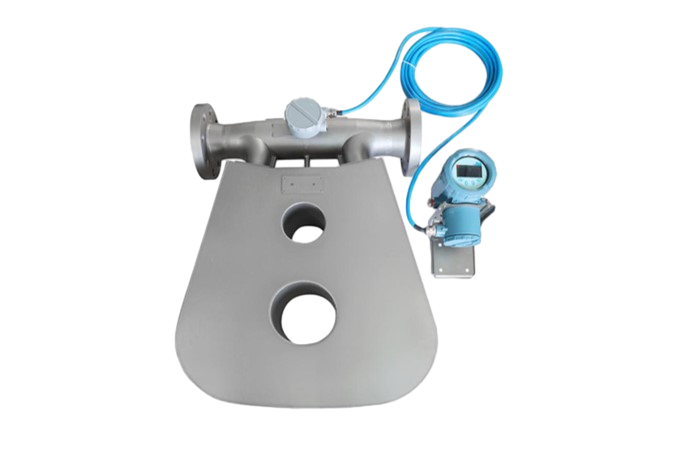
High viscosity flow meter
2024-06-19
1. Types of high-viscosity fluid flowmeters
High viscosity flow meters are flow measuring instruments designed for the measurement of high viscosity fluids. Common types include rotor flowmeters, positive displacement flowmeters (such as elliptical gear flowmeters), Coriolis flowmeters, etc. Each of these flowmeters has its own characteristics and is suitable for different high-viscosity fluid measurement scenarios.
(1) Elliptic gear flow meter: The elliptic gear flowmeter is especially suitable for the measurement of high viscosity media. The standard viscosity range is usually 0.6 to 200mPa·s, while some specially designed high-viscosity flowmeters can be extended to a viscosity range of 200 to 1000mPa·s.
(2) Circular gear flow meter: This flowmeter is especially suitable for small flow, even small flow measurement, its measurement range can be as low as 200L per hour or less. The circular gear flowmeter is suitable for measuring fluids with higher viscosity, and its viscosity range is about 1~25000m ² /s.
(3) Wedge flow meter: Wedge flowmeter is especially suitable for the flow measurement of high viscosity liquids, vapors and gases containing suspended matter. Its viscosity measurement range can be up to 500mPa·s, such as fuel oil, residual oil and heavy oil. In addition, the wedge flowmeter can also be applied to the flow measurement of liquid-solid mixtures containing suspended particles, such as slurry fluids, sewage, etc.
(4) The Coriolis mass flow meter can directly measure the mass of the fluid, and its measurement principle is not affected by the physical characteristics of the fluid, including viscosity and density. This means that Corrioli mass flowmeters are suitable for measuring all kinds of non-Newtonian fluids, all kinds of slurries, suspensions, high viscosity fluids, etc. However, the exact viscosity measurement range may vary depending on the Coriolis mass flowmeter model and specification. Therefore, when selecting and using Coriolis mass flowmeters for viscosity measurement, it is necessary to determine the appropriate model and specification according to the actual application requirements and fluid characteristics, and refer to the corresponding technical specifications or operating manuals to understand the specific measurement range and accuracy and other parameters. 2. Measure the viscosity range
(1) Elliptic gear flow meter: 0.6~200mPa·s (some special designs can reach 200~1000mPa·s)
(2) Circular gear flow meter: 1~25000m㎡/s
(3) Wedge flowmeter: up to 500mPa·s
3. How it works
(1) Rotameter: based on the buoyancy and resistance balance principle of the float in the fluid. When the fluid flows through the flow time, the float is raised by the momentum of the fluid. When the momentum of the float is balanced with the sum of the gravity of the float and the resistance of the fluid to the float, the float is stable at a certain height, and the flow corresponding to the height is the flow of the fluid.
(2) Positive displacement flowmeter: flow measurement by measuring the fixed volume of fluid flow. The positive displacement flowmeter has one or more measuring chambers inside, and when the fluid flows through the measuring chamber, the fluid is transferred from one measuring chamber to another by rotating or reciprocating motion, so as to complete the measurement of flow.
(3) Coriolis flowmeter: Measurement based on Coriolis effect. The fluid flowing in the vibration tube is subjected to the Coriolis force perpendicular to the flow direction, which causes the distortion of the vibration tube. By measuring the deformation of the vibration tube, the flow rate of the fluid can be calculated.
4. Design features
(1) Strong wear resistance: high-viscosity fluids often contain solid particles, and the design of the flow meter needs to consider wear resistance to extend the service life.
(2) Good adaptability: It can adapt to the flow characteristics of high-viscosity fluids at different temperatures.
(3) High measurement accuracy: Advanced measurement principles and technologies are used to ensure the accuracy of measurement under high viscosity fluids.
