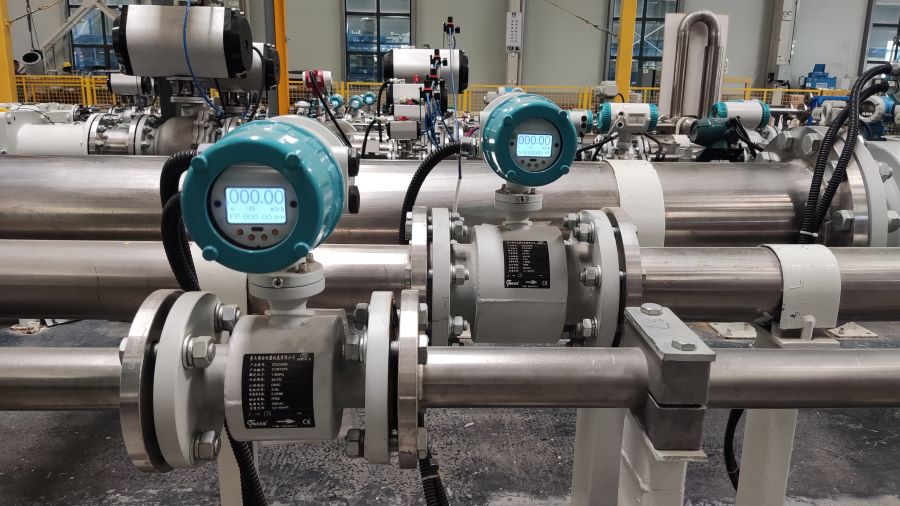
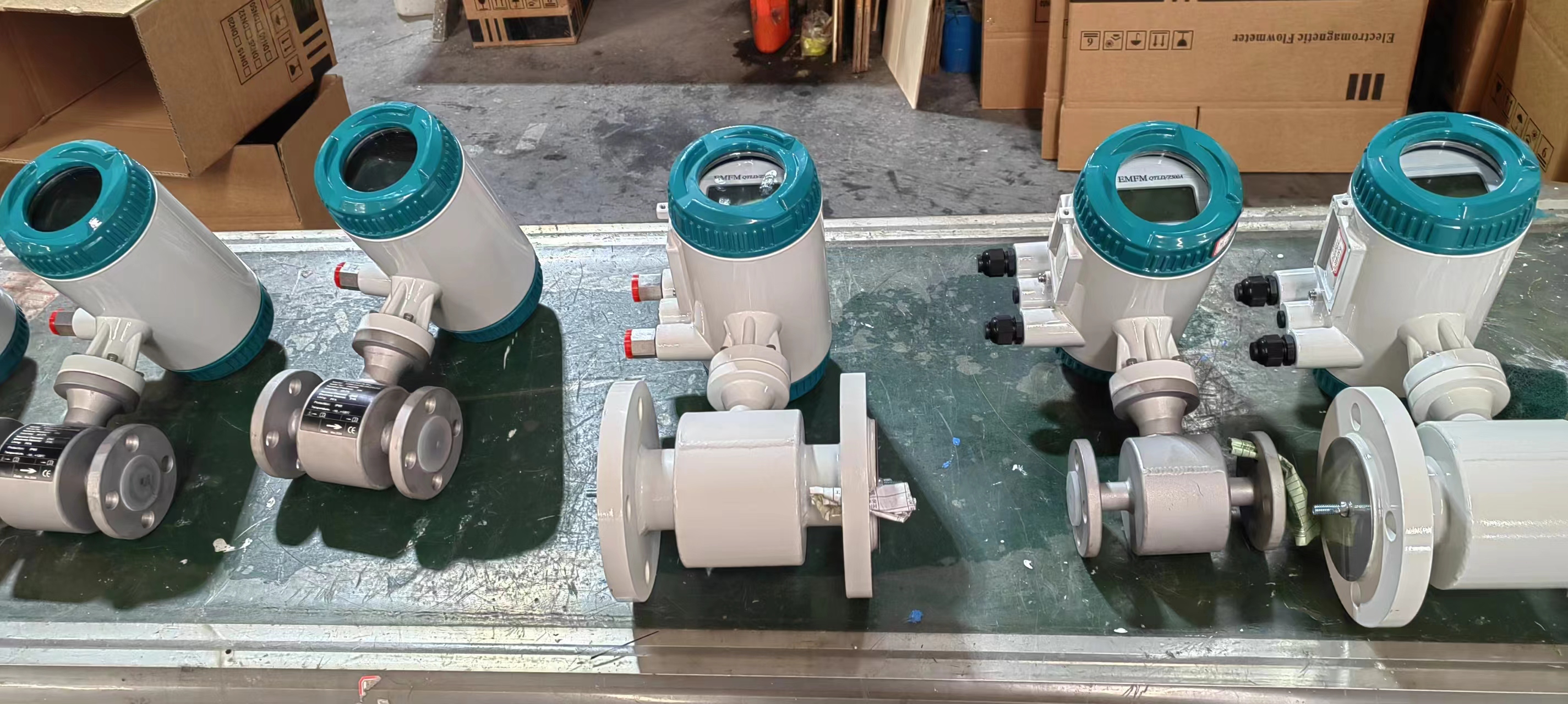
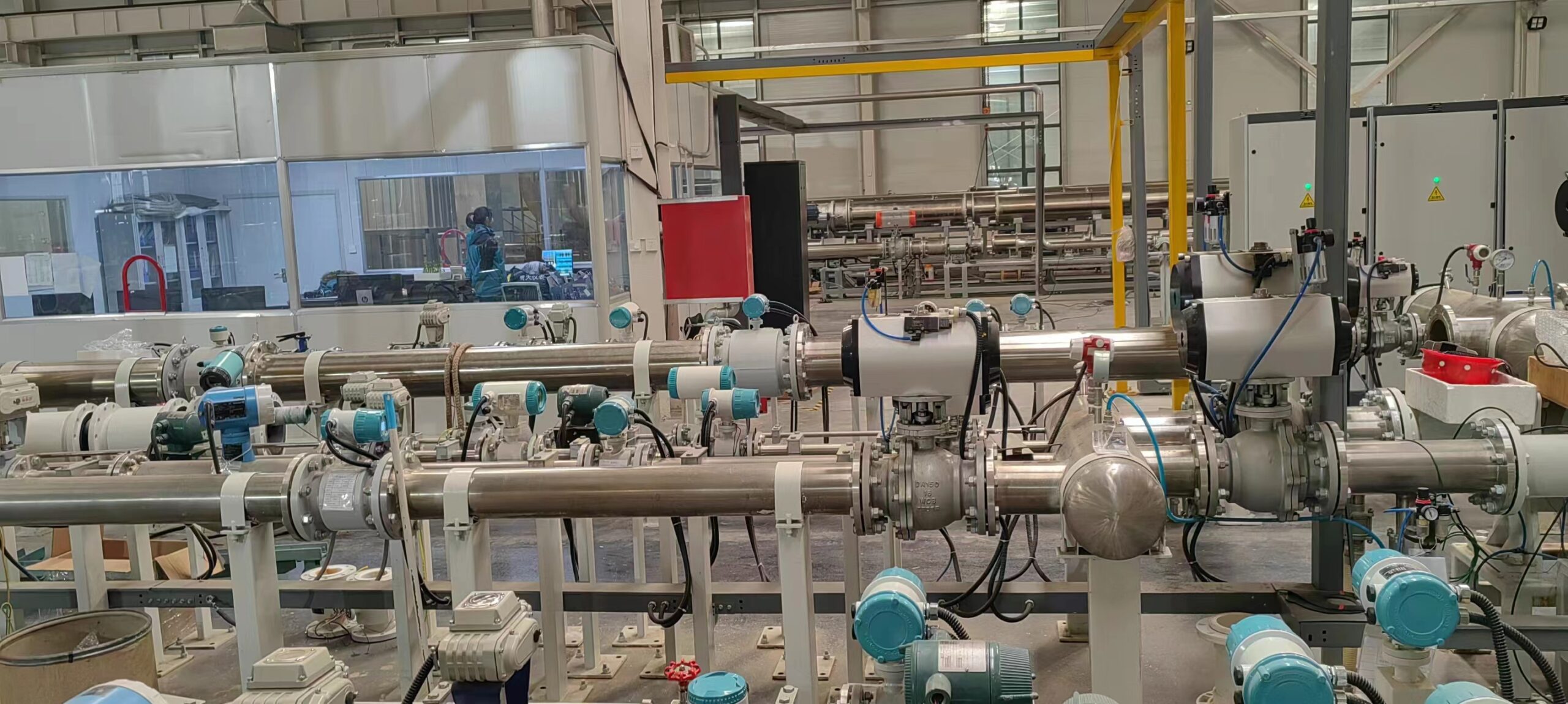
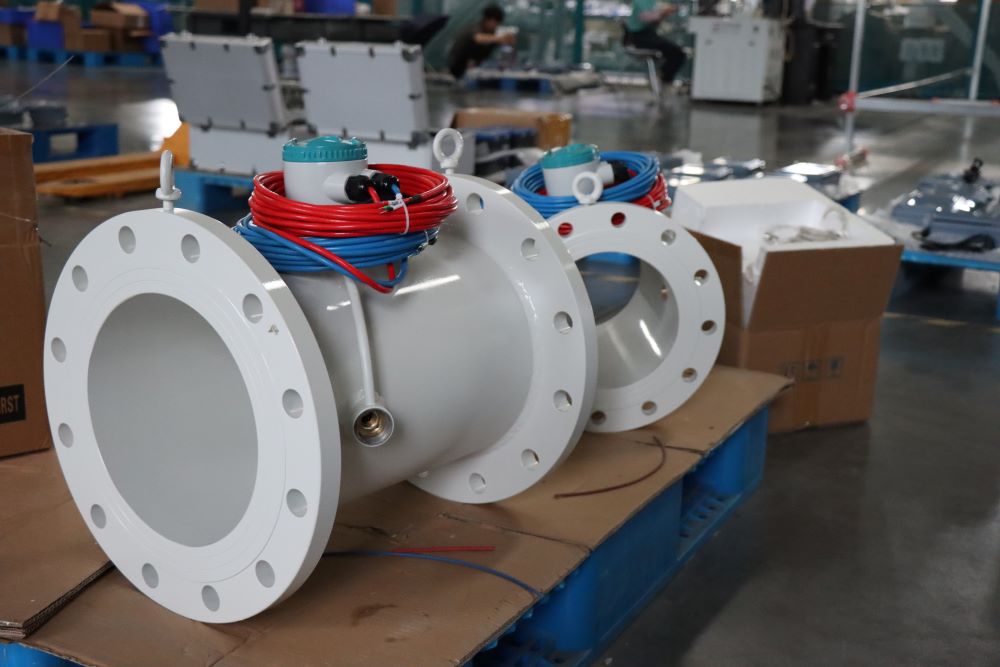
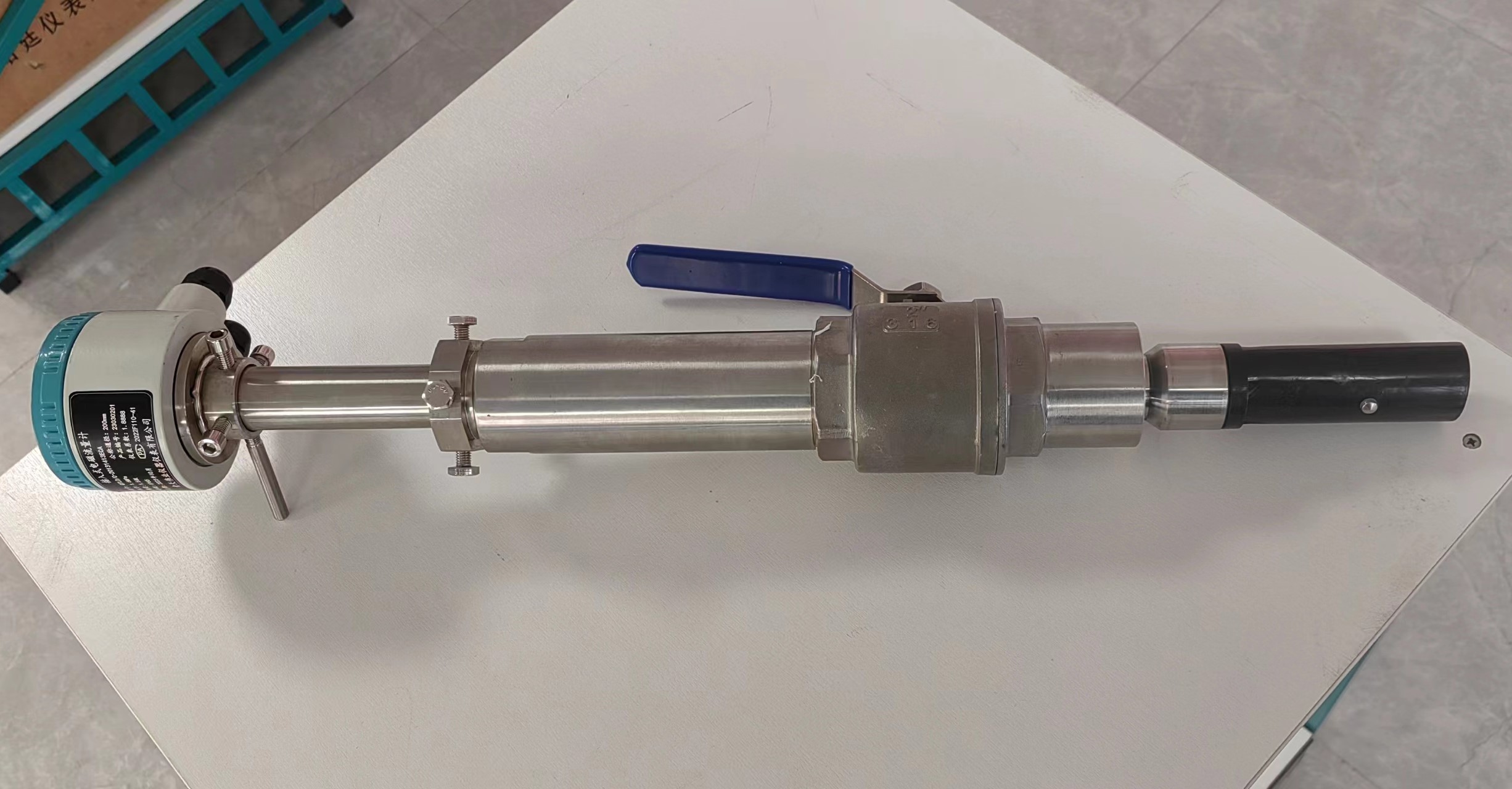
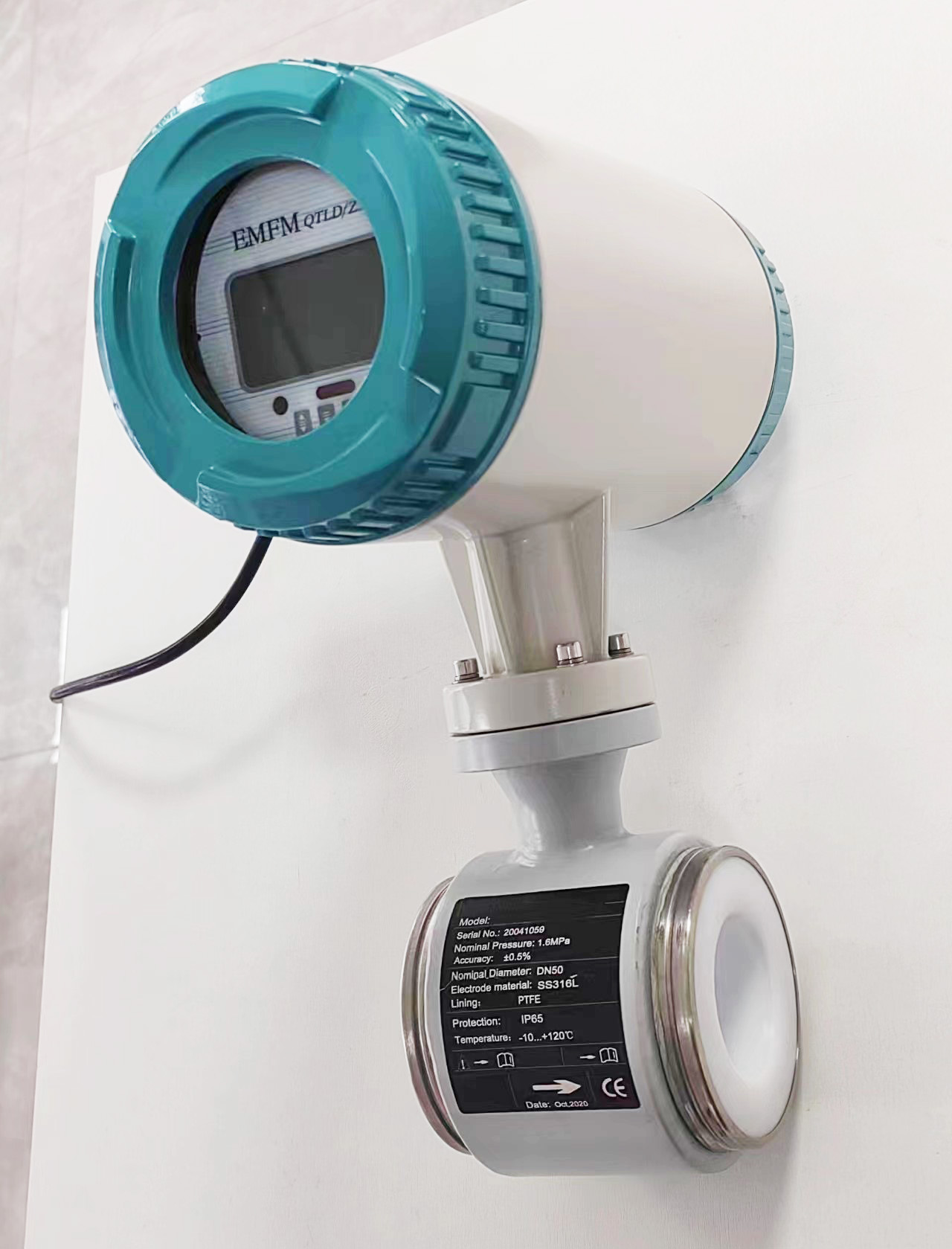
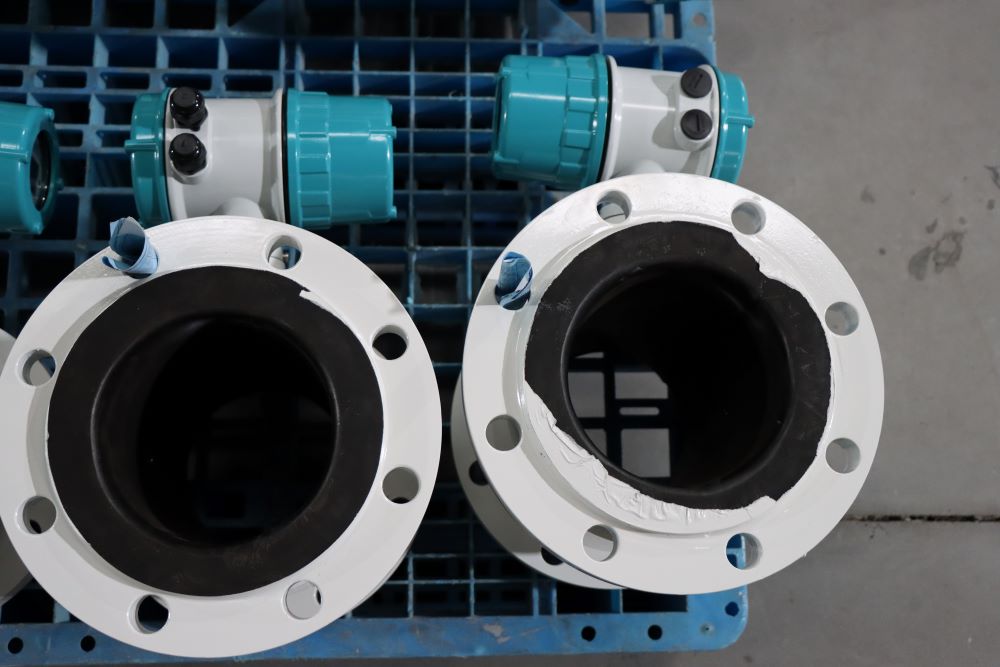
Integrated Remote Control Electromagnetic Flowmeter Waste Water Magnetic Flow Meter
When using electromagnetic flowmeters in the field, it’s important to perform regular checks and maintenance to ensure accurate and reliable flow measurements. Here are some key parameters to check and consider in the field for electromagnetic flowmeter use:
Electrode Condition:
