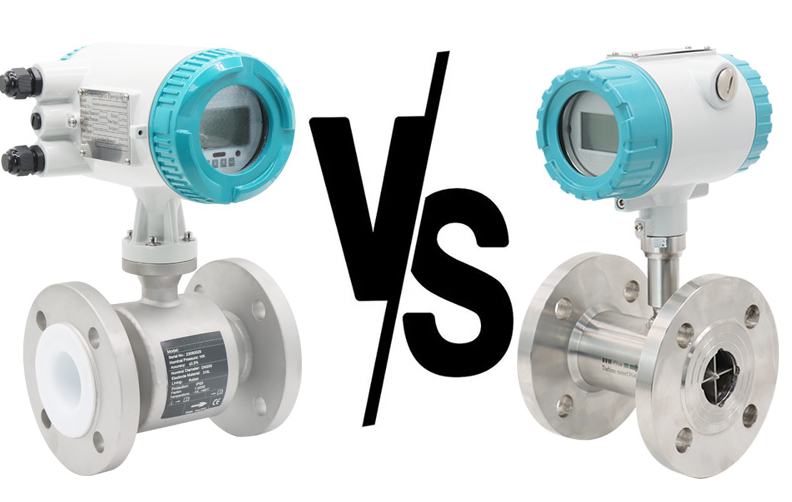
The difference between electromagnetic flowmeter and turbine flowmeter
2024-07-29
Electromagnetic flow meter and Liquid turbine flow meter are both commonly used liquid flowmeters in industrial automation control, but they are significantly different in several aspects. Here are the main differences between the two:
How it works:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: Designed based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. When the conductive liquid moves along the measuring tube in the alternating magnetic field and the magnetic field line moves in the vertical direction, the conductive liquid cuts the magnetic field line to generate the induced potential, which is detected by the two detection electrodes on the measuring tube. Electromagnetic flowmeters are not affected by changes in fluid density, viscosity, temperature, pressure and conductivity.
Turbine flowmeter: A turbine is installed in the center of the flange pipe, and both ends are supported by bearings. As the fluid passes through the pipe, it strikes the turbine blades, causing the turbine to spin. The angular speed of rotation of the turbine is proportional to the flow rate of the fluid, and the liquid flow drives the turbine to rotate, cutting the magnetic field lines generated by the permanent magnetic steel in the housing, creating a magnetic flux change. The sensor coil sends the detected flux periodic change signal to the preamplifier to generate a pulse signal proportional to the flow rate, and the flow value is obtained through the circuit calculation.
Scope of application:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: The measuring medium object must be electrically conductive and suitable for the measurement of corrosive fluids. Because the electromagnetic flowmeter can be lined (rubber, teflon, etc.), it has a wide range of applications.
Turbine flowmeter: Due to the turbine installed in the center of the pipe, it is not suitable for the measurement of fluids with impurities or corrosive, otherwise the turbine flowmeter may not work properly due to impurity adsorption/entanglement or corrosion, affecting the service life.
Accuracy and stability:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: The converter adopts novel excitation mode, low power consumption, zero stability and high accuracy. Flow range up to 150:1.
Turbine flowmeter: with high precision measurement characteristics, high measurement accuracy, generally up to ±0.5%FS, and even up to ±0.2%FS.
Features:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: no obstructing flow parts in the measuring tube, no pressure loss, and low requirements in the straight pipe section. Reasonable selection of sensor lining and electrode material, that is, it has good corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Turbine flowmeter: simple structure, easy maintenance. However, it is sensitive to solid particles and bubbles in the medium and is susceptible to interference.
Price:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: The price is relatively high, but it has a wider applicability and higher stability.
Turbine flowmeter: If high precision is not required and you want an affordable price, turbine flowmeter is an option. However, it should be noted that the applicable pipe diameter of the turbine flowmeter is generally below DN200, and more than DN200 may need to be customized by the manufacturer.
In summary, there are significant differences between electromagnetic flowmeters and turbine flowmeters in terms of working principle, scope of application, accuracy and stability, characteristics and price. In the selection, should be based on the actual needs and media characteristics for comprehensive consideration.
If you want to know more about the flow meter or flow meter selection, please consult the Aister flow meter manufacturer email: sales@aistermeter.com for help.
Electromagnetic flowmeter: Designed based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. When the conductive liquid moves along the measuring tube in the alternating magnetic field and the magnetic field line moves in the vertical direction, the conductive liquid cuts the magnetic field line to generate the induced potential, which is detected by the two detection electrodes on the measuring tube. Electromagnetic flowmeters are not affected by changes in fluid density, viscosity, temperature, pressure and conductivity.
Turbine flowmeter: A turbine is installed in the center of the flange pipe, and both ends are supported by bearings. As the fluid passes through the pipe, it strikes the turbine blades, causing the turbine to spin. The angular speed of rotation of the turbine is proportional to the flow rate of the fluid, and the liquid flow drives the turbine to rotate, cutting the magnetic field lines generated by the permanent magnetic steel in the housing, creating a magnetic flux change. The sensor coil sends the detected flux periodic change signal to the preamplifier to generate a pulse signal proportional to the flow rate, and the flow value is obtained through the circuit calculation.
Scope of application:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: The measuring medium object must be electrically conductive and suitable for the measurement of corrosive fluids. Because the electromagnetic flowmeter can be lined (rubber, teflon, etc.), it has a wide range of applications.
Turbine flowmeter: Due to the turbine installed in the center of the pipe, it is not suitable for the measurement of fluids with impurities or corrosive, otherwise the turbine flowmeter may not work properly due to impurity adsorption/entanglement or corrosion, affecting the service life.
Accuracy and stability:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: The converter adopts novel excitation mode, low power consumption, zero stability and high accuracy. Flow range up to 150:1.
Turbine flowmeter: with high precision measurement characteristics, high measurement accuracy, generally up to ±0.5%FS, and even up to ±0.2%FS.
Features:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: no obstructing flow parts in the measuring tube, no pressure loss, and low requirements in the straight pipe section. Reasonable selection of sensor lining and electrode material, that is, it has good corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Turbine flowmeter: simple structure, easy maintenance. However, it is sensitive to solid particles and bubbles in the medium and is susceptible to interference.
Price:
Electromagnetic flowmeter: The price is relatively high, but it has a wider applicability and higher stability.
Turbine flowmeter: If high precision is not required and you want an affordable price, turbine flowmeter is an option. However, it should be noted that the applicable pipe diameter of the turbine flowmeter is generally below DN200, and more than DN200 may need to be customized by the manufacturer.
In summary, there are significant differences between electromagnetic flowmeters and turbine flowmeters in terms of working principle, scope of application, accuracy and stability, characteristics and price. In the selection, should be based on the actual needs and media characteristics for comprehensive consideration.
If you want to know more about the flow meter or flow meter selection, please consult the Aister flow meter manufacturer email: sales@aistermeter.com for help.
Share To:
News
- Why is the thermal gas mass flowmeter not affected by pressure strength and temperature?
- What to do when a thermal gas mass flow meter fails?
- How are thermal gas mass flow meters used? What are the applications?
- Under what circumstances is the gas measurement need to be regulated compensated vortex flowmeter
- Why Is The Aister Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter So Popular ?
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturers explain their main advantages in measurement
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturer Aister instrument field experience summary
- Aister Instrument Empowerment Conference