5. Application field
High viscosity flow meters are widely used in petrochemical, pharmaceutical, food processing, paper making, environmental protection and other industries, for measuring the flow of various high viscosity liquids (such as glue, syrup, paint, polymer solution, etc.).
6. Installation and maintenance
(1) Installation: The flow meter should be installed on the straight pipe section to avoid installation at the outlet of the pump or elbow, valve and other parts that may produce eddy currents. When installing, ensure that the flow meter is concentric with the pipe to avoid stress.
(2) Maintenance: regularly check the operating status of the flow meter, clean the scale and impurities inside the flow meter, and keep the flow meter clean. For parts that need lubrication, lubricating oil should be filled regularly.
7. Performance parameters
(1) Measuring range: The minimum flow and maximum flow range that the flowmeter can measure.
(2) Accuracy: error range of flowmeter measurement results.
(3) Repeatability: consistency of multiple measurement results under the same conditions.
(4) Response time: the response time of the flowmeter to the flow change.
(5) Working pressure: the pressure range within which the flowmeter can work normally.
(6) Operating temperature: the temperature range within which the flowmeter can work normally.
8. Selection guide
(1) Determine the measurement range: Determine the minimum flow rate and maximum flow rate to be measured according to the actual application scenario.
(2) Consider fluid characteristics: understand the viscosity, density, corrosion and other characteristics of high-viscosity fluids, and choose the appropriate flowmeter type.
(3) Consider environmental conditions: understand the temperature, pressure and other environmental conditions of the flowmeter installation location, and choose a flowmeter that can adapt to these conditions.
(4) Reference user evaluation: Understand other users' evaluation of this type of flowmeter, including measurement accuracy, stability, service life, etc.
9. Precautions
(1) Avoid vibration: The installation position of the flow meter should be far away from the vibration source to reduce the impact of vibration on the measurement results.
(2) Avoid electromagnetic interference: For flowmeters using electronic technology (such as Coriolis flowmeters), installation in a strong electromagnetic interference environment should be avoided.
(3) Regular calibration: In order to maintain measurement accuracy, the flow meter should be calibrated regularly.
(4) Pay attention to safety: in the process of installation, maintenance and commissioning, safety operation procedures should be observed to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
Please note that different models and designs of flowmeters may have different measuring ranges and accuracy. In the selection of suitable high-viscosity fluid flow timing, it is necessary to consider the actual application scenario, fluid characteristics and environmental conditions. At the same time, regular calibration and maintenance of the flow meter is also an important measure to ensure measurement accuracy and extend service life.
If you want to know more about the flow meter or flow meter selection, please consult the Aister flow meter manufacturer email: sales@aistermeter.com for help.
High viscosity flow meters are flow measuring instruments designed for the measurement of high viscosity fluids. Common types include rotor flowmeters, positive displacement flowmeters (such as elliptical gear flowmeters), Coriolis flowmeters, etc. Each of these flowmeters has its own characteristics and is suitable for different high-viscosity fluid measurement scenarios.
(1) Elliptic gear flow meter: The elliptic gear flowmeter is especially suitable for the measurement of high viscosity media. The standard viscosity range is usually 0.6 to 200mPa·s, while some specially designed high-viscosity flowmeters can be extended to a viscosity range of 200 to 1000mPa·s.
(2) Circular gear flow meter: This flowmeter is especially suitable for small flow, even small flow measurement, its measurement range can be as low as 200L per hour or less. The circular gear flowmeter is suitable for measuring fluids with higher viscosity, and its viscosity range is about 1~25000m ² /s.
(3) Wedge flow meter: Wedge flowmeter is especially suitable for the flow measurement of high viscosity liquids, vapors and gases containing suspended matter. Its viscosity measurement range can be up to 500mPa·s, such as fuel oil, residual oil and heavy oil. In addition, the wedge flowmeter can also be applied to the flow measurement of liquid-solid mixtures containing suspended particles, such as slurry fluids, sewage, etc.
(4) The Coriolis mass flow meter can directly measure the mass of the fluid, and its measurement principle is not affected by the physical characteristics of the fluid, including viscosity and density. This means that Corrioli mass flowmeters are suitable for measuring all kinds of non-Newtonian fluids, all kinds of slurries, suspensions, high viscosity fluids, etc. However, the exact viscosity measurement range may vary depending on the Coriolis mass flowmeter model and specification. Therefore, when selecting and using Coriolis mass flowmeters for viscosity measurement, it is necessary to determine the appropriate model and specification according to the actual application requirements and fluid characteristics, and refer to the corresponding technical specifications or operating manuals to understand the specific measurement range and accuracy and other parameters. 2. Measure the viscosity range
(1) Elliptic gear flow meter: 0.6~200mPa·s (some special designs can reach 200~1000mPa·s)
(2) Circular gear flow meter: 1~25000m㎡/s
(3) Wedge flowmeter: up to 500mPa·s
3. How it works
(1) Rotameter: based on the buoyancy and resistance balance principle of the float in the fluid. When the fluid flows through the flow time, the float is raised by the momentum of the fluid. When the momentum of the float is balanced with the sum of the gravity of the float and the resistance of the fluid to the float, the float is stable at a certain height, and the flow corresponding to the height is the flow of the fluid.
