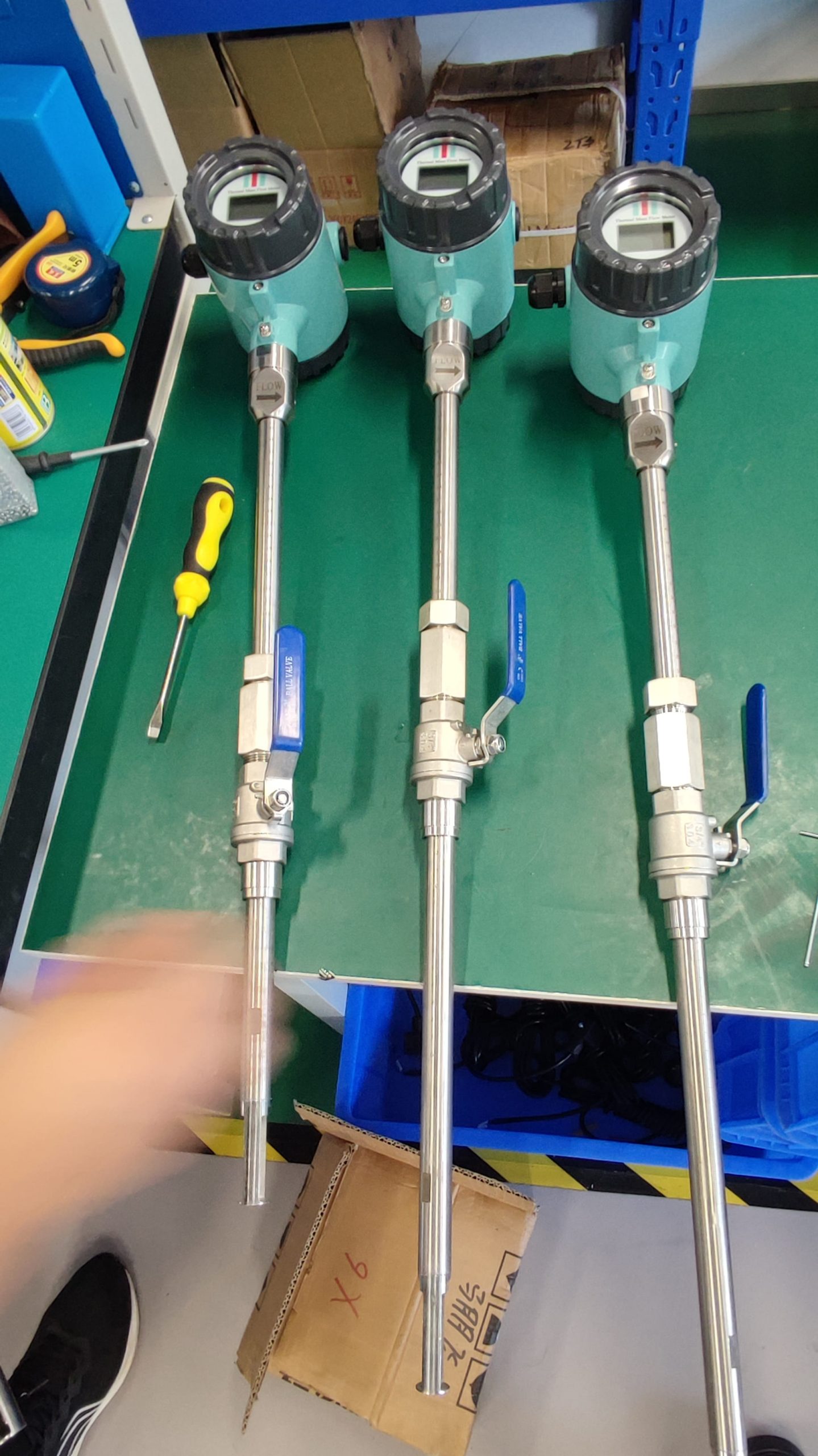
