What is the difference between ultrasonic flow meter and electromagnetic flow meter?
2023-12-14
Flow measurement is a critical aspect in various industrial processes, water management systems, and other applications where the accurate monitoring of fluid flow is essential. Two prominent technologies employed for this purpose are ultrasonic flow meter and electromagnetic flow meter. This essay aims to explore the differences between these two types of flow measurement devices, highlighting their principles of operation, advantages, limitations, and application areas.


Principles of Operation:
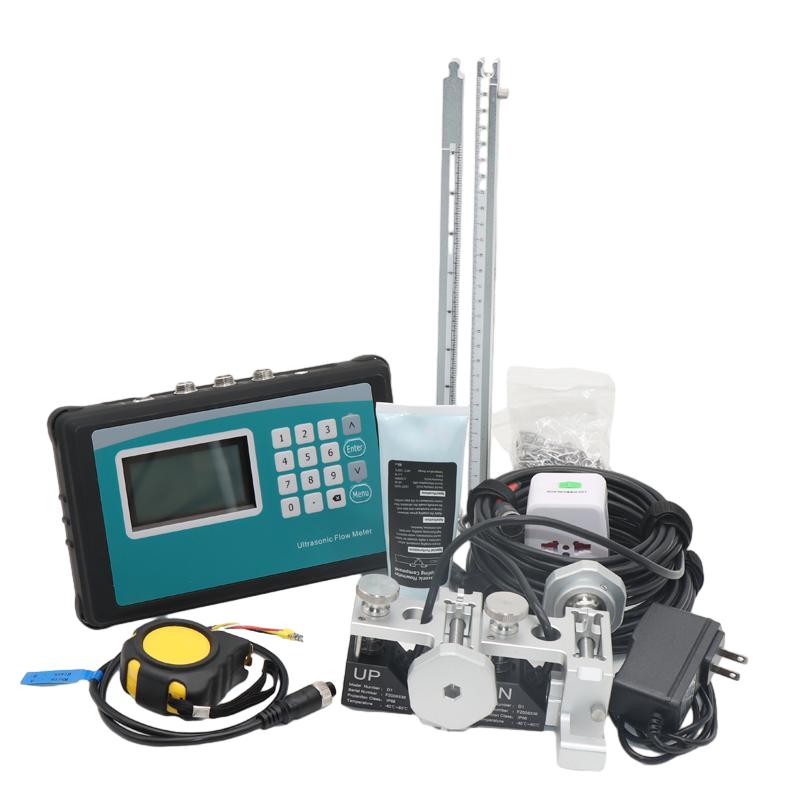
Ultrasonic Flowmeters:
Ultrasonic flowmeters utilize the principle of ultrasonic waves to measure the flow rate of fluids. These devices employ ultrasonic transducers that generate ultrasonic waves and measure the time it takes for these waves to travel between transducers in the upstream and downstream directions. By analyzing the time-of-flight and velocity of the ultrasonic waves, the flow rate of the fluid can be accurately determined.
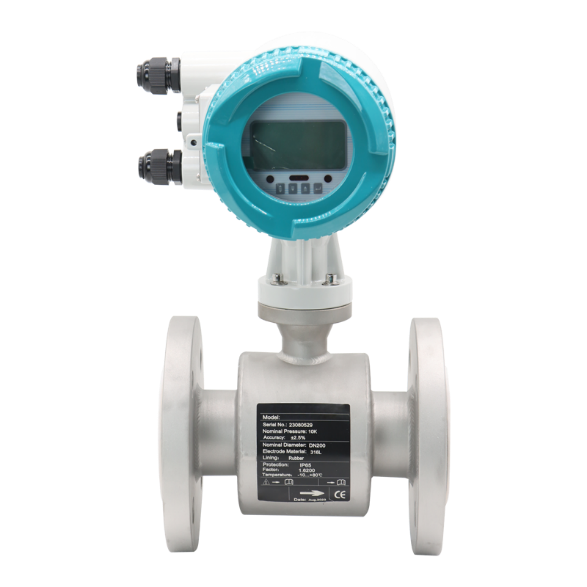
Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Electromagnetic flowmeters, on the other hand, operate based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. These flowmeters consist of a pipe through which the fluid flows and electrodes placed on the pipe walls. When a conductive fluid flows through a magnetic field created by the flowmeter, a voltage is induced across the electrodes proportional to the velocity of the fluid. The magnitude of this induced voltage is directly related to the flow rate.
Advantages and Limitations:
Ultrasonic Flowmeters:
Advantages:
Non-intrusive: Ultrasonic flowmeters do not require direct contact with the fluid, making them suitable for applications with corrosive or abrasive fluids.
Versatility: These flowmeters can be used for both liquids and gases.