Inspect the condition of the electrodes regularly. Ensure they are clean, free from corrosion, scaling, or any coating that could affect conductivity. If necessary, clean the electrodes to maintain good electrical contact with the flowing liquid.
Insulation Integrity:
Check the insulation integrity of the flowmeter. Inspect the insulation between electrodes and the grounding. Any compromise in insulation can lead to inaccurate measurements and potential safety hazards.
Grounding and Earthing:
Verify proper grounding and earthing of the flowmeter. Inadequate grounding can introduce electrical noise into the system, affecting measurement accuracy. Ensure that the grounding connections are secure and meet the manufacturer’s specifications.
Straight Pipe Lengths:
Confirm that the required straight pipe lengths upstream and downstream of the flowmeter are maintained. Proper straight pipe lengths are essential for achieving a stable and well-defined flow profile.
Flow Profile Conditions:
Assess the flow conditions to ensure that the flow profile is stable and free from disturbances. Verify that there are no obstructions, bends, or valves in close proximity to the flowmeter that could impact the accuracy of measurements.
Calibration Verification:
Periodically check and verify the calibration of the electromagnetic flowmeter. Calibration drift over time can occur, and regular verification against a known standard helps maintain measurement accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended calibration intervals and procedures.
Fluid Conductivity:
Ensure that the fluid being measured has sufficient conductivity. Electromagnetic flowmeters require a minimum level of fluid conductivity for accurate measurements. If the conductivity is too low, it may affect the generation of the electromagnetic signal.
Power Supply Stability:
Check the stability of the power supply to the flowmeter. Fluctuations in the power supply can impact the performance of the flowmeter. Confirm that the power source meets the specified requirements.
Communication Signals:
Verify the output signals from the flowmeter, whether they are analog (4-20 mA or 0-10 V), frequency/pulse, or digital signals (HART, Modbus, etc.). Ensure that the signals are within the expected range and are compatible with the receiving devices or control systems.
Temperature and Viscosity:
Consider the impact of changes in fluid temperature and viscosity on the flowmeter performance. Some electromagnetic flowmeters have temperature compensation features, but it’s essential to operate within the specified temperature and viscosity ranges.
Status/Alarm Outputs:
Check the status and alarm outputs of the flowmeter. Monitor for any alarms related to low flow, sensor faults, or other diagnostic information.
Environmental Conditions:
Consider the environmental conditions such as ambient temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to corrosive substances. Ensure that the flowmeter is suitable for the operating environment.
Regular field checks and maintenance help identify potential issues early on, ensuring the electromagnetic flowmeter continues to provide accurate and reliable flow measurements. Following manufacturer guidelines and industry best practices is crucial for the proper operation and longevity of the flowmeter system.















-.jpg)





-.jpg)