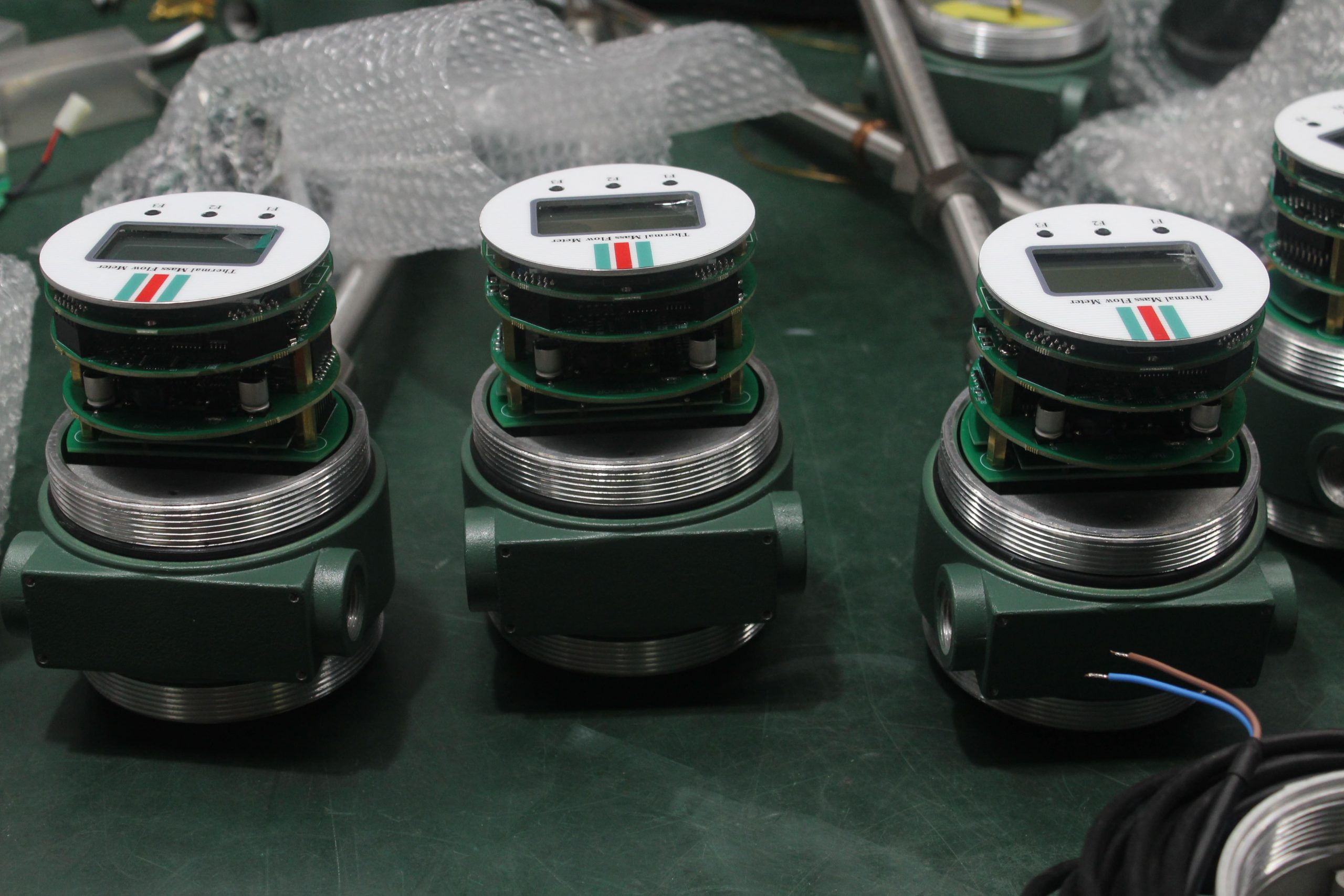
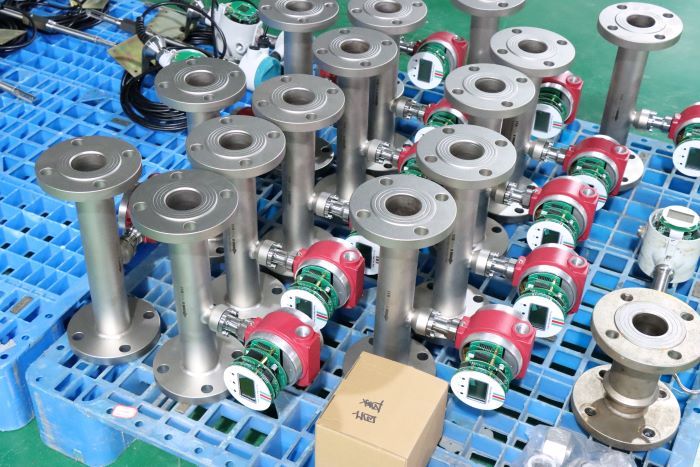
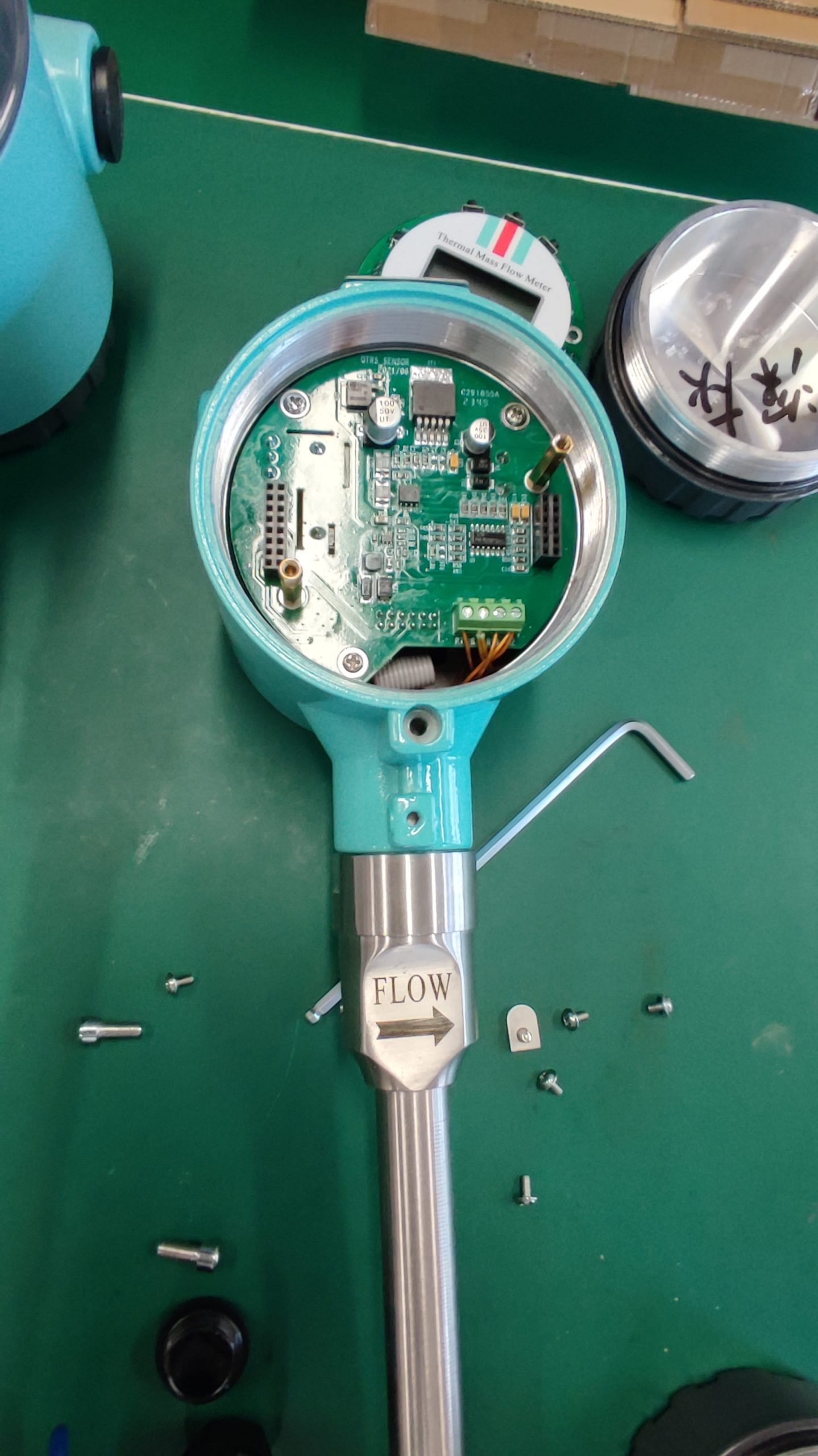
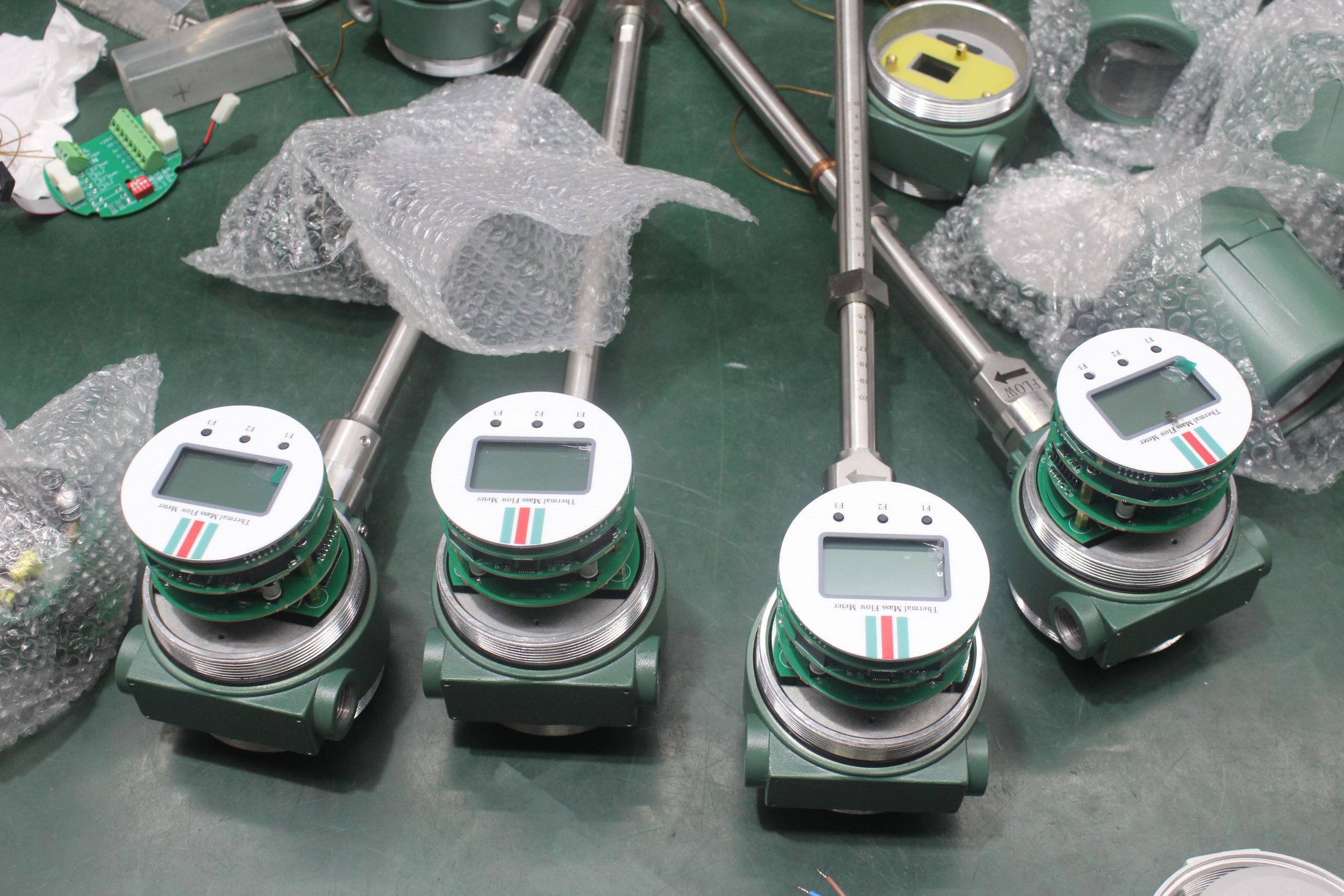
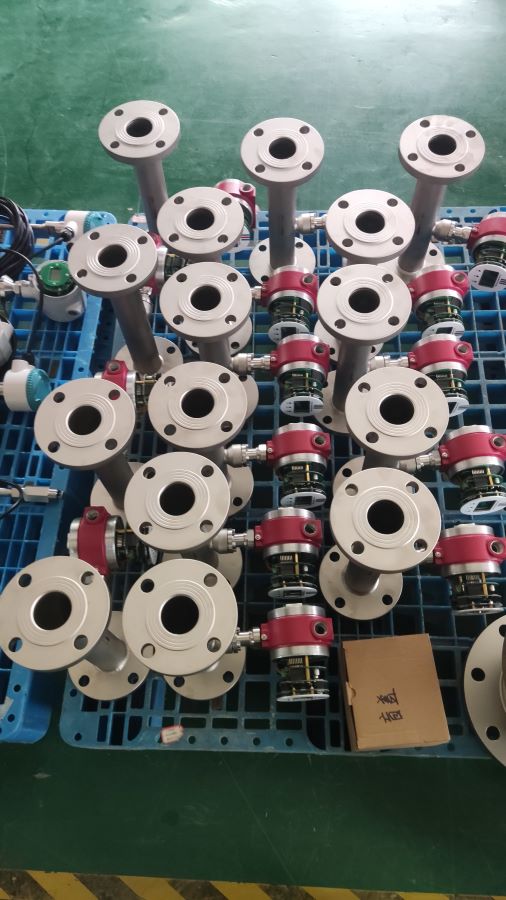
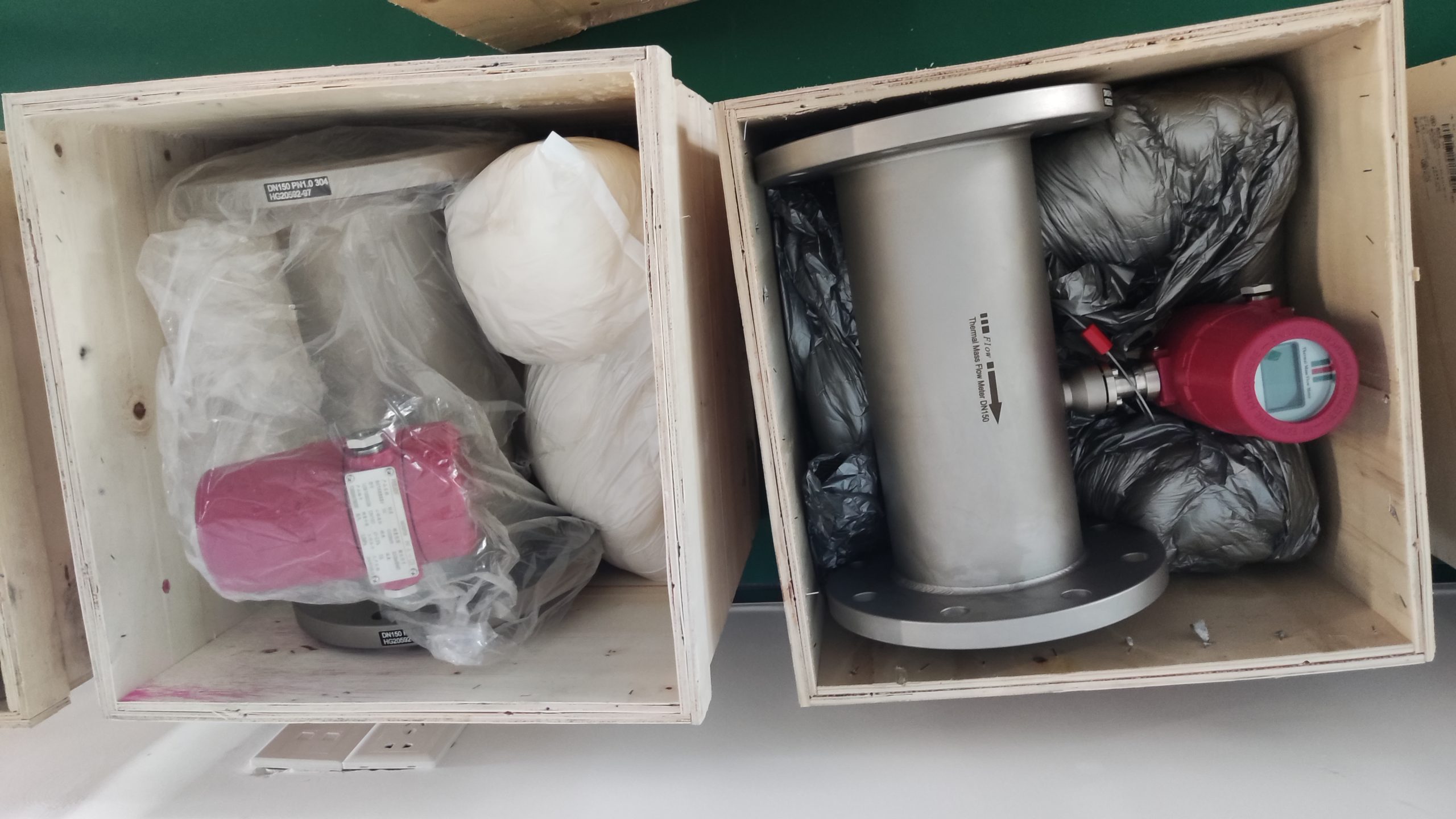
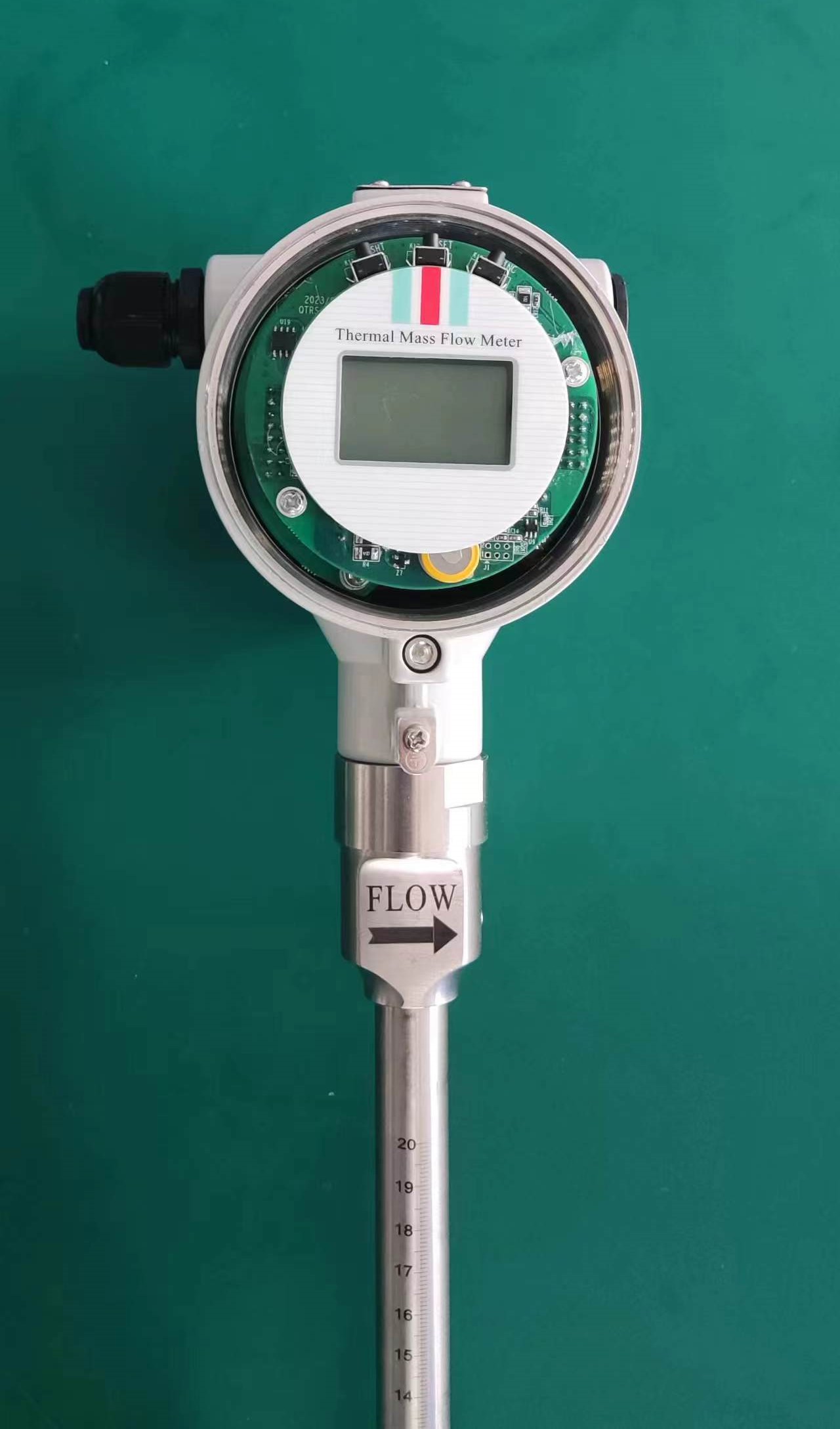
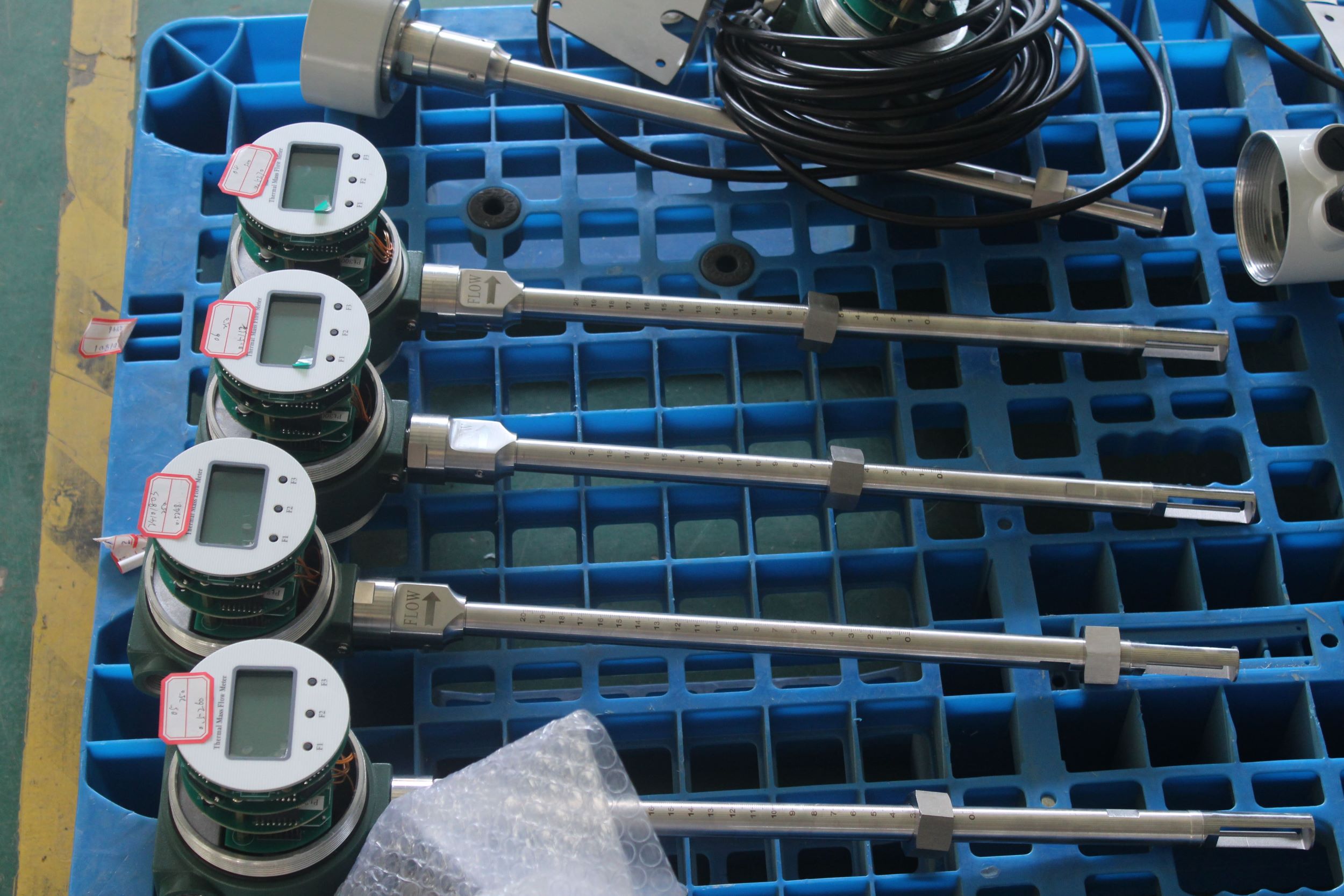
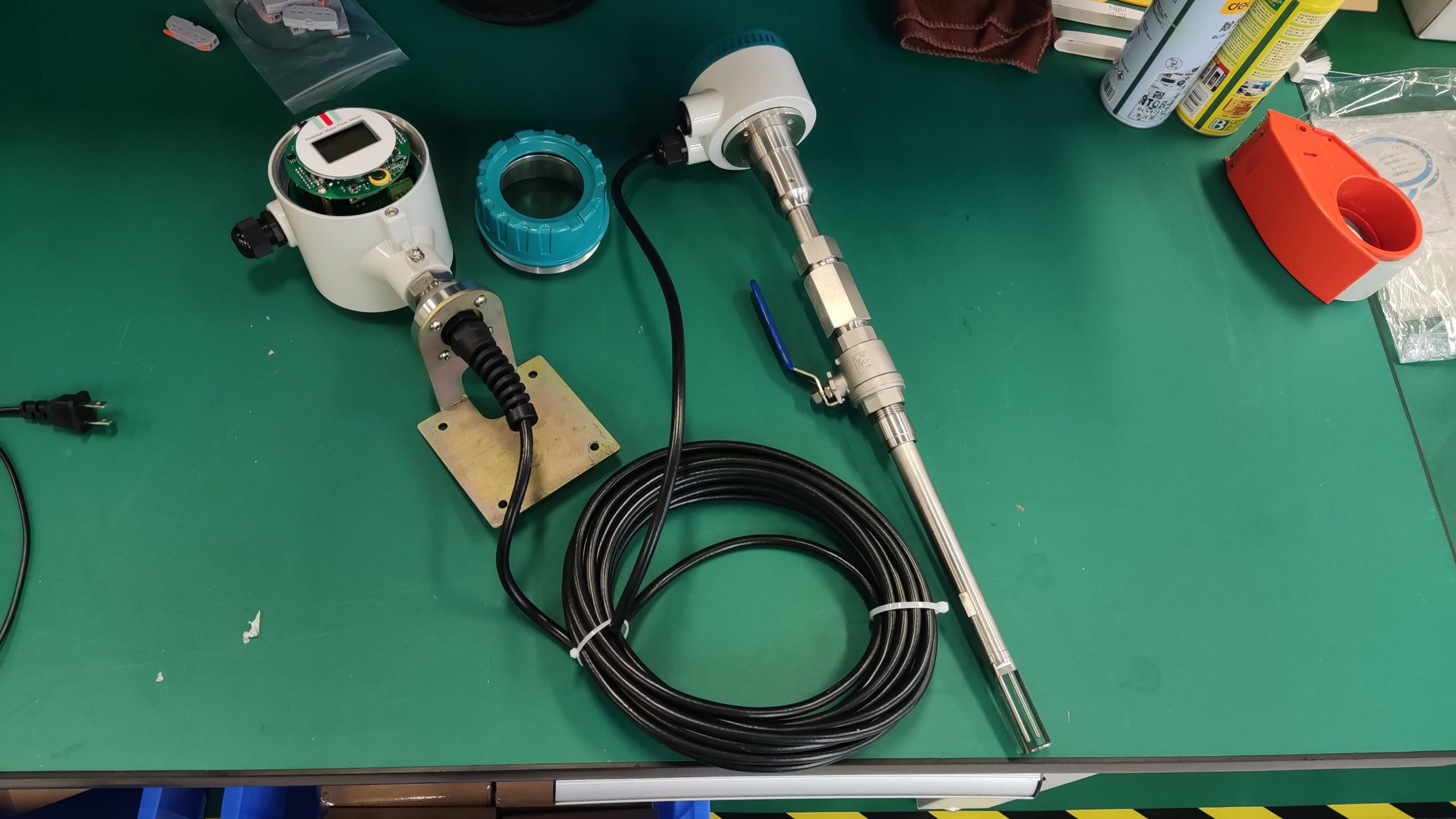
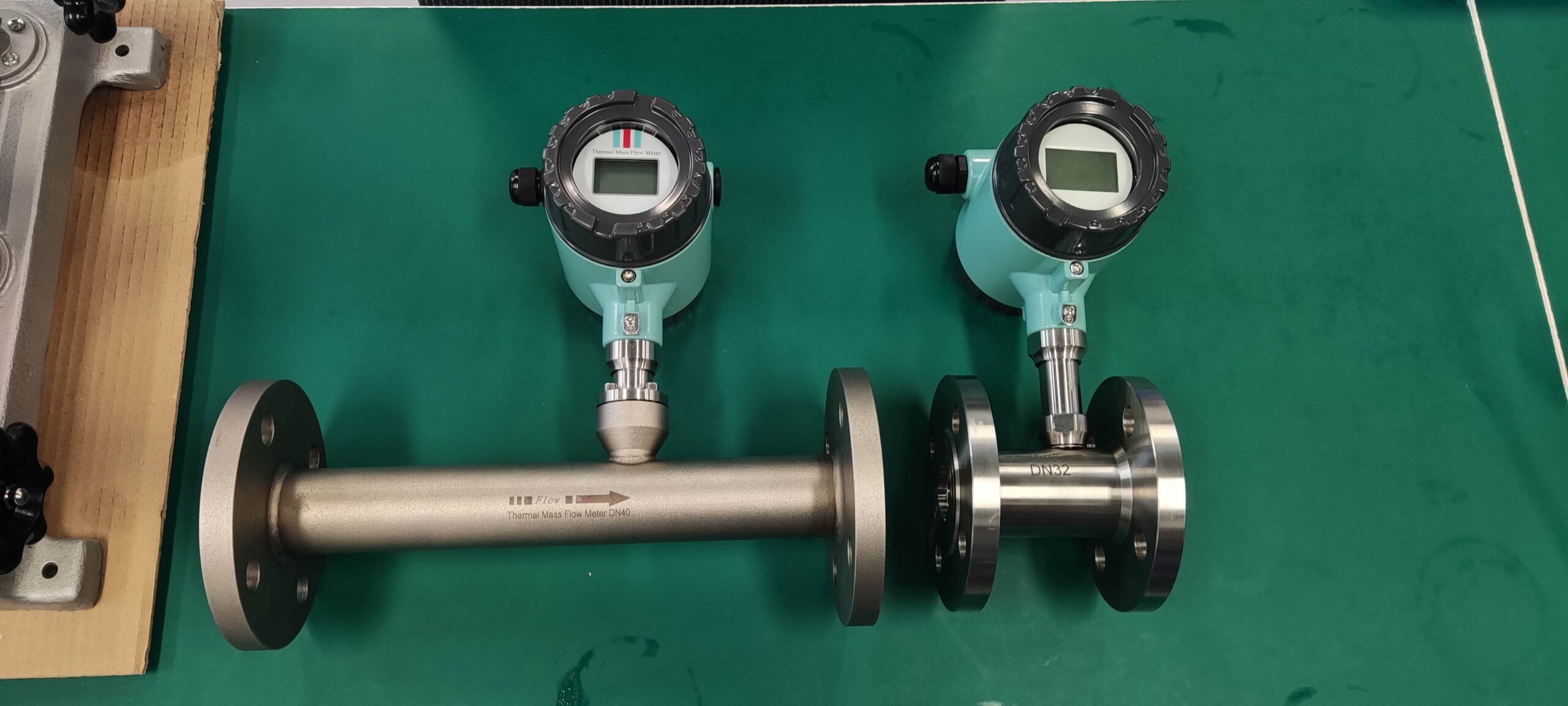
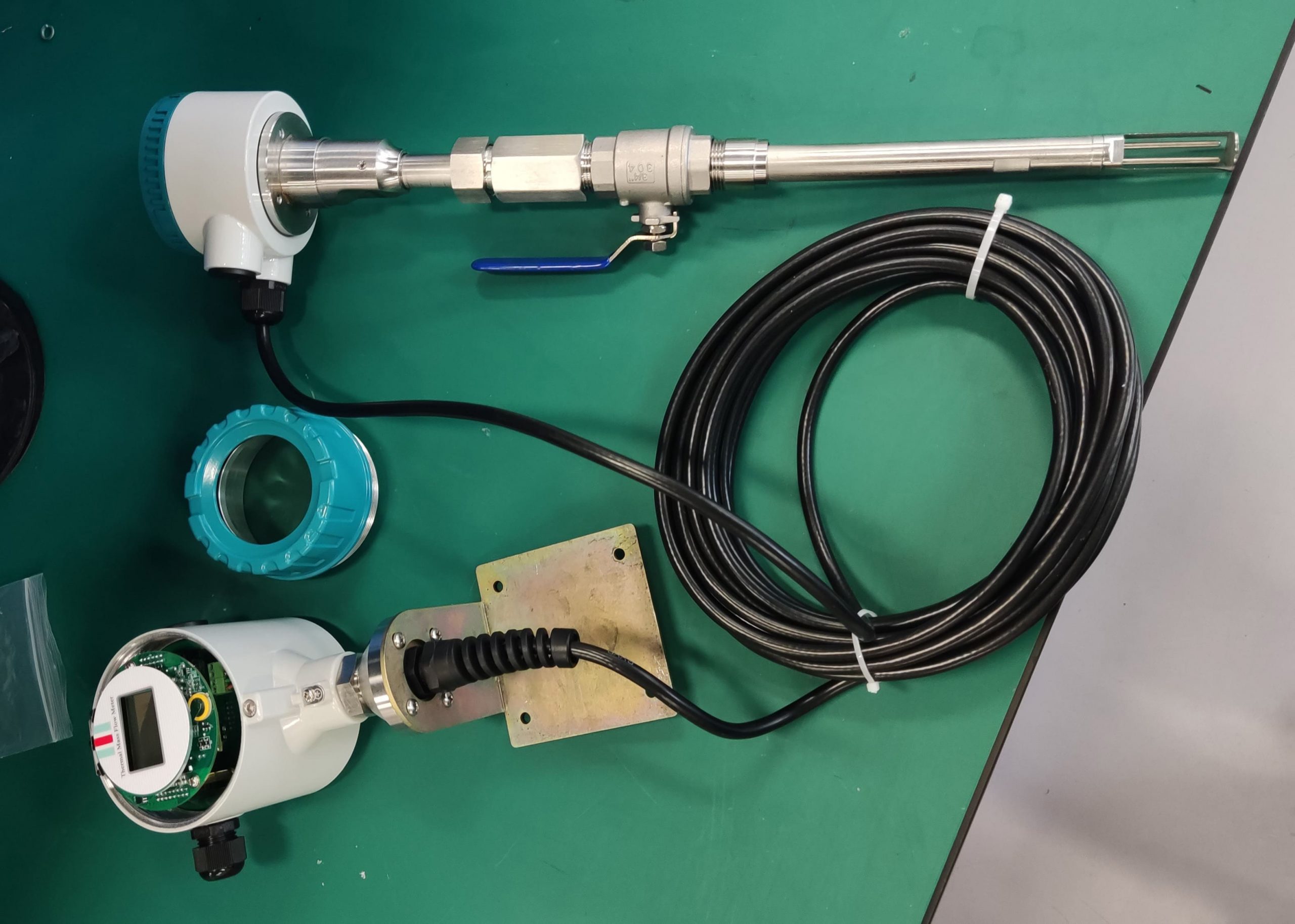
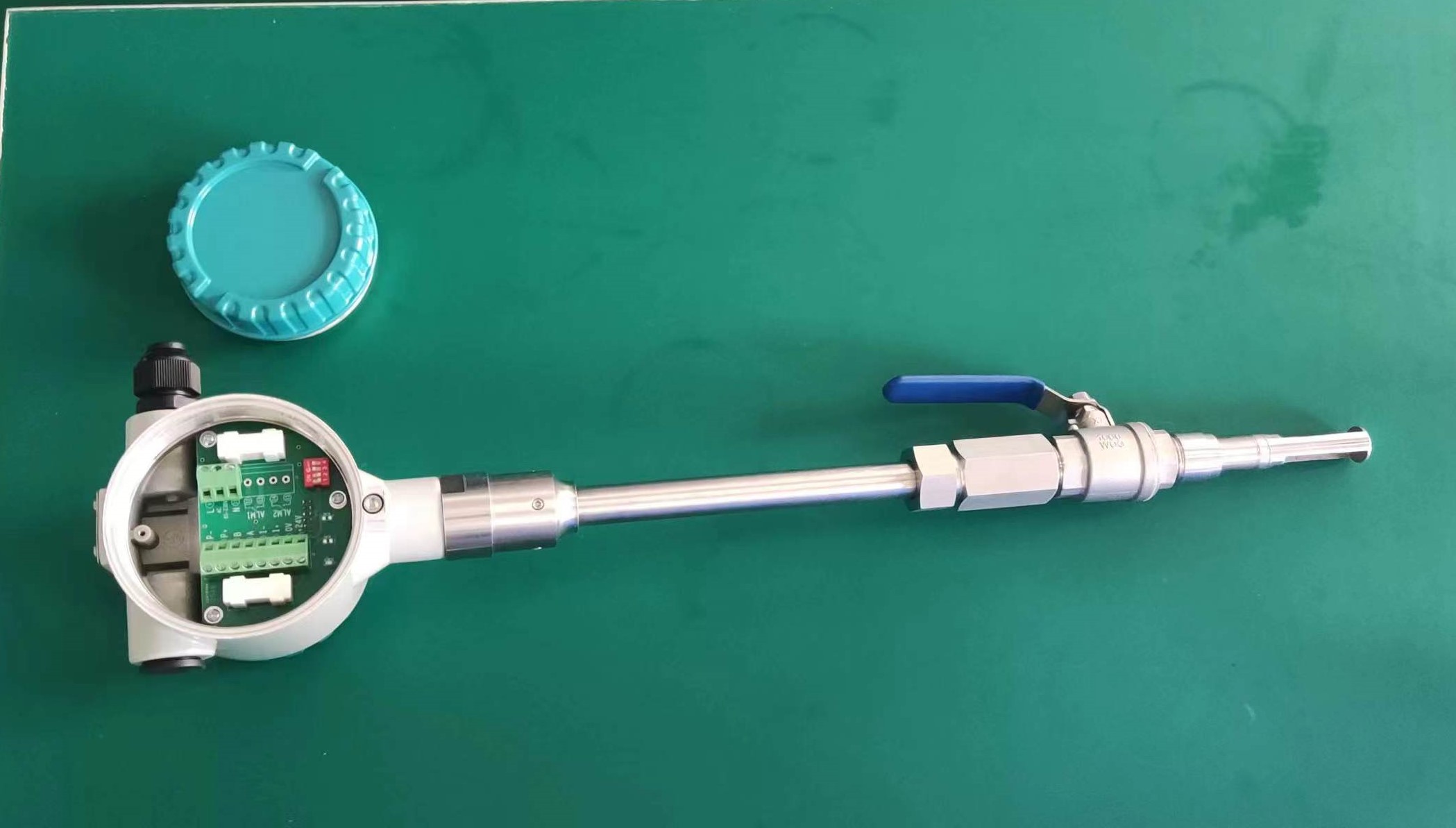