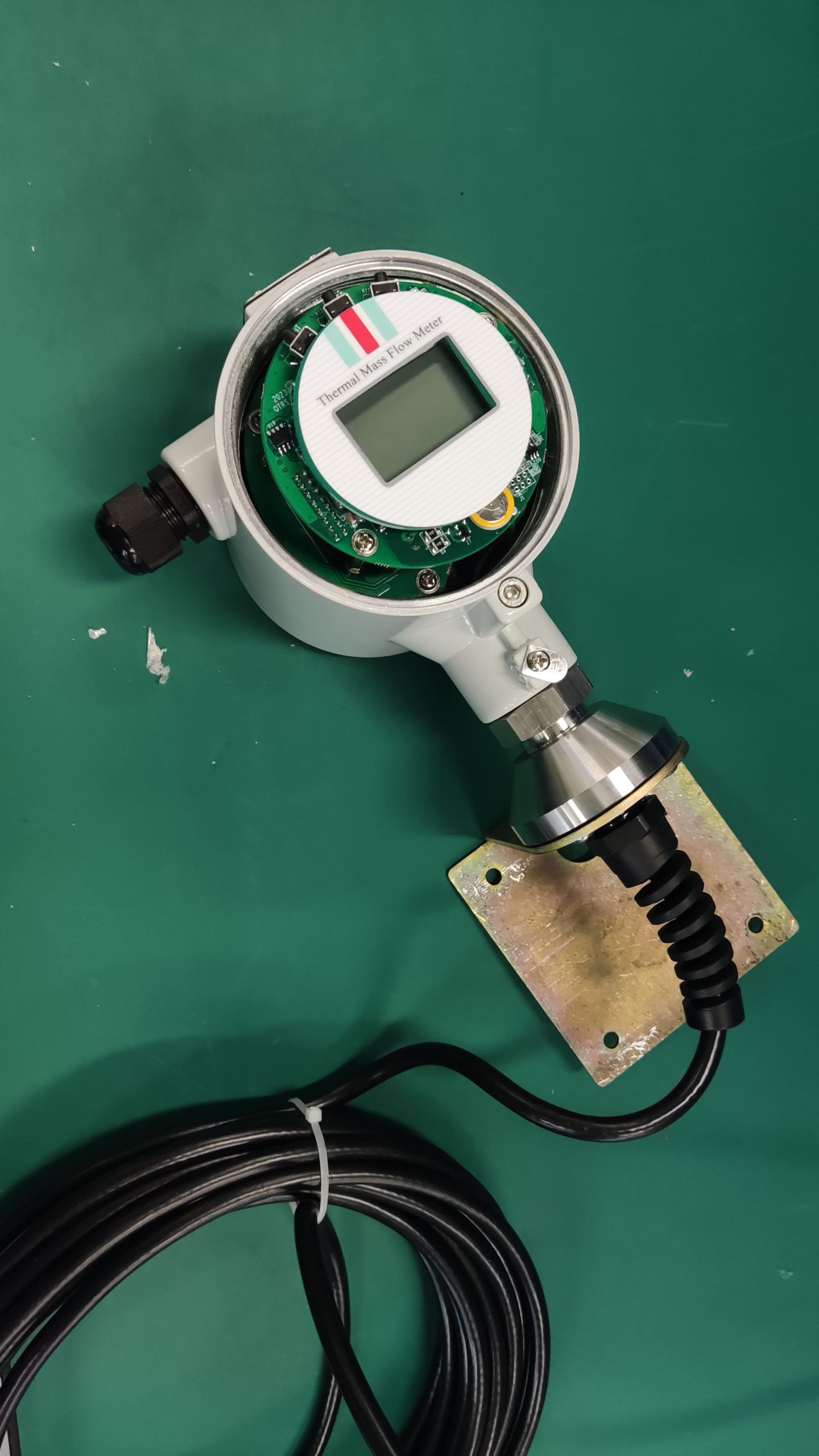
