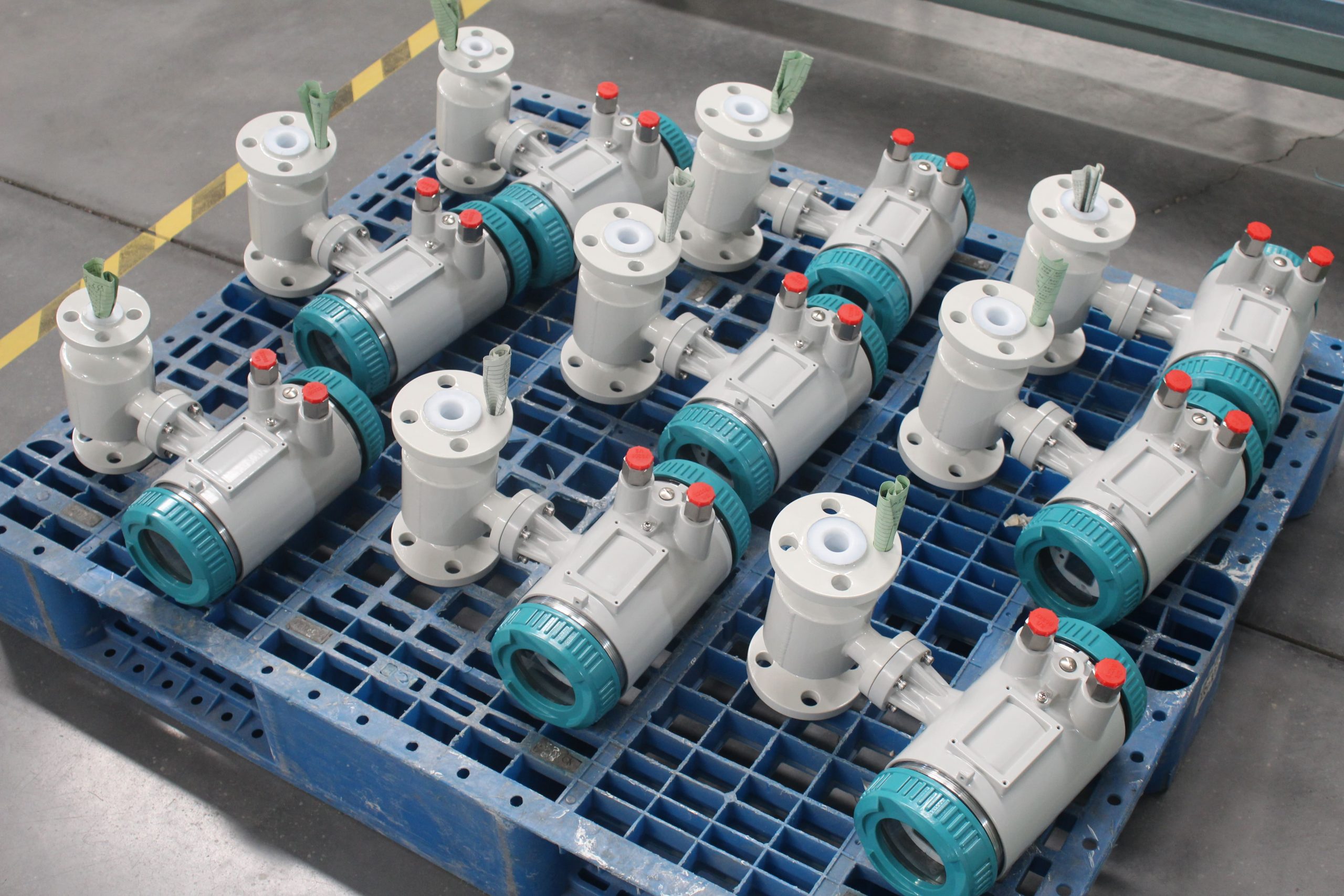
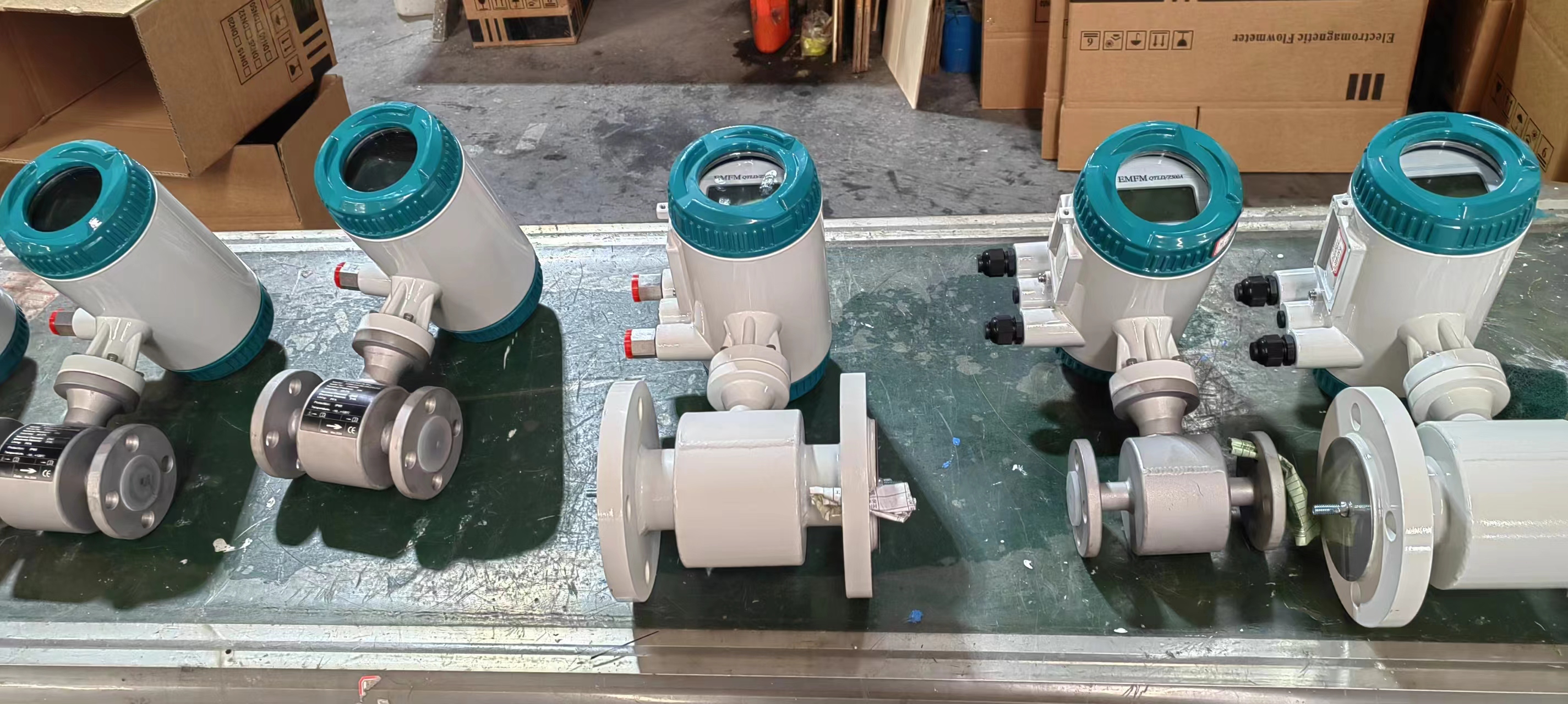
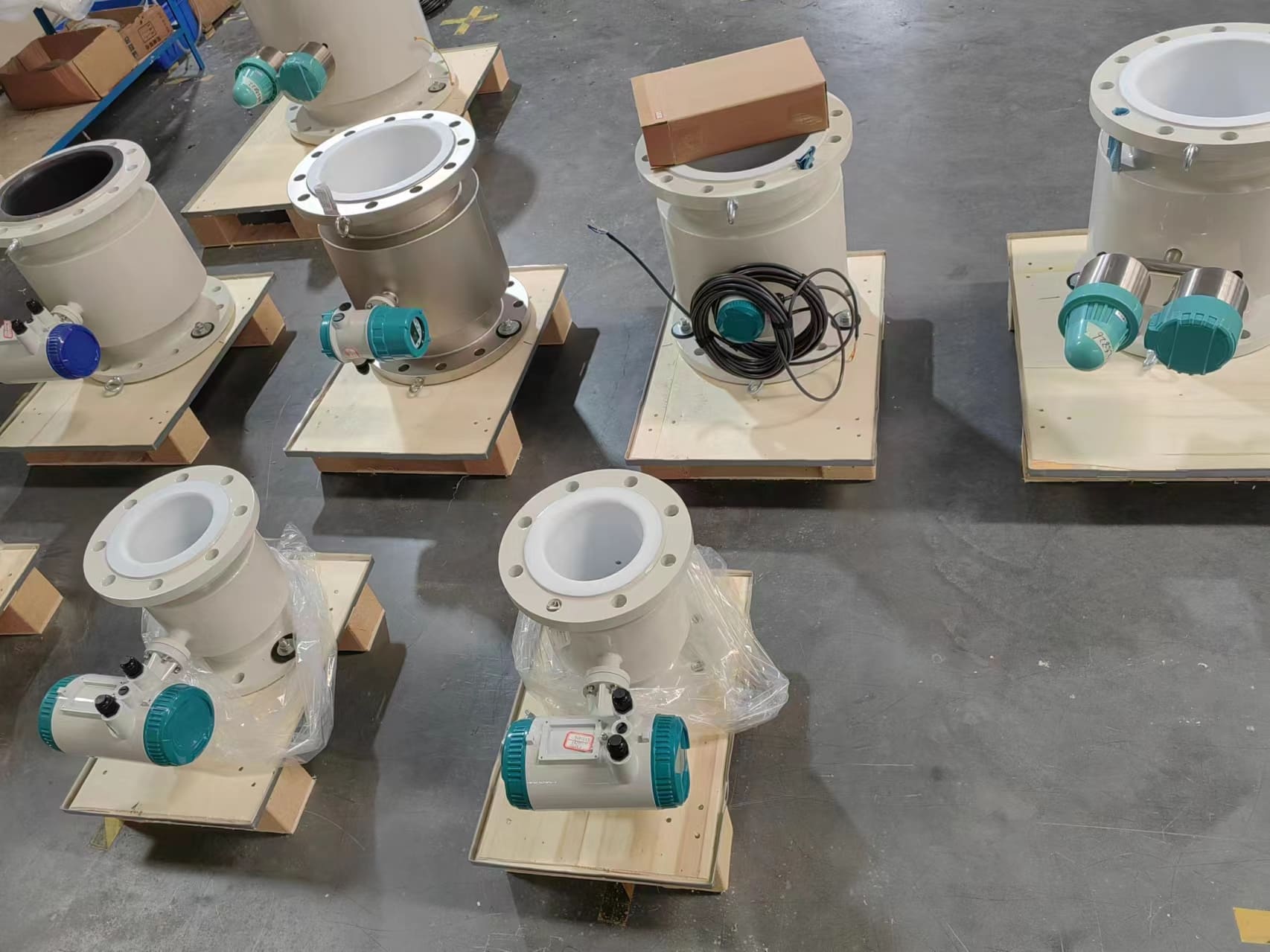
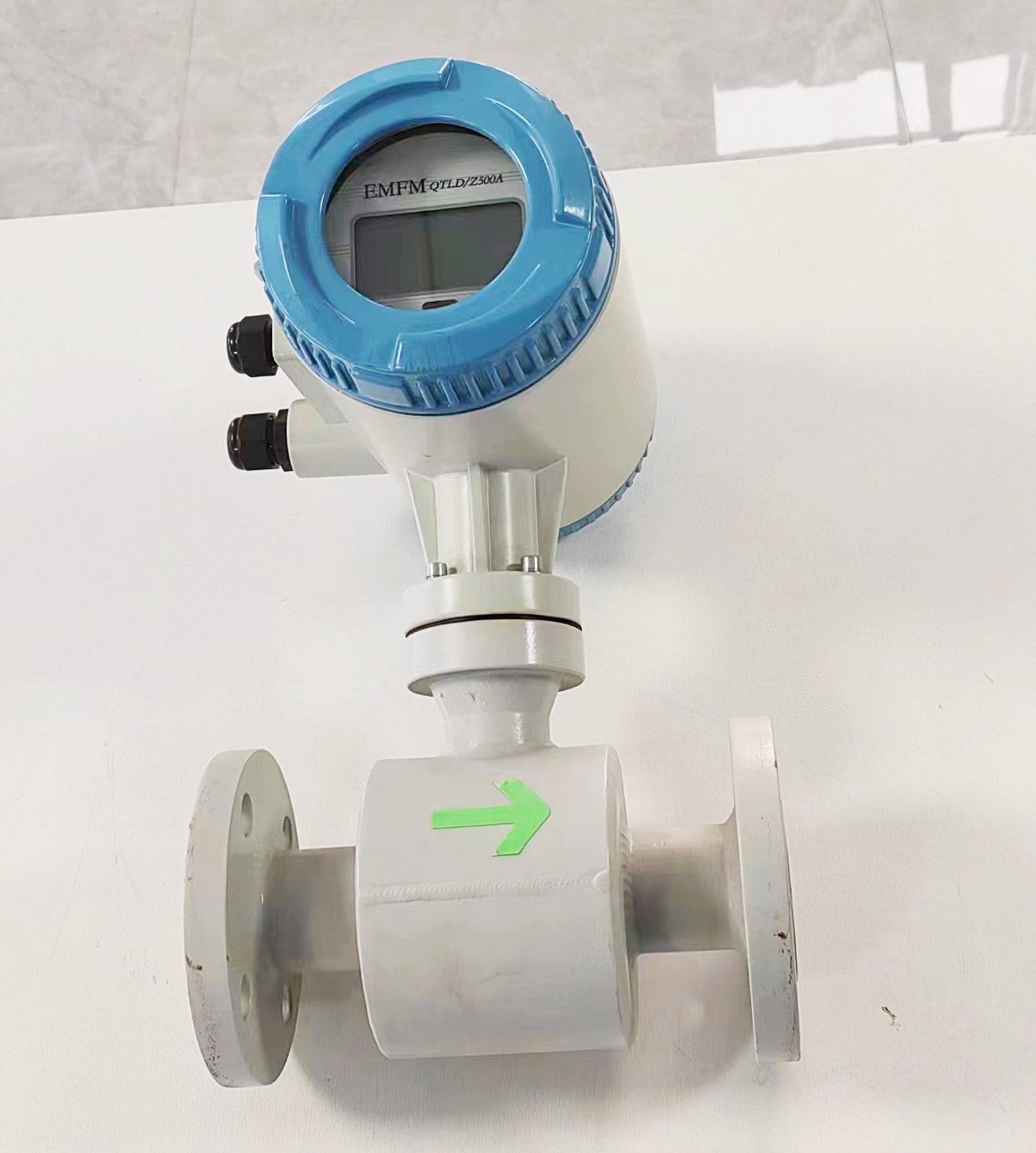
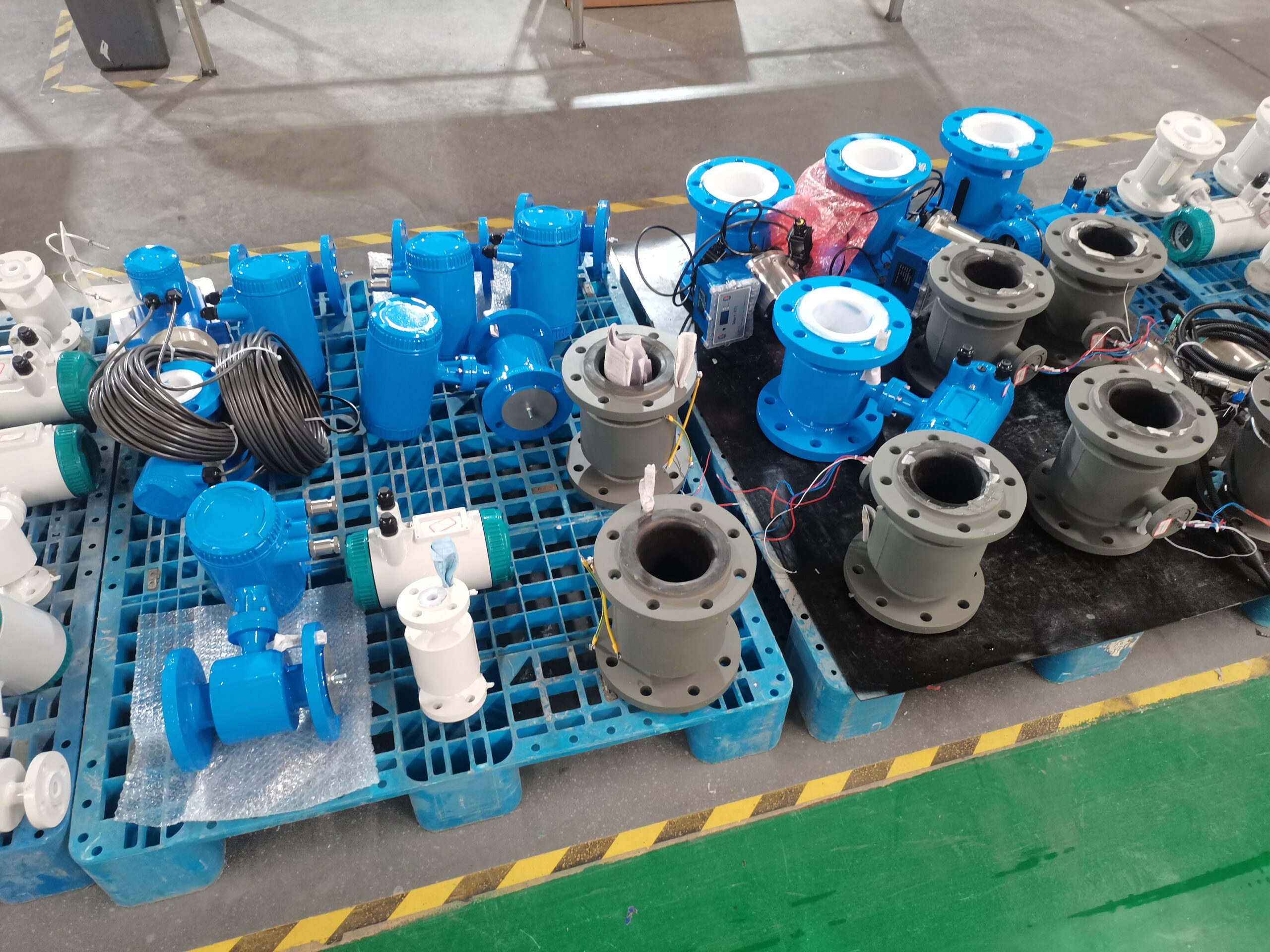
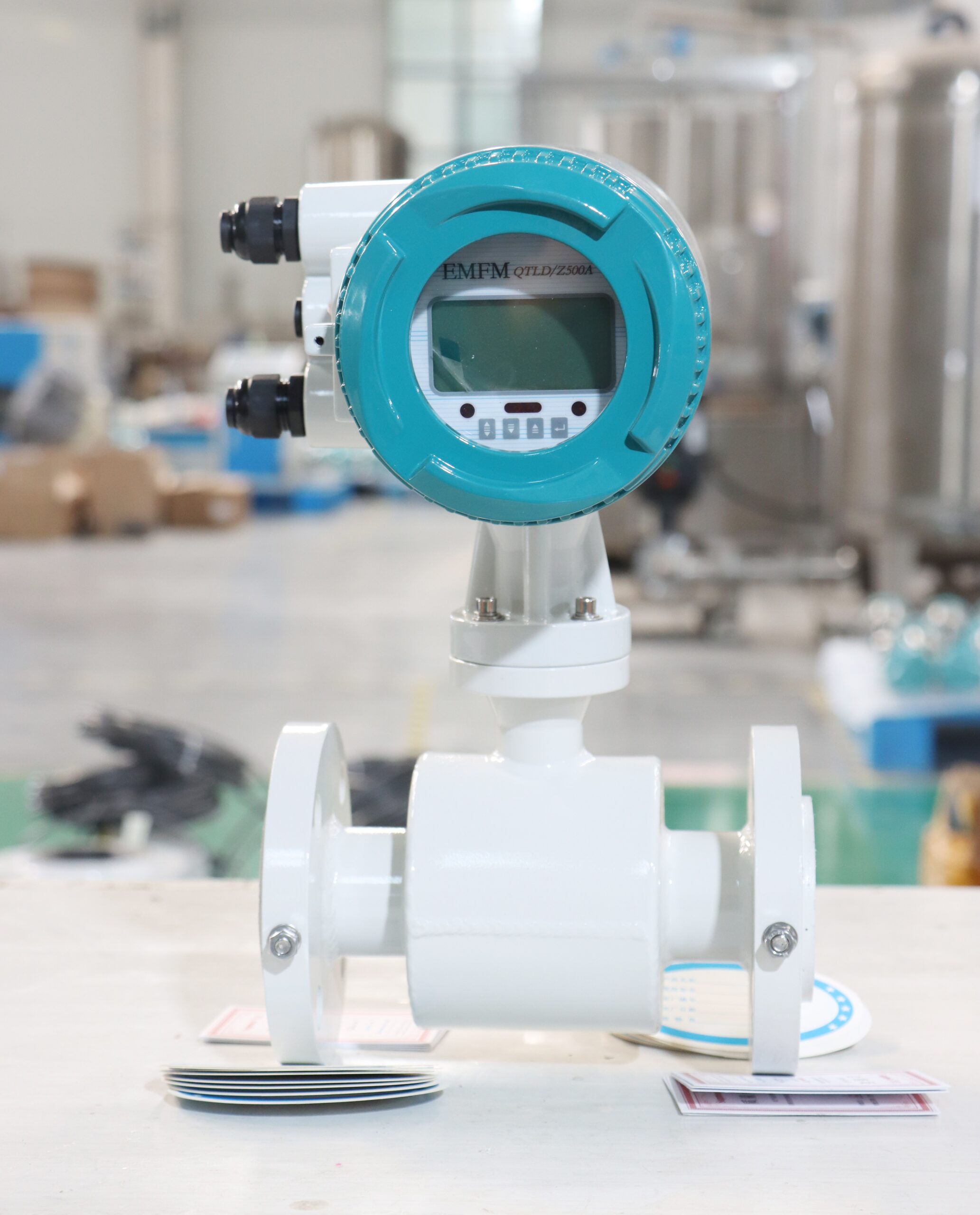
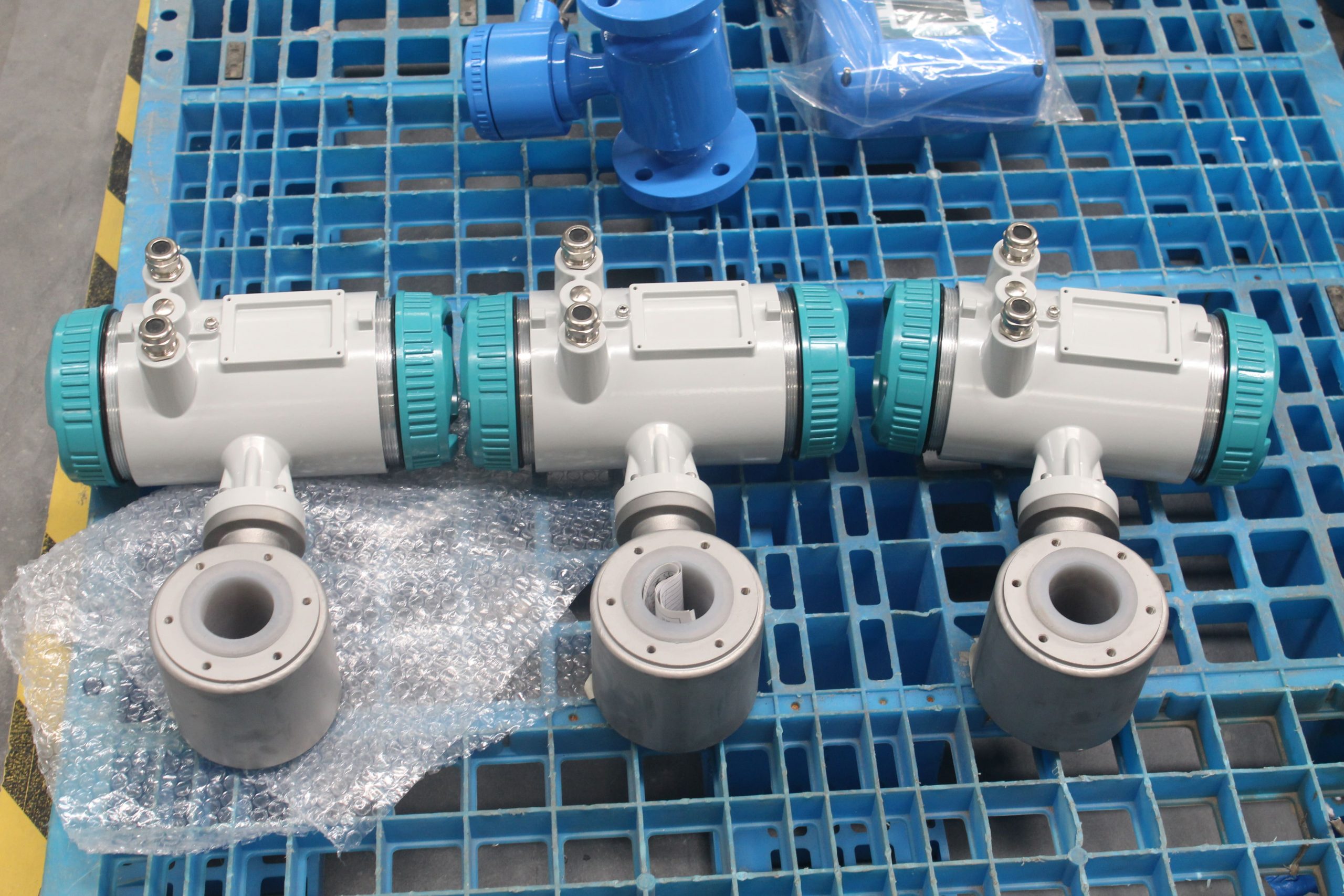
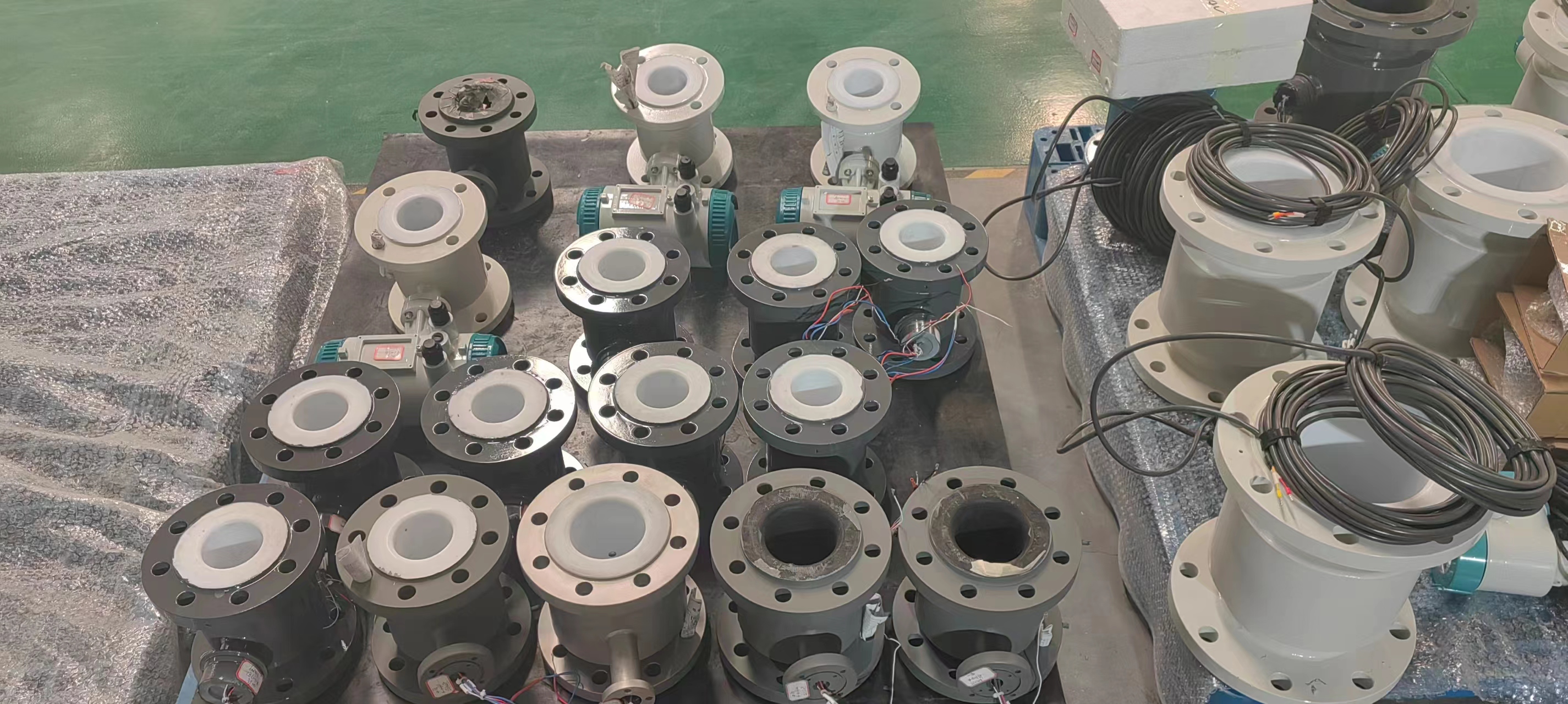
LCD Display Water Flowmeter Pipeline Water Pump Liquid Electromagnetic Magnetic Flow Meter