Wide turndown ratio: Ultrasonic flowmeters can handle a broad range of flow rates.
Limitations:
Cost: Ultrasonic flowmeters can be more expensive compared to some other flow measurement technologies.
Installation complexity: Achieving accurate measurements may require careful installation and positioning of transducers.
Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Advantages:
High accuracy: Electromagnetic flowmeters provide precise measurements, especially for conductive fluids.
Low maintenance: With no moving parts and no obstruction to flow, electromagnetic flowmeters require minimal maintenance.
Suitable for various applications: They are ideal for applications involving clean, conductive fluids.
Limitations:
Unsuitable for non-conductive fluids: Electromagnetic flowmeters are not effective for fluids with low conductivity.
Size limitations: Large pipe diameters may pose challenges for installation and calibration.
External magnetic interference: Strong external magnetic fields can affect the accuracy of measurements.
Applications:
Ultrasonic Flowmeters:
Commonly used in water and wastewater management.
Suitable for applications with various fluid types, including chemicals and oils.
Widely employed in the oil and gas industry for custody transfer applications.
Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Widely used in water and wastewater treatment plants.
Commonly applied in industries dealing with conductive fluids, such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Found in applications where accuracy and low maintenance are critical.
In conclusion, both ultrasonic flowmeters and electromagnetic flowmeters play crucial roles in fluid flow measurement, each with its unique set of advantages and limitations. The selection between these technologies depends on factors such as the characteristics of the fluid, the application requirements, and budget considerations. As technology advances, ongoing research and development are likely to further enhance the capabilities and widen the scope of these flow measurement devices.


Principles of Operation:
Ultrasonic Flowmeters:
Ultrasonic flowmeters utilize the principle of ultrasonic waves to measure the flow rate of fluids. These devices employ ultrasonic transducers that generate ultrasonic waves and measure the time it takes for these waves to travel between transducers in the upstream and downstream directions. By analyzing the time-of-flight and velocity of the ultrasonic waves, the flow rate of the fluid can be accurately determined.
Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Electromagnetic flowmeters, on the other hand, operate based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. These flowmeters consist of a pipe through which the fluid flows and electrodes placed on the pipe walls. When a conductive fluid flows through a magnetic field created by the flowmeter, a voltage is induced across the electrodes proportional to the velocity of the fluid. The magnitude of this induced voltage is directly related to the flow rate.
Advantages and Limitations:
Ultrasonic Flowmeters:
Advantages:
Non-intrusive: Ultrasonic flowmeters do not require direct contact with the fluid, making them suitable for applications with corrosive or abrasive fluids.
Versatility: These flowmeters can be used for both liquids and gases.
Wide turndown ratio: Ultrasonic flowmeters can handle a broad range of flow rates.
Limitations:
Cost: Ultrasonic flowmeters can be more expensive compared to some other flow measurement technologies.
Installation complexity: Achieving accurate measurements may require careful installation and positioning of transducers.
Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Advantages:
High accuracy: Electromagnetic flowmeters provide precise measurements, especially for conductive fluids.
Low maintenance: With no moving parts and no obstruction to flow, electromagnetic flowmeters require minimal maintenance.
Suitable for various applications: They are ideal for applications involving clean, conductive fluids.
Limitations:
Unsuitable for non-conductive fluids: Electromagnetic flowmeters are not effective for fluids with low conductivity.
Size limitations: Large pipe diameters may pose challenges for installation and calibration.
External magnetic interference: Strong external magnetic fields can affect the accuracy of measurements.
Applications:
Ultrasonic Flowmeters:
Commonly used in water and wastewater management.
Suitable for applications with various fluid types, including chemicals and oils.
Widely employed in the oil and gas industry for custody transfer applications.
Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Widely used in water and wastewater treatment plants.
Commonly applied in industries dealing with conductive fluids, such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Found in applications where accuracy and low maintenance are critical.
In conclusion, both ultrasonic flowmeters and electromagnetic flowmeters play crucial roles in fluid flow measurement, each with its unique set of advantages and limitations. The selection between these technologies depends on factors such as the characteristics of the fluid, the application requirements, and budget considerations. As technology advances, ongoing research and development are likely to further enhance the capabilities and widen the scope of these flow measurement devices.
Share To:
News
- Why is the thermal gas mass flowmeter not affected by pressure strength and temperature?
- What to do when a thermal gas mass flow meter fails?
- How are thermal gas mass flow meters used? What are the applications?
- Under what circumstances is the gas measurement need to be regulated compensated vortex flowmeter
- Why Is The Aister Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter So Popular ?
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturers explain their main advantages in measurement
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturer Aister instrument field experience summary
- Aister Instrument Empowerment Conference