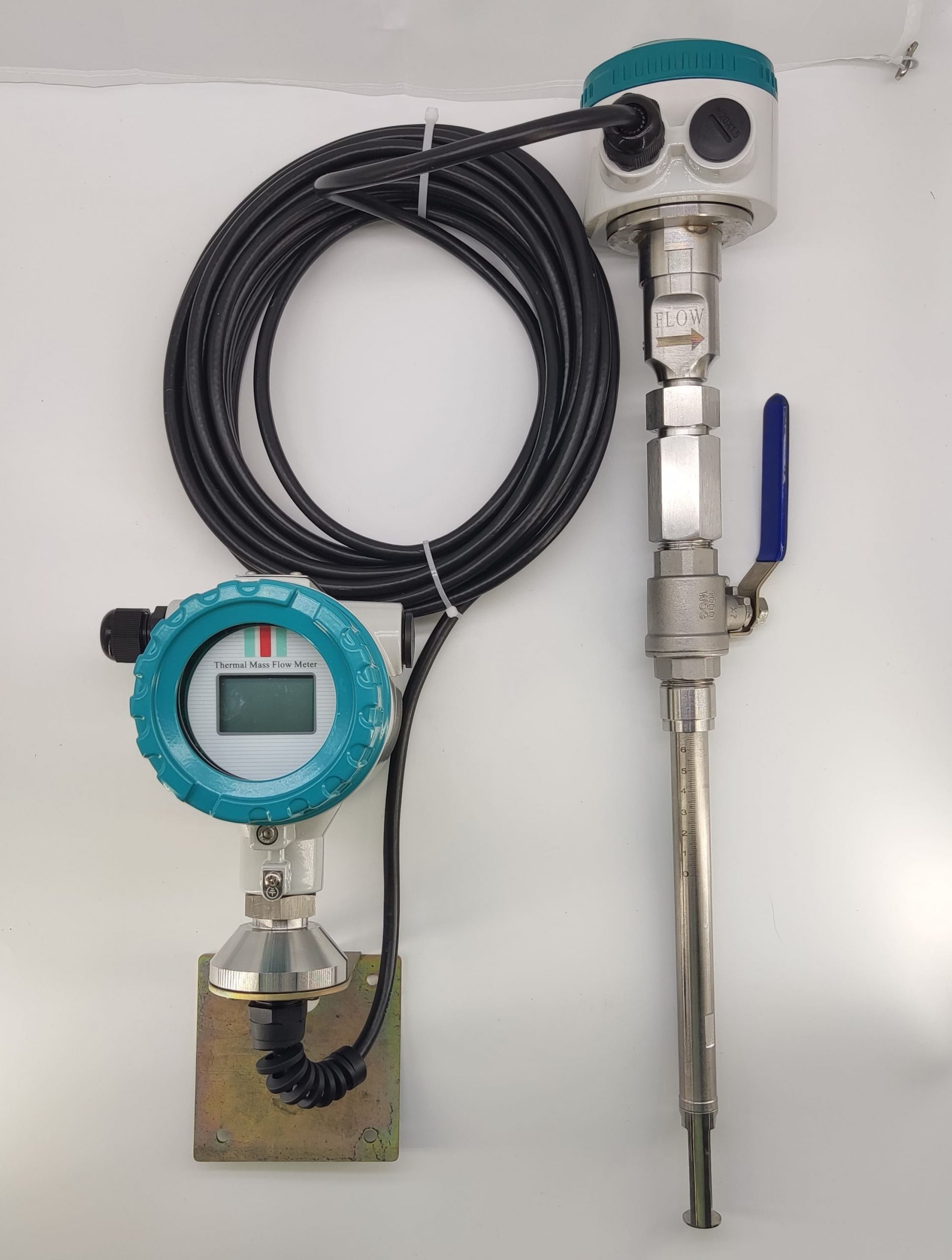
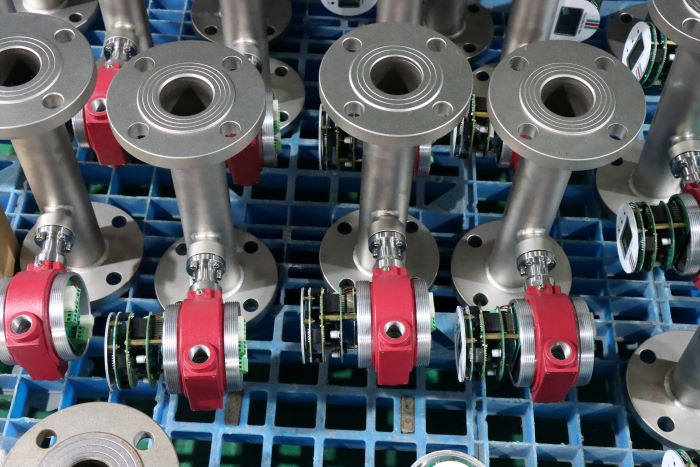
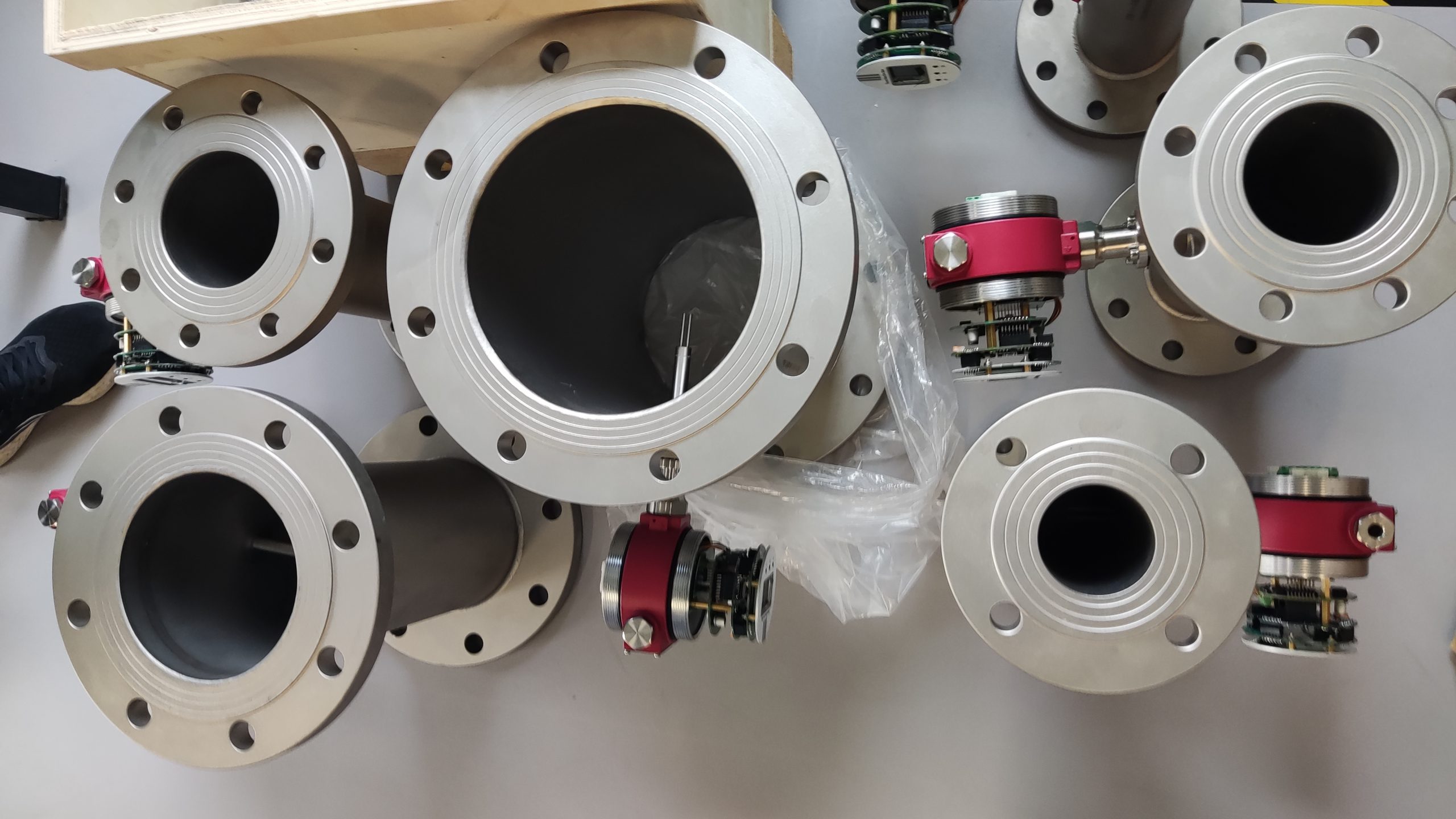
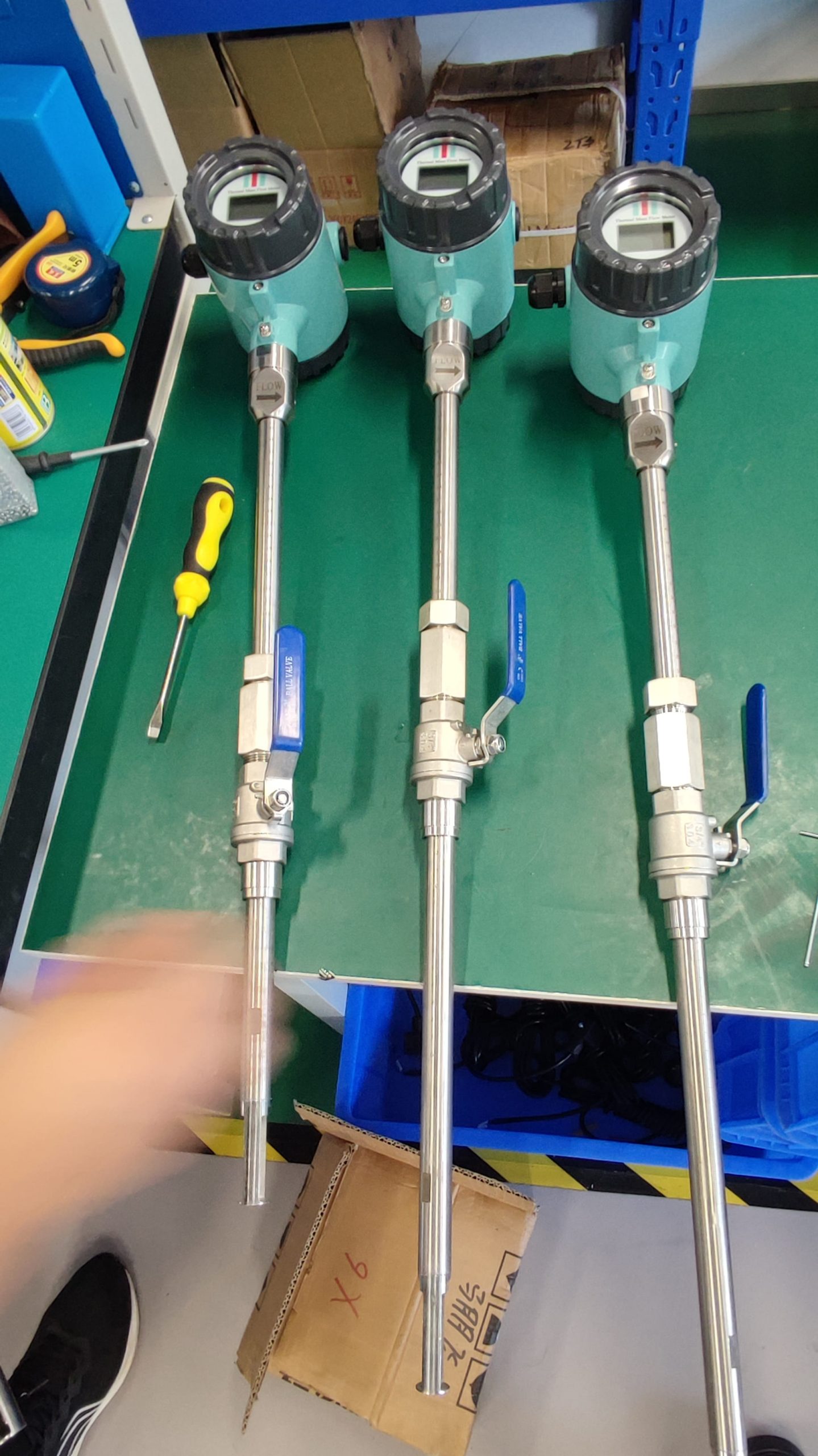
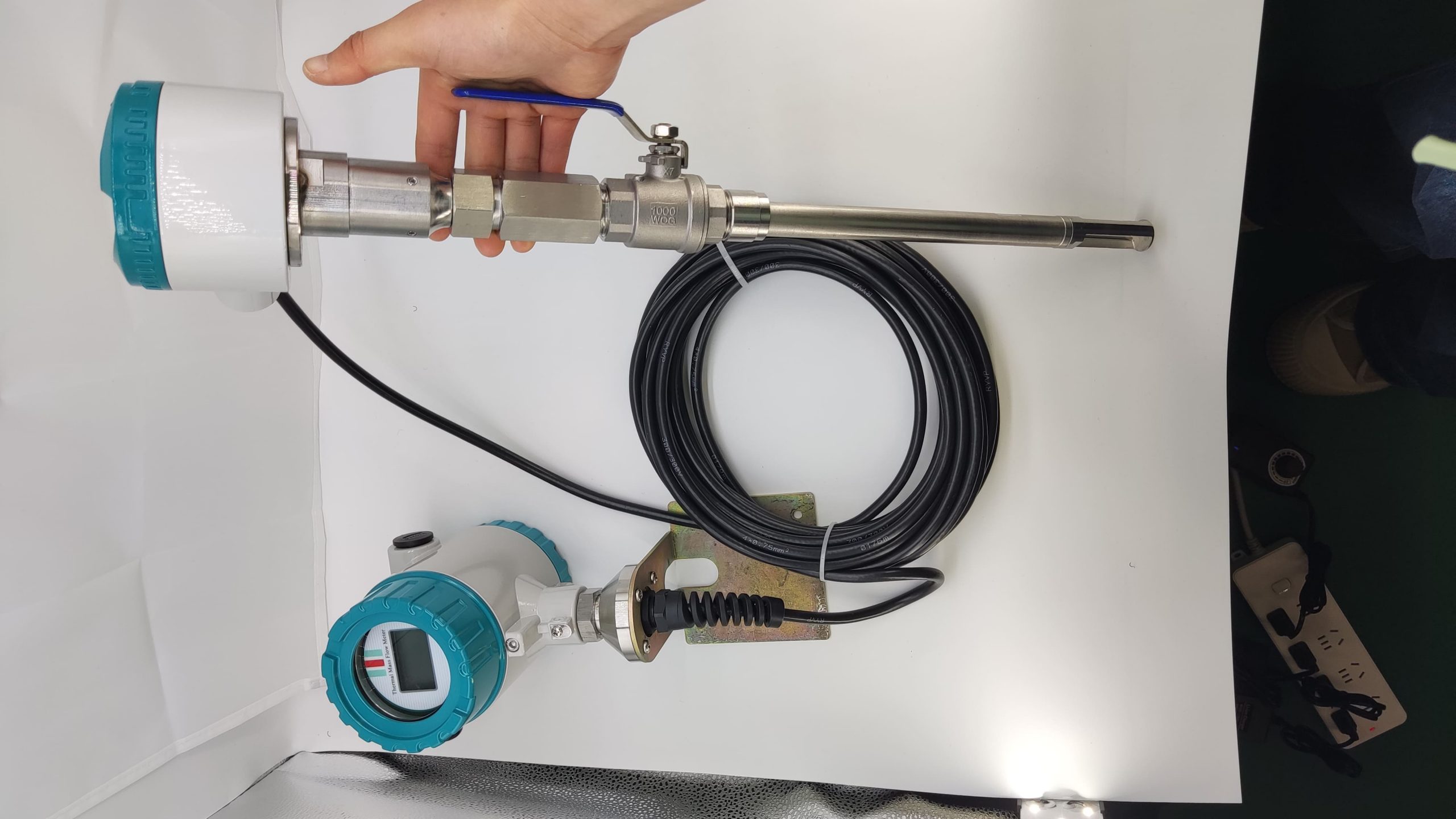
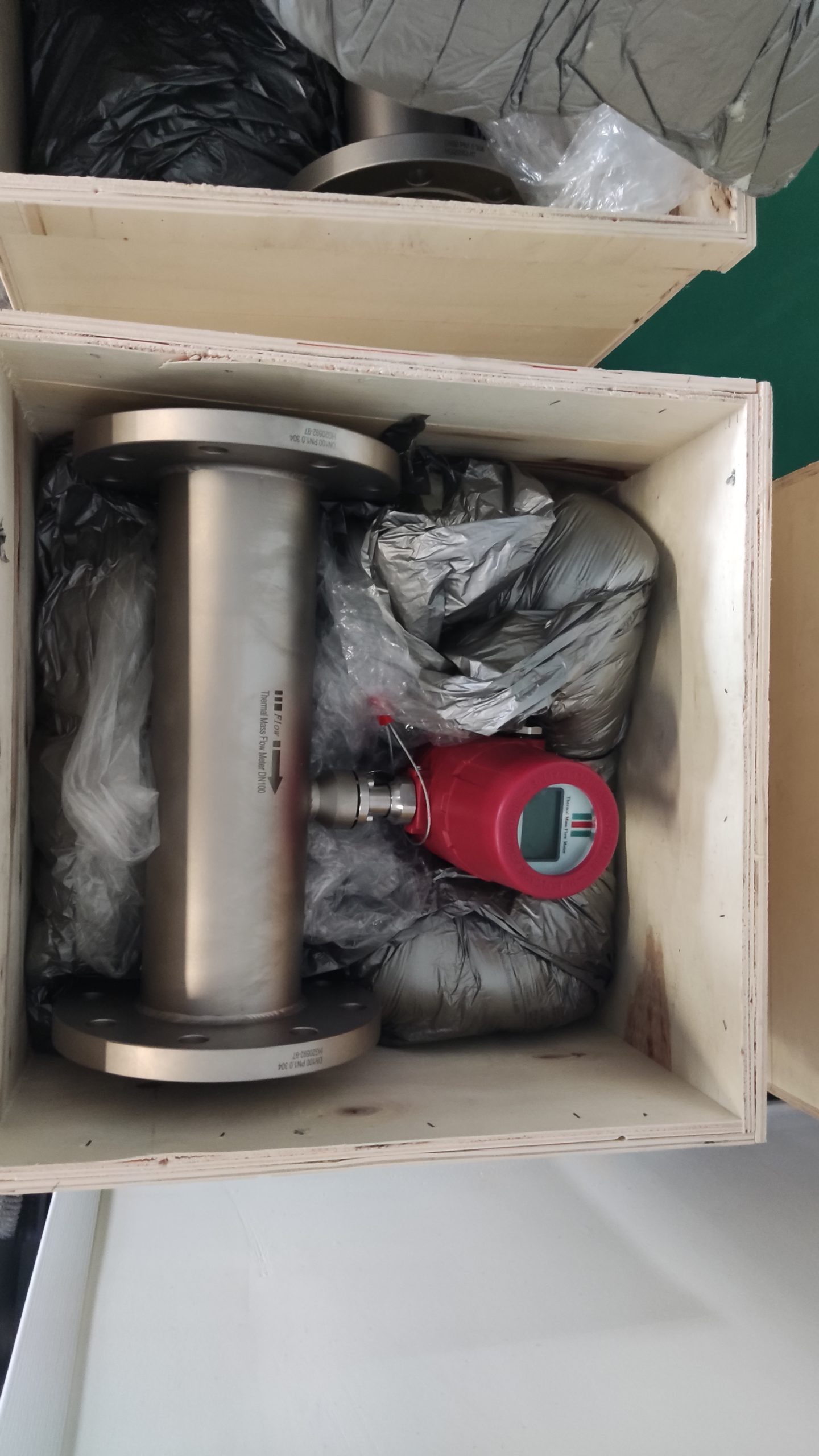
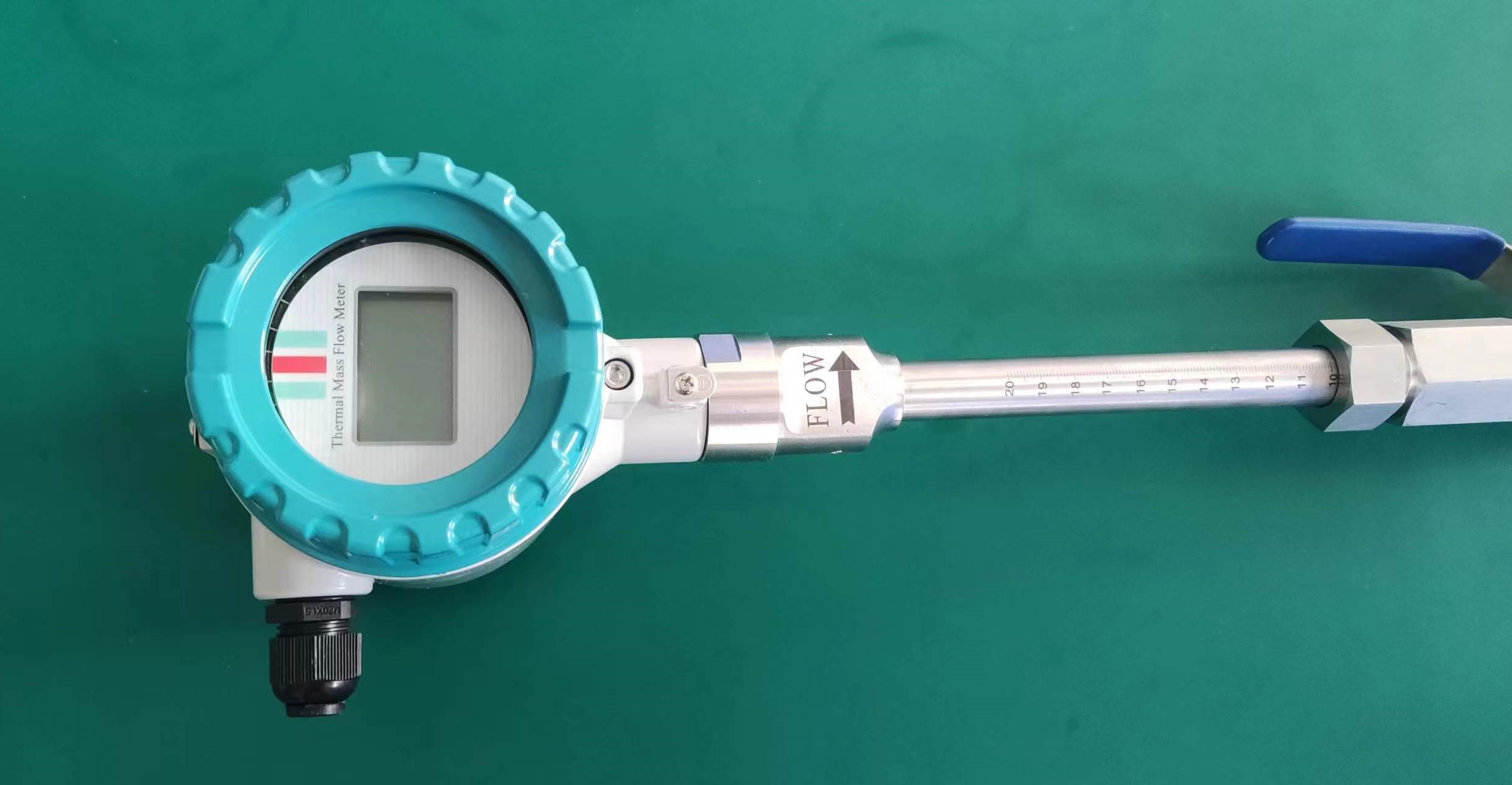
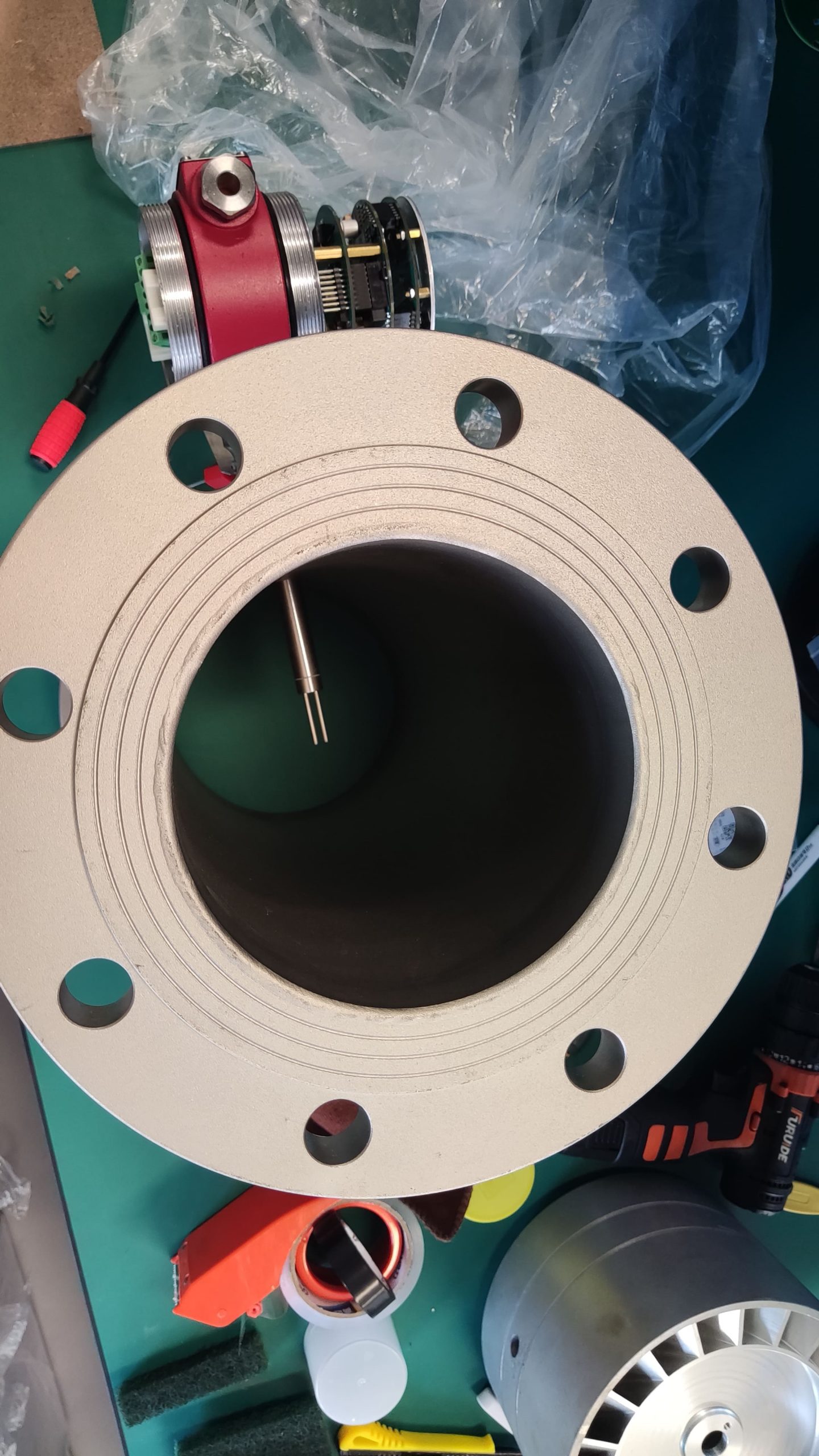
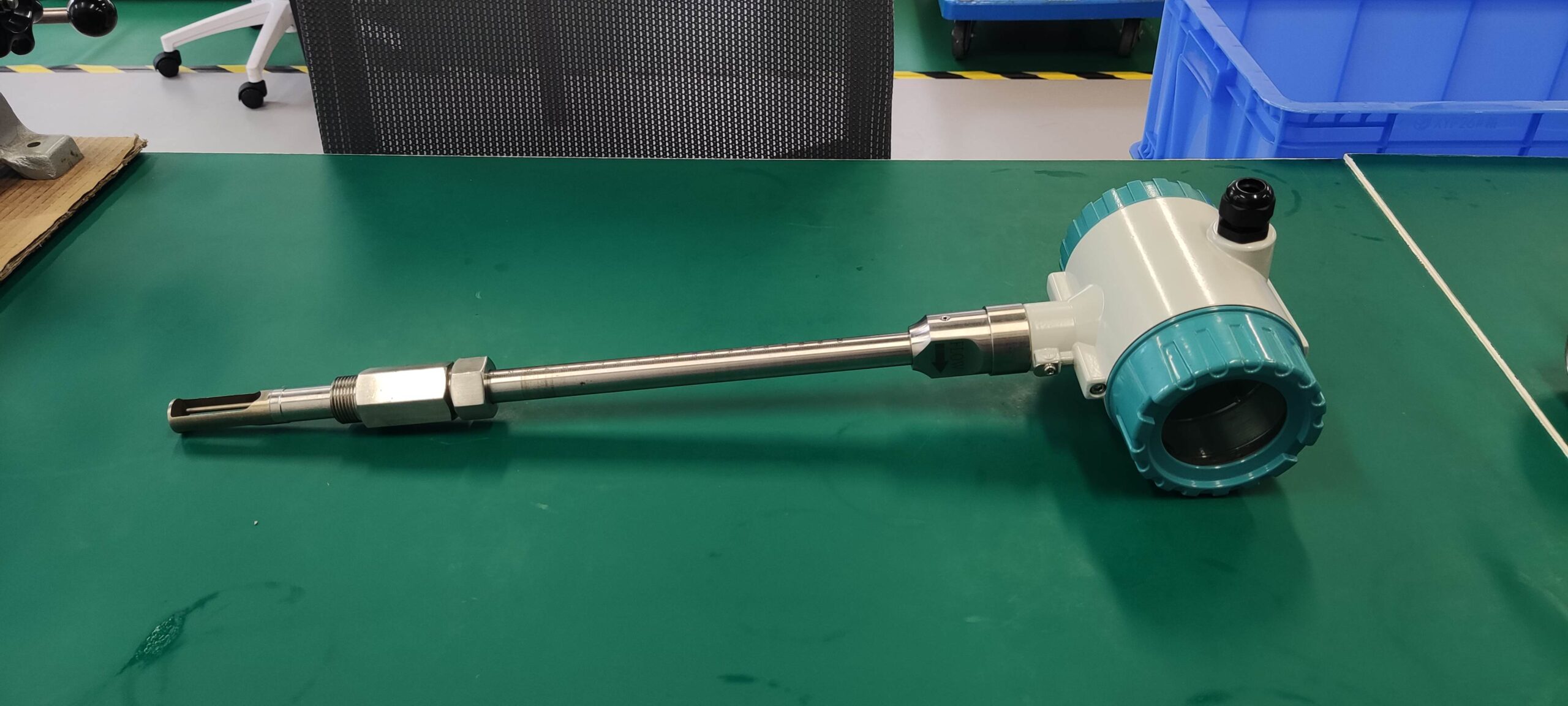
Industrial Stainless Shell Insertion Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter Flow Meter