Electromagnetic flowmeters, also known as magmeters, are widely used in various industries for measuring the flow rate of conductive fluids. They operate based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, where a voltage is induced in a conductor (the fluid) as it moves through a magnetic field. These flowmeters are favored for their accuracy, reliability, and suitability for a wide range of applications. Here are different categories of electromagnetic flowmeters and their fields of application:
General Purpose Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
These flowmeters are designed for general industrial applications where the fluid conductivity is relatively high and the flow rates are moderate to high.
Applications include water and wastewater treatment, chemical processing, pulp and paper, mining, and food and beverage industries.
Sanitary Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
These flowmeters are specifically designed for hygienic applications where cleanliness and sterility are paramount.
Commonly used in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, dairy, and food processing industries where strict sanitary standards must be met.
High-Temperature Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Designed to withstand high temperatures encountered in various industrial processes.
Used in industries such as steel manufacturing, power generation (steam flow measurement), and chemical processing where elevated temperatures are present.
Corrosive Fluid Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Constructed with materials resistant to corrosion from aggressive fluids such as acids, alkalis, and corrosive chemicals.
Applications include chemical processing, metal refining, and petrochemical industries.
Abrasive Fluid Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
These flowmeters are equipped with liners and electrodes that can withstand abrasion caused by particulate matter present in the fluid.
Commonly used in mining, slurry handling, and wastewater treatment applications.
