The Application of Radar Level Meters in Industrial Processes
2023-12-14
In the dynamic landscape of industrial processes, accurate and reliable level measurement is paramount for ensuring operational efficiency, safety, and regulatory compliance. One technology that has significantly contributed to the improvement of level measurement is the Radar Level Meter. This article delves into the applications of radar level meters, exploring their principles, advantages, and diverse use cases across various industries.
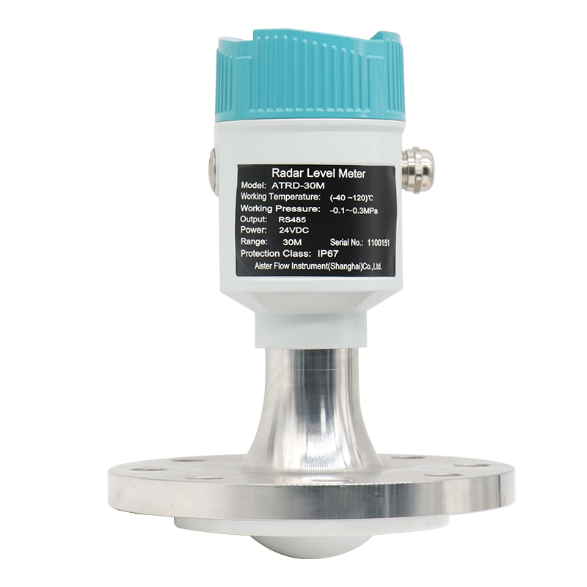

Principles of Operation:
Radar level meters operate on the principle of electromagnetic waves, typically in the microwave frequency range. They emit a radar signal towards the material whose level is to be measured and then analyze the reflected signal. The time taken for the signal to travel to the material and back allows the radar level meter to calculate the distance and, consequently, the level of the material with high precision.
Applications in Industrial Processes:
Liquid Level Measurement:
Tank Farms: Radar level meters find extensive use in tank farms for measuring liquid levels in storage tanks. Industries such as petrochemicals, oil and gas, and water treatment rely on radar level meters to ensure accurate inventory management and prevent overflow or shortages.
Chemical Processing: In chemical plants, radar level meters are employed for monitoring liquid levels in various vessels and reactors. The non-contact nature of radar technology makes it suitable for corrosive or hazardous substances.
Solid Level Measurement:
Silos and Hoppers: Industries dealing with bulk solids, such as agriculture and food processing, utilize radar level meters to monitor material levels in silos and hoppers. This ensures efficient inventory control and prevents issues like material bridging or overfilling.
Mining and Minerals: Radar level meters play a crucial role in measuring the levels of bulk materials like coal, ores, and minerals in mining operations. Their ability to penetrate dust and withstand harsh environmental conditions makes them well-suited for such applications.
Environmental Monitoring:
Water and Wastewater Treatment: Municipalities and industrial facilities utilize radar level meters in water and wastewater treatment plants to monitor the levels of liquid in various treatment basins, ensuring optimal processing and preventing overflows.
River and Reservoir Monitoring: In hydrological applications, radar level meters are employed to measure water levels in rivers, reservoirs, and dams. This information is vital for flood control, water resource management, and environmental monitoring.
Advantages of Radar Level Meters:
Non-Contact Measurement:
Radar level meters operate without physical contact with the material being measured, minimizing wear and tear and reducing the need for maintenance.
Versatility:
Radar technology is versatile and can be applied to measure levels in liquids, bulk solids, and even in challenging environments such as those with extreme temperatures or dust.
High Accuracy:
Radar level meters offer high accuracy and precision, making them suitable for applications where precise level measurements are critical.
Adaptability to Harsh Conditions:
These meters are designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, including temperature variations, corrosive substances, and atmospheric disturbances.
Conclusion:
The application of radar level meters has revolutionized level measurement in industrial processes, providing accurate, reliable, and versatile solutions across a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, radar level meters are expected to further advance, offering enhanced features and capabilities to meet the evolving demands of modern industries. Their role in optimizing processes, ensuring safety, and facilitating environmental monitoring underscores their significance in the industrial landscape.

Principles of Operation:
Radar level meters operate on the principle of electromagnetic waves, typically in the microwave frequency range. They emit a radar signal towards the material whose level is to be measured and then analyze the reflected signal. The time taken for the signal to travel to the material and back allows the radar level meter to calculate the distance and, consequently, the level of the material with high precision.
Applications in Industrial Processes:
Liquid Level Measurement:
Tank Farms: Radar level meters find extensive use in tank farms for measuring liquid levels in storage tanks. Industries such as petrochemicals, oil and gas, and water treatment rely on radar level meters to ensure accurate inventory management and prevent overflow or shortages.
Chemical Processing: In chemical plants, radar level meters are employed for monitoring liquid levels in various vessels and reactors. The non-contact nature of radar technology makes it suitable for corrosive or hazardous substances.
Solid Level Measurement:
Silos and Hoppers: Industries dealing with bulk solids, such as agriculture and food processing, utilize radar level meters to monitor material levels in silos and hoppers. This ensures efficient inventory control and prevents issues like material bridging or overfilling.
Mining and Minerals: Radar level meters play a crucial role in measuring the levels of bulk materials like coal, ores, and minerals in mining operations. Their ability to penetrate dust and withstand harsh environmental conditions makes them well-suited for such applications.
Environmental Monitoring:
Water and Wastewater Treatment: Municipalities and industrial facilities utilize radar level meters in water and wastewater treatment plants to monitor the levels of liquid in various treatment basins, ensuring optimal processing and preventing overflows.
River and Reservoir Monitoring: In hydrological applications, radar level meters are employed to measure water levels in rivers, reservoirs, and dams. This information is vital for flood control, water resource management, and environmental monitoring.
Advantages of Radar Level Meters:
Non-Contact Measurement:
Radar level meters operate without physical contact with the material being measured, minimizing wear and tear and reducing the need for maintenance.
Versatility:
Radar technology is versatile and can be applied to measure levels in liquids, bulk solids, and even in challenging environments such as those with extreme temperatures or dust.
High Accuracy:
Radar level meters offer high accuracy and precision, making them suitable for applications where precise level measurements are critical.
Adaptability to Harsh Conditions:
These meters are designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, including temperature variations, corrosive substances, and atmospheric disturbances.
Conclusion:
The application of radar level meters has revolutionized level measurement in industrial processes, providing accurate, reliable, and versatile solutions across a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, radar level meters are expected to further advance, offering enhanced features and capabilities to meet the evolving demands of modern industries. Their role in optimizing processes, ensuring safety, and facilitating environmental monitoring underscores their significance in the industrial landscape.
Share To:
News
- Why is the thermal gas mass flowmeter not affected by pressure strength and temperature?
- What to do when a thermal gas mass flow meter fails?
- How are thermal gas mass flow meters used? What are the applications?
- Under what circumstances is the gas measurement need to be regulated compensated vortex flowmeter
- Why Is The Aister Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter So Popular ?
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturers explain their main advantages in measurement
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturer Aister instrument field experience summary
- Aister Instrument Empowerment Conference