Thermal mass flowmeters offer several advantages and disadvantages, which are important to consider when selecting a flow measurement solution. Here are some of the key advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages:
Direct Mass Flow Measurement: One of the primary advantages of thermal mass flowmeters is that they measure mass flow directly, without the need for additional pressure or temperature compensation. This provides accurate measurements even if the fluid properties change.
Wide Rangeability: Thermal mass flowmeters typically have a wide turndown ratio, allowing them to accurately measure flow rates over a broad range of flow conditions. This versatility makes them suitable for various applications.
No Moving Parts: Thermal mass flowmeters have no moving parts in the flow stream, which enhances their reliability and reduces maintenance requirements. They are less prone to wear and tear compared to flowmeters with mechanical components.
Fast Response Time: Thermal mass flowmeters offer fast response times, allowing for real-time measurement and control of flow rates. This makes them suitable for dynamic processes where rapid changes in flow rates occur.
Low Pressure Drop: Thermal mass flowmeters typically have low pressure drop across the sensor, minimizing energy losses and preserving system efficiency.
Wide Applicability: Thermal mass flowmeters can measure the flow rates of various gases, including clean gases, dirty gases, corrosive gases, and mixed gases. This makes them versatile and suitable for use in diverse industries and applications.
Disadvantages:
Limited to Gas Flow: Thermal mass flowmeters are primarily designed for measuring the flow of gases and are not suitable for measuring liquid flow. If liquid flow measurement is required, alternative flow measurement technologies need to be considered.
Susceptibility to Contamination: Thermal mass flowmeters can be sensitive to contaminants such as dust, particulates, and condensates in the gas stream. Contamination can affect the accuracy of measurements and may require periodic maintenance and cleaning.
Temperature Sensitivity: Changes in gas temperature can affect the accuracy of thermal mass flowmeters, particularly if the temperature varies significantly from the calibration temperature. Temperature compensation techniques are employed to mitigate this effect, but careful consideration is needed in temperature-varying applications.
Initial Cost: Thermal mass flowmeters may have a higher initial cost compared to some other flow measurement technologies. However, their long-term reliability, accuracy, and low maintenance requirements often justify the initial investment.
Orientation Sensitivity: Some thermal mass flowmeters may exhibit sensitivity to the orientation of the flow sensor. Proper installation and orientation are necessary to ensure accurate measurements.
Despite these limitations, thermal mass flowmeters remain a popular choice for many applications due to their high accuracy, reliability, and suitability for a wide range of gas flow measurement requirements.