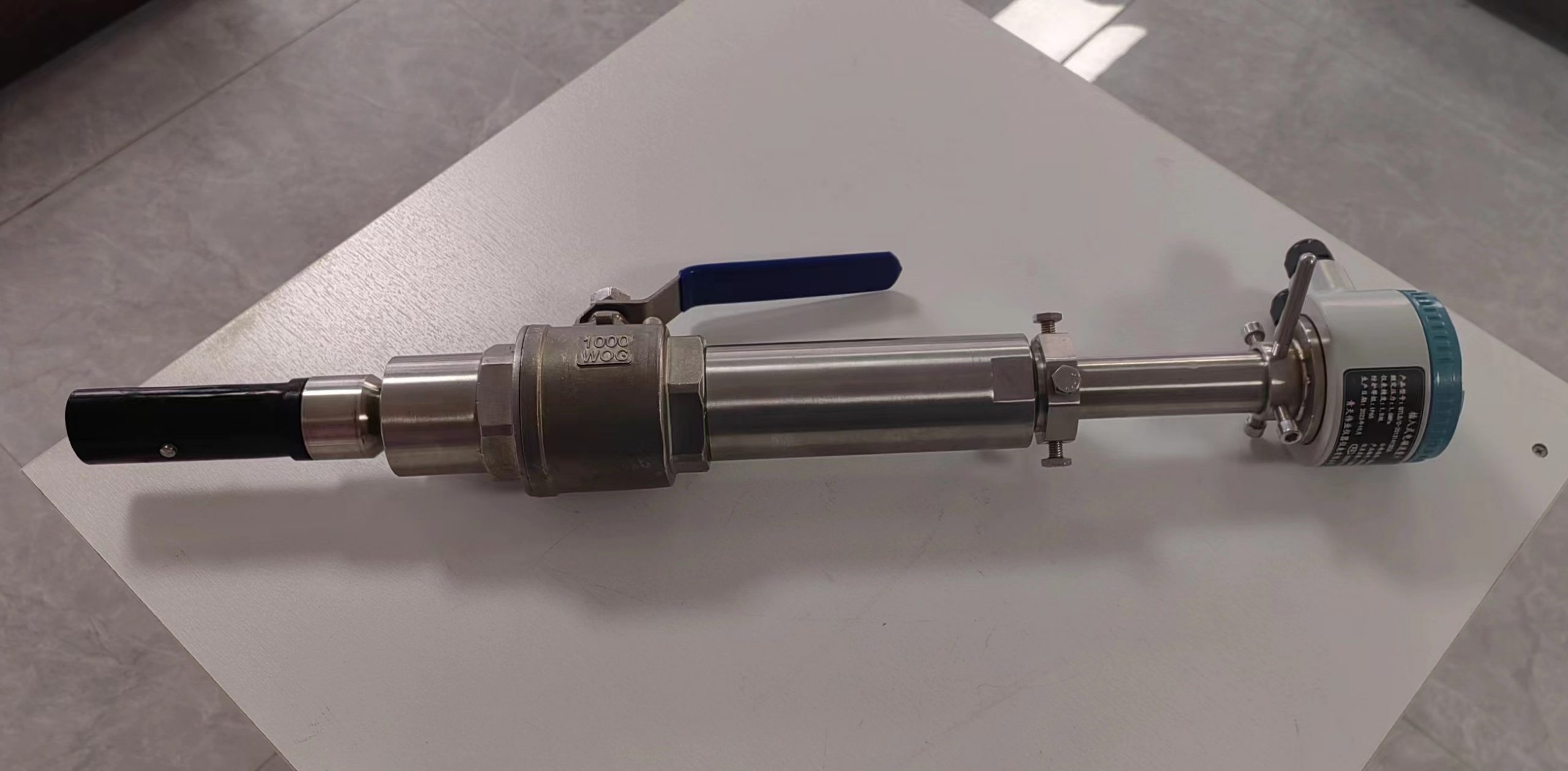
Low-Flow Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Designed to accurately measure low flow rates typically encountered in laboratory, research, and pilot plant applications.
Useful in industries such as pharmaceuticals, research laboratories, and small-scale chemical processing.
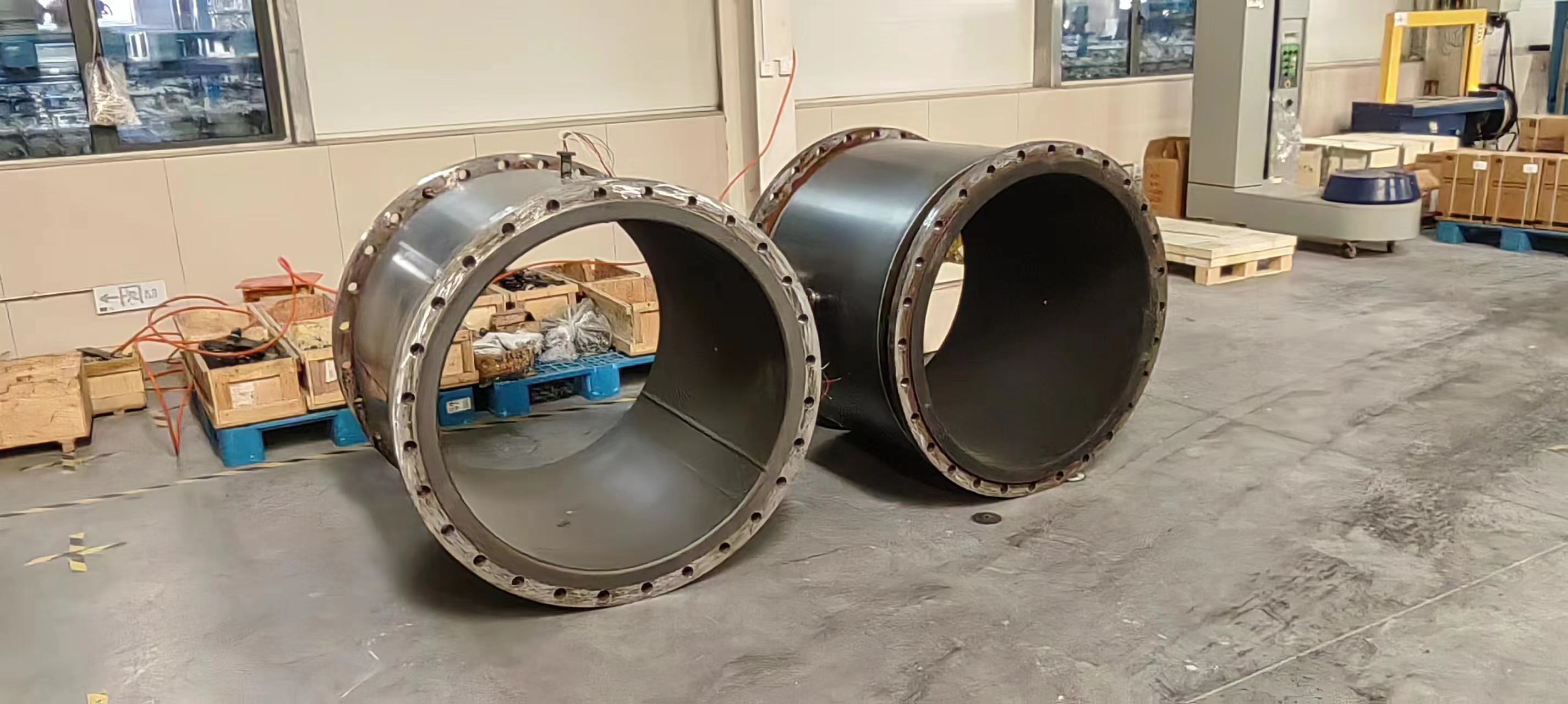
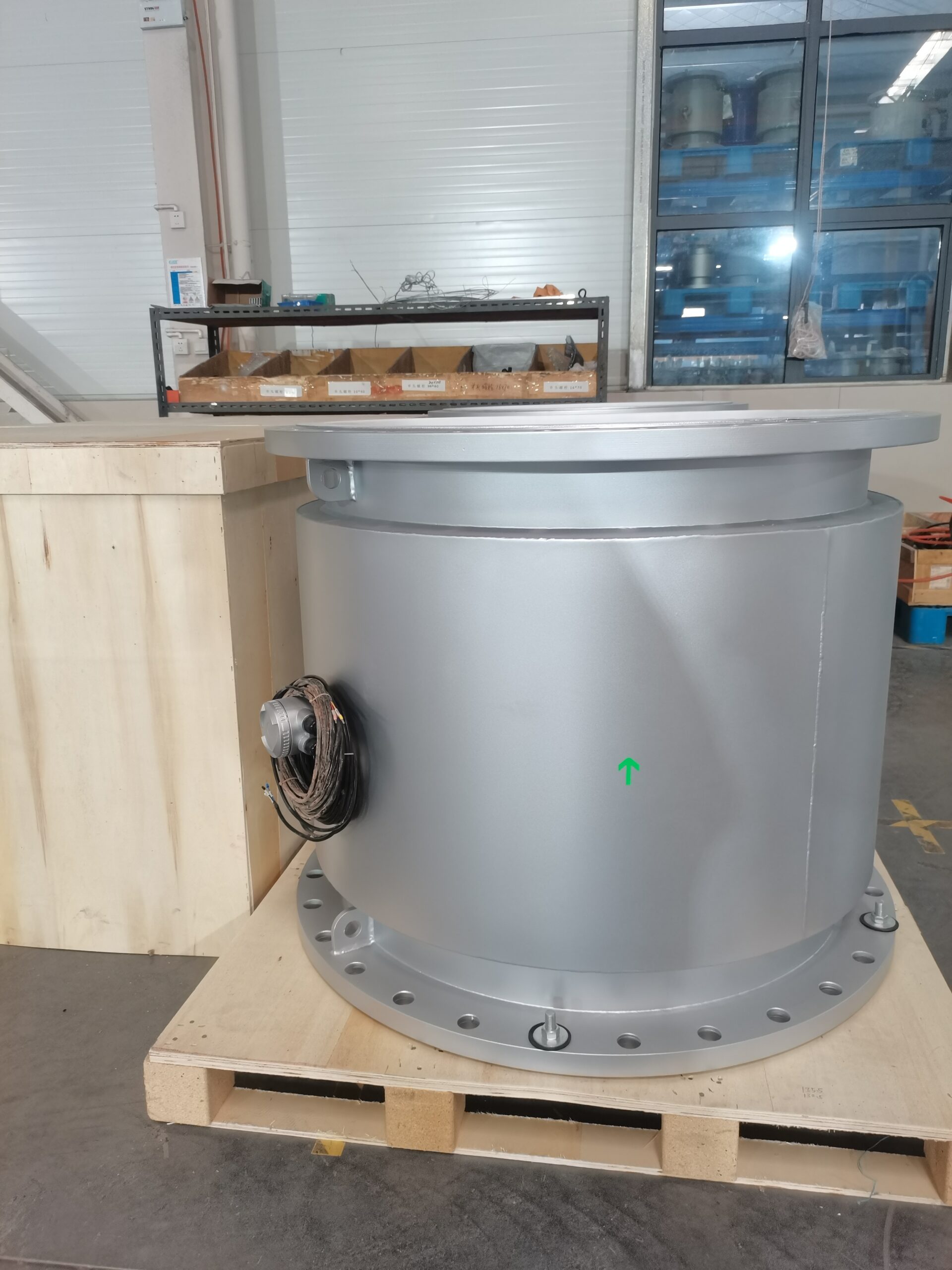
Large Diameter Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Engineered to measure flow rates in large pipes and ducts where conventional flow measurement technologies may be impractical.
Used in water distribution networks, wastewater treatment plants, and large-scale industrial processes.
Battery-Powered Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
These flowmeters are equipped with battery power sources, making them suitable for applications where access to a power supply is limited or impractical.
Often used in remote monitoring applications, mobile water distribution systems, and temporary installations.
Smart Electromagnetic Flowmeters:
Incorporate advanced digital communication protocols (such as Modbus, HART, or Profibus) and onboard diagnostics for remote monitoring, control, and integration with automation systems.
Suitable for industries requiring real-time flow data and integration with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, such as water and wastewater management, and industrial process control.
















-.jpg)






-.jpg)