennas are characterized by a narrow, elongated slot cut into a conducting surface. They are commonly used in radar level gauges for applications with limited space. Slot antennas provide a compromise between beam width and directivity, making them suitable for various tank configurations.
Dipole Antenna:
Dipole antennas consist of two conductive elements, typically a pair of wires or rods. They are often used in radar level gauges for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Dipole antennas may have a broader beam angle compared to other types, making them suitable for applications where a wider coverage area is required.
Patch Antenna:
Patch antennas are flat, compact antennas that consist of a conducting patch on a dielectric substrate. They are known for their low profile and are commonly used in radar level gauges where space constraints are a concern. Patch antennas can be designed for specific frequency bands and offer good directional characteristics.
Conical Horn Antenna:
Conical horn antennas have a tapered, cone-shaped structure. They provide a compromise between the wide beam angle of horn antennas and the directivity of parabolic antennas. Conical horn antennas are suitable for applications where moderate directivity and coverage are required.
Hemispherical Antenna:
Hemispherical antennas provide a 180-degree coverage pattern, making them suitable for applications where a wide area needs to be monitored. They are commonly used in radar level gauges for applications where the liquid or solid surface is not well-defined.
The selection of the appropriate antenna type depends on factors such as the tank geometry, the characteristics of the measured medium, and the desired level of measurement precision. It's crucial to consider the specific requirements of the application when choosing a radar level gauge antenna.

Horn Antenna:
Horn antennas are widely used in radar level gauges. They have a flared, horn-shaped structure and are known for their wide beam angles. Horn antennas are suitable for applications where a broad beam is required to cover a large surface area, or when dealing with materials that may cause signal reflections.
Parabolic Antenna:
Parabolic antennas are characterized by their dish-like shape with a curved reflective surface. These antennas are used when a narrow beam angle and high directivity are essential for accurate and focused level measurements. Parabolic antennas are particularly effective in applications where precision is critical.
Planar Array Antenna:
Planar array antennas consist of multiple radiating elements arranged in a flat or planar structure. They offer flexibility in beam shaping and can be used to create different beam patterns. Planar array antennas are suitable for applications with specific geometric constraints or where a customized beam shape is required.
Slot Antenna:
Slot antennas are characterized by a narrow, elongated slot cut into a conducting surface. They are commonly used in radar level gauges for applications with limited space. Slot antennas provide a compromise between beam width and directivity, making them suitable for various tank configurations.
Dipole Antenna:
Dipole antennas consist of two conductive elements, typically a pair of wires or rods. They are often used in radar level gauges for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Dipole antennas may have a broader beam angle compared to other types, making them suitable for applications where a wider coverage area is required.
Patch Antenna:
Patch antennas are flat, compact antennas that consist of a conducting patch on a dielectric substrate. They are known for their low profile and are commonly used in radar level gauges where space constraints are a concern. Patch antennas can be designed for specific frequency bands and offer good directional characteristics.
Conical Horn Antenna:
Conical horn antennas have a tapered, cone-shaped structure. They provide a compromise between the wide beam angle of horn antennas and the directivity of parabolic antennas. Conical horn antennas are suitable for applications where moderate directivity and coverage are required.
Hemispherical Antenna:
Hemispherical antennas provide a 180-degree coverage pattern, making them suitable for applications where a wide area needs to be monitored. They are commonly used in radar level gauges for applications where the liquid or solid surface is not well-defined.
The selection of the appropriate antenna type depends on factors such as the tank geometry, the characteristics of the measured medium, and the desired level of measurement precision. It's crucial to consider the specific requirements of the application when choosing a radar level gauge antenna.
Share To:
News
- Why is the thermal gas mass flowmeter not affected by pressure strength and temperature?
- What to do when a thermal gas mass flow meter fails?
- How are thermal gas mass flow meters used? What are the applications?
- Under what circumstances is the gas measurement need to be regulated compensated vortex flowmeter
- Why Is The Aister Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter So Popular ?
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturers explain their main advantages in measurement
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturer Aister instrument field experience summary
- Aister Instrument Empowerment Conference