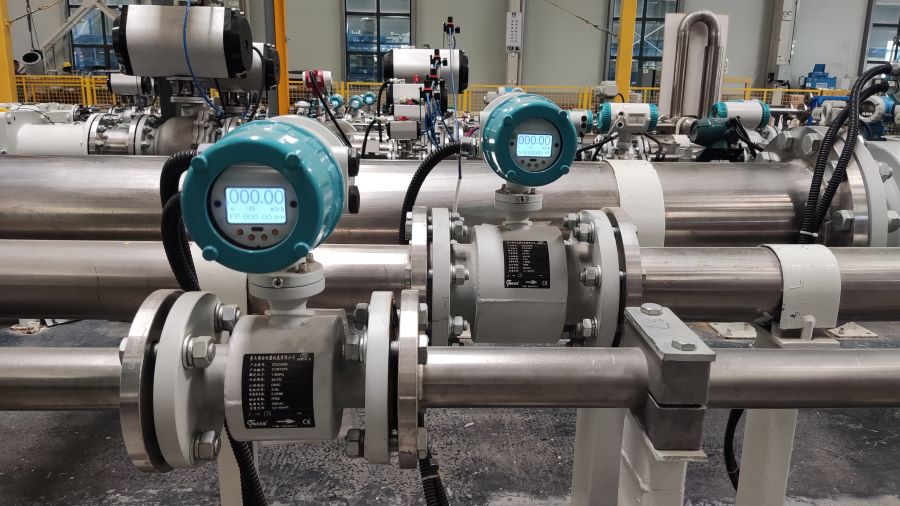
Low Consumption Electromagnetic Flowmeter Water Pump Liquid Magnetic Flow Meter
Electromagnetic flowmeters, also known as magmeters or magnetic flowmeters, are widely used for measuring the flow rate of conductive liquids in various industries. Several factors can influence the accuracy of electromagnetic flowmeters. Understanding and addressing these factors are essential to ensure precise and reliable flow measurements. Here are some key factors that can affect the accuracy of electromagnetic flowmeters:
Conductivity of the Fluid:
Electromagnetic flowmeters rely on the conductivity of the liquid to generate a measurable signal. The fluid must be conductive for the magnetic field to induce a voltage. Extremely low-conductivity fluids may not generate a sufficient signal, leading to inaccurate measurements.
Electrode Material and Condition:
The material and condition of the electrodes can impact accuracy. Corrosion, scaling, or coating on the electrode surfaces can affect the electrical conductivity and result in inaccurate readings. Using electrodes made of corrosion-resistant materials helps maintain measurement accuracy.
Electrode Alignment:
Proper alignment of the electrodes is crucial for accurate measurements. Misalignment can lead to uneven flow profiles, causing variations in the induced voltage and resulting in inaccurate readings. Ensuring correct installation and alignment is essential.
Flow Profile:
Electromagnetic flowmeters perform best when the fluid flow is fully developed and exhibits a stable, well-defined profile. Turbulent or uneven flow profiles can lead to inaccuracies in the measurements. Adequate straight pipe lengths upstream and downstream of the flowmeter are often required for optimal performance.
Pipe Material and Size:
The material and size of the pipe can affect the performance of the electromagnetic flowmeter. Changes in the pipe material or size can influence the magnetic field and induce measurement errors. Calibration may be necessary when installing the flowmeter on pipes with different materials or sizes.
Grounding and Earthing:
Proper grounding and earthing are crucial for electromagnetic flowmeters. Inadequate grounding can introduce electrical noise into the system, affecting the accuracy of measurements. Ensuring a good electrical connection to the ground helps minimize interference.
Temperature and Viscosity:
Changes in fluid temperature and viscosity can impact the accuracy of electromagnetic flowmeters. Some meters are equipped with temperature compensation features, but variations outside the specified range may require additional correction factors.
Flow Rate Range:
Electromagnetic flowmeters are designed for a specific flow rate range. Operating the flowmeter outside this range may result in reduced accuracy. It’s essential to select a flowmeter with an appropriate range for the expected flow conditions.
Power Supply Stability:
Fluctuations in the power supply can affect the performance of electromagnetic flowmeters. Ensure a stable and consistent power supply to maintain accuracy. Voltage spikes or dips can lead to measurement errors.
Calibration:
Regular calibration is critical for maintaining accuracy over time. Calibration should be performed under actual operating conditions, and any changes in the system or fluid properties may necessitate recalibration.
Installation and Grounding Practices:
Following proper installation practices, including correct grounding and earthing, is essential. Avoiding air pockets, ensuring a stable and uniform flow, and minimizing disturbances in the pipe are crucial for accurate measurements.
External Magnetic Fields:
External magnetic fields from nearby electrical equipment can interfere with electromagnetic flowmeter readings. Proper shielding or installation in areas with minimal electromagnetic interference can help mitigate this factor.






-.jpg)







-.jpg)