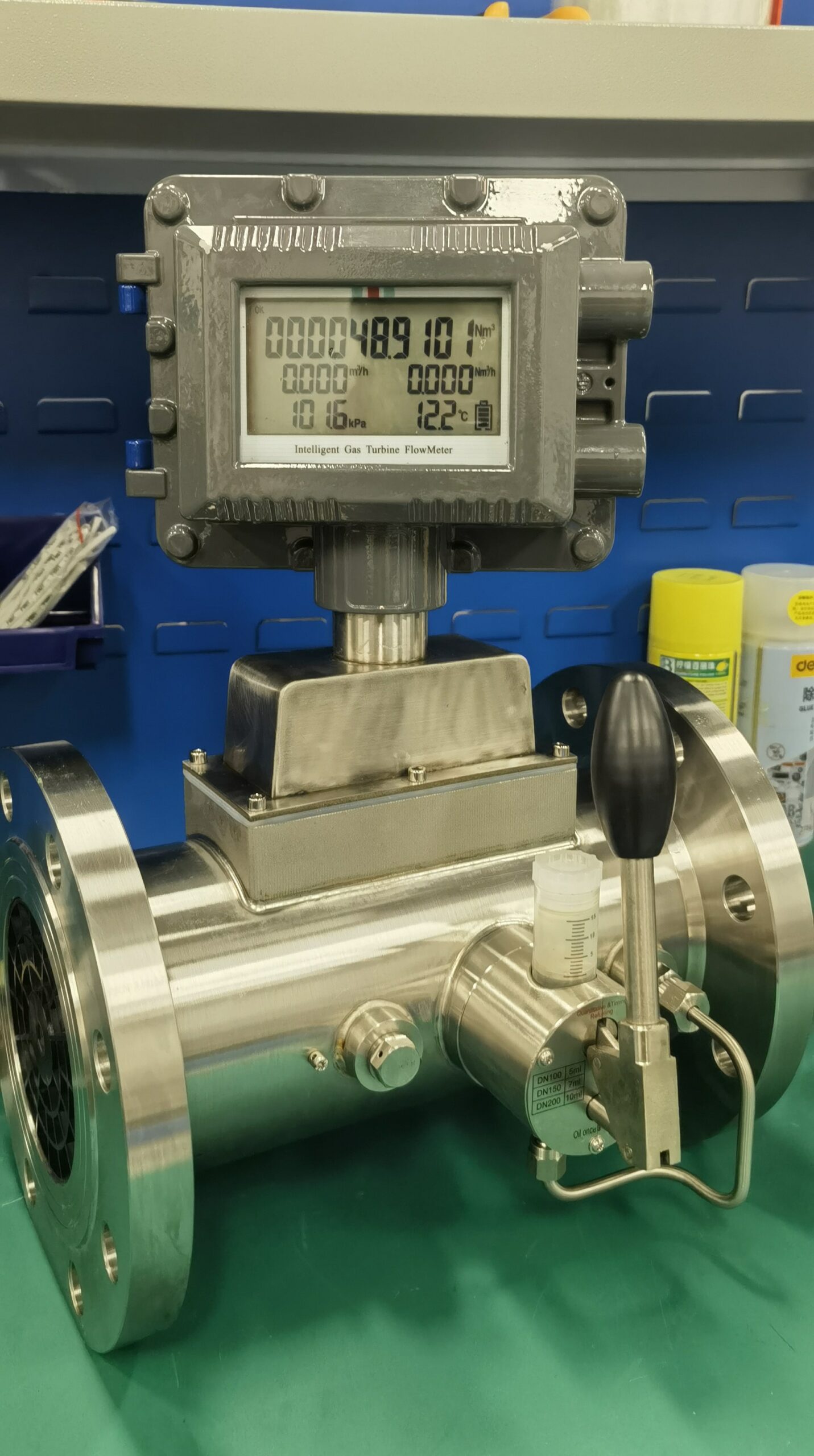
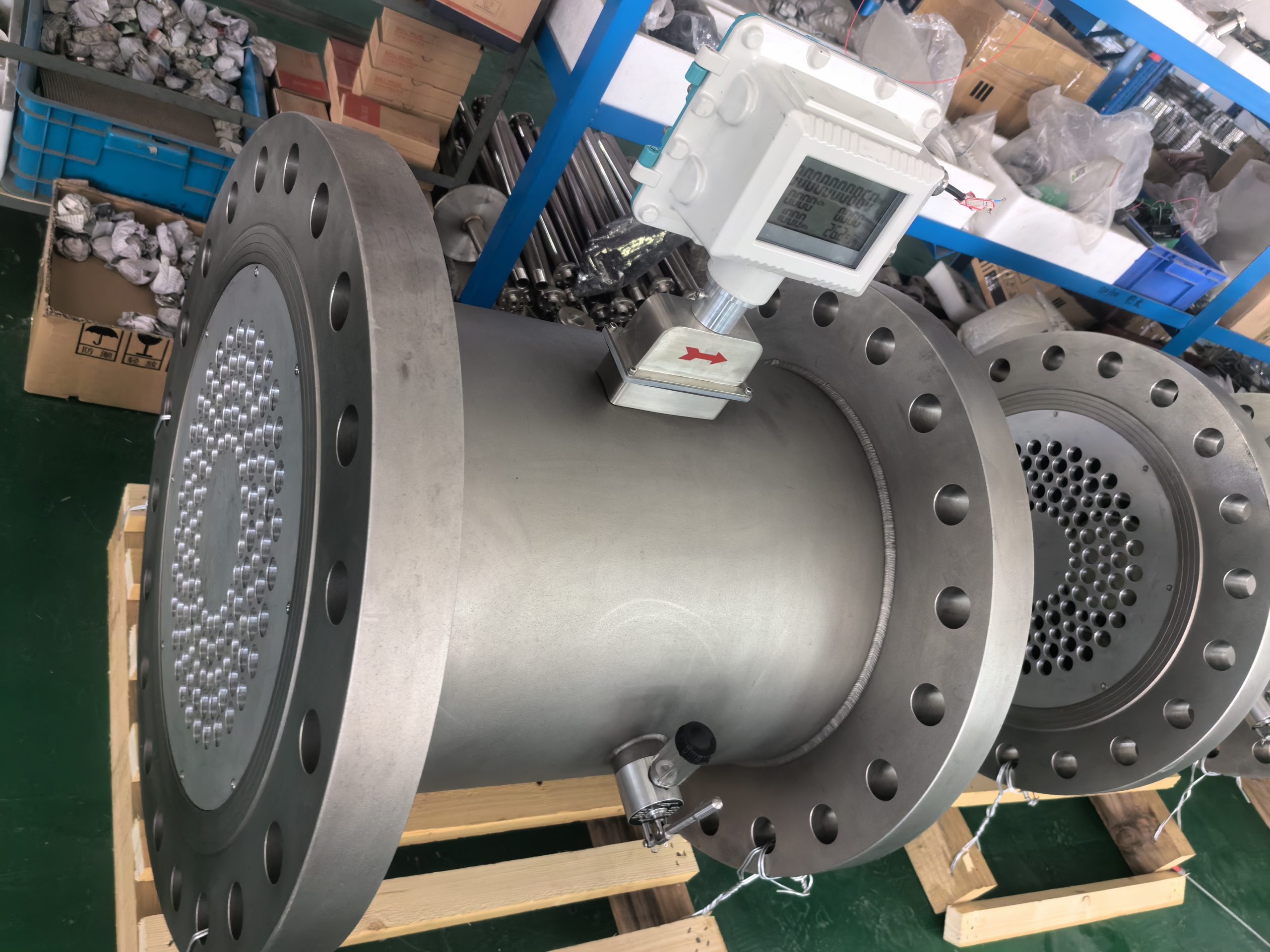
The difference between gas turbine flow meter and gas roots flow meter
There are significant differences between gas turbine flowmeters and waist flowmeters in many aspects, which are mainly reflected in the working principle, measurement range, performance characteristics, application occasions and maintenance costs. Here’s a breakdown of the differences:
1. How it works
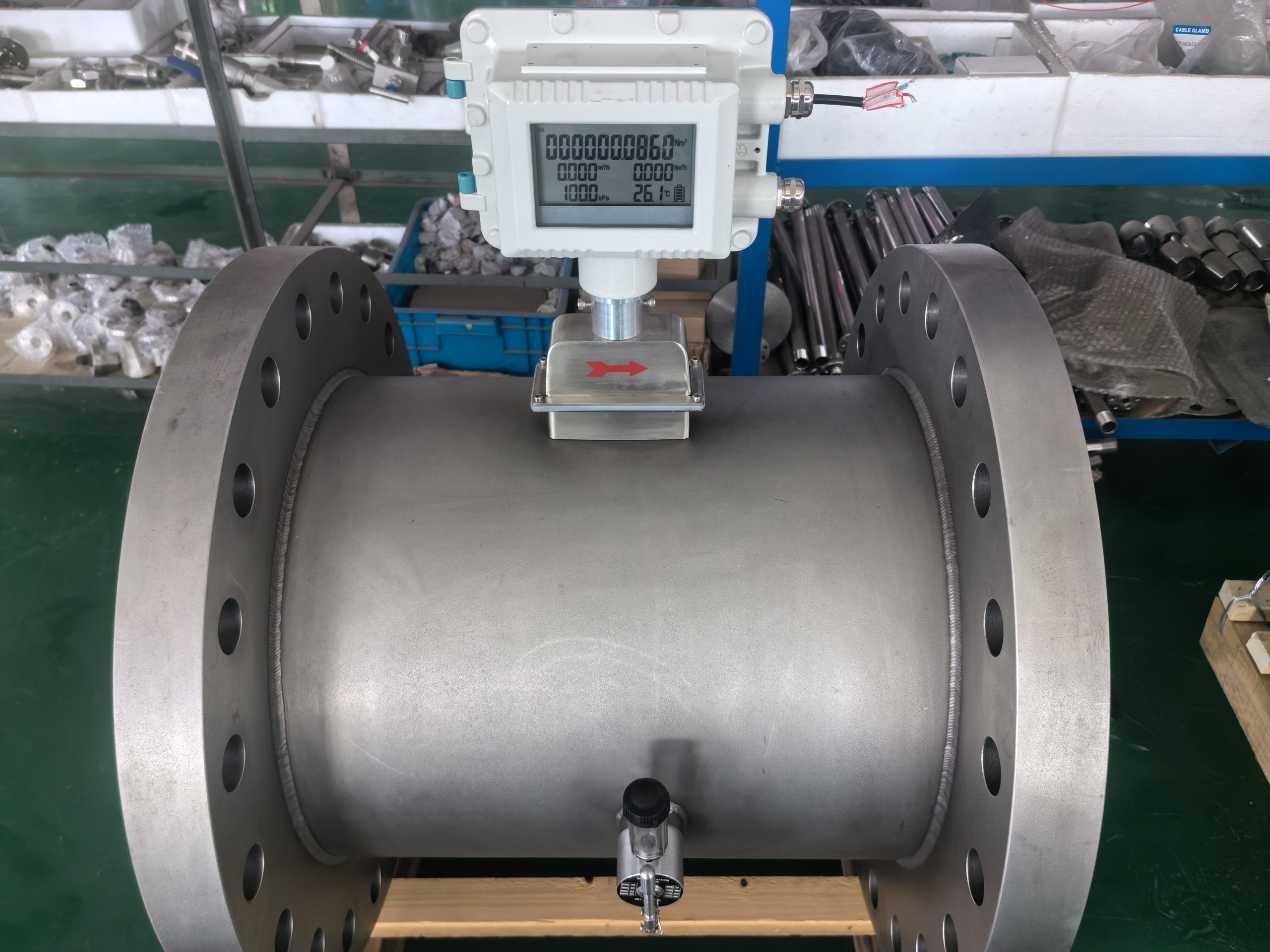
Gas turbine flowmeter: works based on the proportional relationship between the turbine rotation speed and the gas flow rate. When the gas passes through the sensor of the turbine flow meter, the high-speed rotating turbine blade is subjected to the impact of the gas. The rotating speed of the turbine is converted into an electrical signal by the magnetoelectric conversion device, and then the gas flow rate is calculated through signal processing. This flowmeter is a typical velocity flowmeter.
Gas Waist Wheel flowmeter (also known as Roots flowmeter or rotameter) : Its working principle is based on positive displacement measurement. There is a measuring chamber in the shell of the waist wheel flowmeter, and there are one or two pairs of waist wheels that can be tangentially rotated in the measuring chamber. When a fluid passes through the flow meter, the waist wheel rotates under the action of the differential pressure of the fluid, and the total amount of fluid is determined by measuring the fixed volume passed by the waist wheel during the rotation process.