(2) Positive displacement flowmeter: flow measurement by measuring the fixed volume of fluid flow. The positive displacement flowmeter has one or more measuring chambers inside, and when the fluid flows through the measuring chamber, the fluid is transferred from one measuring chamber to another by rotating or reciprocating motion, so as to complete the measurement of flow.
(3) Coriolis flowmeter: Measurement based on Coriolis effect. The fluid flowing in the vibration tube is subjected to the Coriolis force perpendicular to the flow direction, which causes the distortion of the vibration tube. By measuring the deformation of the vibration tube, the flow rate of the fluid can be calculated.
4. Design features
(1) Strong wear resistance: high-viscosity fluids often contain solid particles, and the design of the flow meter needs to consider wear resistance to extend the service life.
(2) Good adaptability: It can adapt to the flow characteristics of high-viscosity fluids at different temperatures.
(3) High measurement accuracy: Advanced measurement principles and technologies are used to ensure the accuracy of measurement under high viscosity fluids.
5. Application field
High viscosity flow meters are widely used in petrochemical, pharmaceutical, food processing, paper making, environmental protection and other industries, for measuring the flow of various high viscosity liquids (such as glue, syrup, paint, polymer solution, etc.).
6. Installation and maintenance
(1) Installation: The flow meter should be installed on the straight pipe section to avoid installation at the outlet of the pump or elbow, valve and other parts that may produce eddy currents. When installing, ensure that the flow meter is concentric with the pipe to avoid stress.
(2) Maintenance: regularly check the operating status of the flow meter, clean the scale and impurities inside the flow meter, and keep the flow meter clean. For parts that need lubrication, lubricating oil should be filled regularly.
7. Performance parameters
(1) Measuring range: The minimum flow and maximum flow range that the flowmeter can measure.
(2) Accuracy: error range of flowmeter measurement results.
(3) Repeatability: consistency of multiple measurement results under the same conditions.
(4) Response time: the response time of the flowmeter to the flow change.
(5) Working pressure: the pressure range within which the flowmeter can work normally.
(6) Operating temperature: the temperature range within which the flowmeter can work normally.
8. Selection guide
(1) Determine the measurement range: Determine the minimum flow rate and maximum flow rate to be measured according to the actual application scenario.
(2) Consider fluid characteristics: understand the viscosity, density, corrosion and other characteristics of high-viscosity fluids, and choose the appropriate flowmeter type.
(3) Consider environmental conditions: understand the temperature, pressure and other environmental conditions of the flowmeter installation location, and choose a flowmeter that can adapt to these conditions.
(4) Reference user evaluation: Understand other users' evaluation of this type of flowmeter, including measurement accuracy, stability, service life, etc.
9. Precautions
(1) Avoid vibration: The installation position of the flow meter should be far away from the vibration source to reduce the impact of vibration on the measurement results.
(2) Avoid electromagnetic interference: For flowmeters using electronic technology (such as Coriolis flowmeters), installation in a strong electromagnetic interference environment should be avoided.
(3) Regular calibration: In order to maintain measurement accuracy, the flow meter should be calibrated regularly.
(4) Pay attention to safety: in the process of installation, maintenance and commissioning, safety operation procedures should be observed to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
Please note that different models and designs of flowmeters may have different measuring ranges and accuracy. In the selection of suitable high-viscosity fluid flow timing, it is necessary to consider the actual application scenario, fluid characteristics and environmental conditions. At the same time, regular calibration and maintenance of the flow meter is also an important measure to ensure measurement accuracy and extend service life.
If you want to know more about the flow meter or flow meter selection, please consult the Aister flow meter manufacturer email: sales@aistermeter.com for help.
Share To:
Previous Post:
Next Post:
News
- Why is the thermal gas mass flowmeter not affected by pressure strength and temperature?
- What to do when a thermal gas mass flow meter fails?
- How are thermal gas mass flow meters used? What are the applications?
- Under what circumstances is the gas measurement need to be regulated compensated vortex flowmeter
- Why Is The Aister Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter So Popular ?
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturers explain their main advantages in measurement
- Gas turbine flowmeter manufacturer Aister instrument field experience summary
- Aister Instrument Empowerment Conference