2. Measurement range and performance characteristics
Gas turbine flowmeters: Suitable for medium to high flow ranges, especially for measuring low viscosity, clean fluids. It usually provides high measurement accuracy, especially under ideal working conditions. However, it is sensitive to changes in fluid state, such as pulsating flow or fluid state changes that may affect its accuracy. In addition, turbine flowmeters respond quickly and can reflect flow changes in real time, but long-term operation can lead to wear and tear, requiring regular maintenance and calibration.
Roots flow meter: suitable for small to medium flow range, especially suitable for measuring a variety of liquids, but also some gas applications. When dealing with fluids with high viscosity or containing small particles, the waist-wheel flowmeter has advantages because of its large contact area, easy plugging, and good wear resistance. Its accuracy may be slightly lower than the turbine flowmeter, but the measurement results are more stable and the anti-interference ability is strong, especially when dealing with unstable fluid conditions. The response speed of the waist wheel flowmeter is relatively slow, which is more suitable for continuous and stable flow measurement, and the mechanical component design is durable, the service life is long, and the maintenance cycle is relatively long.
3. Application situation
Gas turbine flowmeter: widely used in petroleum, organic liquid, inorganic liquid, liquefied gas, natural gas and low temperature fluid and other fields. In the power generation and cogeneration and heating industries; Aviation, aerospace, shipbuilding, nuclear energy and weapons industries; Machinery, metallurgy, coal mining and automobile manufacturing; Petroleum and chemical industry; Pharmaceutical, food and tobacco and alcohol manufacturing industries; Forest industry, agricultural reclamation and light industry are used.
Roots flowmeter: often used in industrial pipelines large diameter gas, liquid, steam medium fluid flow measurement. It is also widely used in petrochemical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage production, water supply system, gas supply system and other fields.
4. Maintenance costs
Gas turbine flowmeter: Due to the existence of its high-speed rotating parts, long-term operation may lead to wear, so regular maintenance and calibration are required, which may increase certain maintenance costs.
Roots flowmeter: Because of its mechanical component design is robust, long service life, and relatively long maintenance cycle, it may be relatively low in terms of maintenance costs.
Summary: Gas turbine flowmeter and waist wheel flowmeter have their own advantages and application scenarios. In the selection, should be based on the actual working conditions, the required measurement accuracy, media characteristics and maintenance costs and other factors considered.