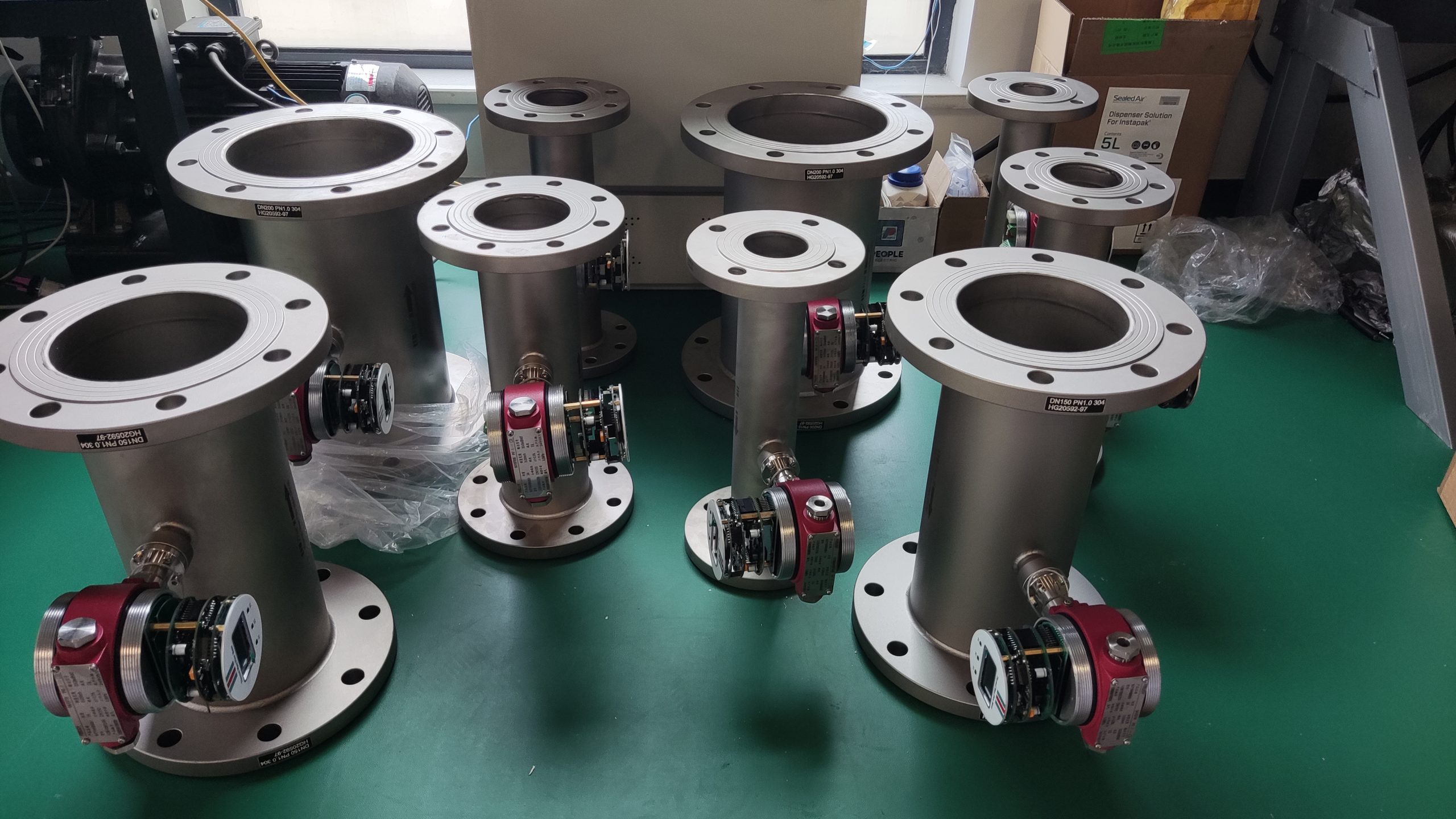
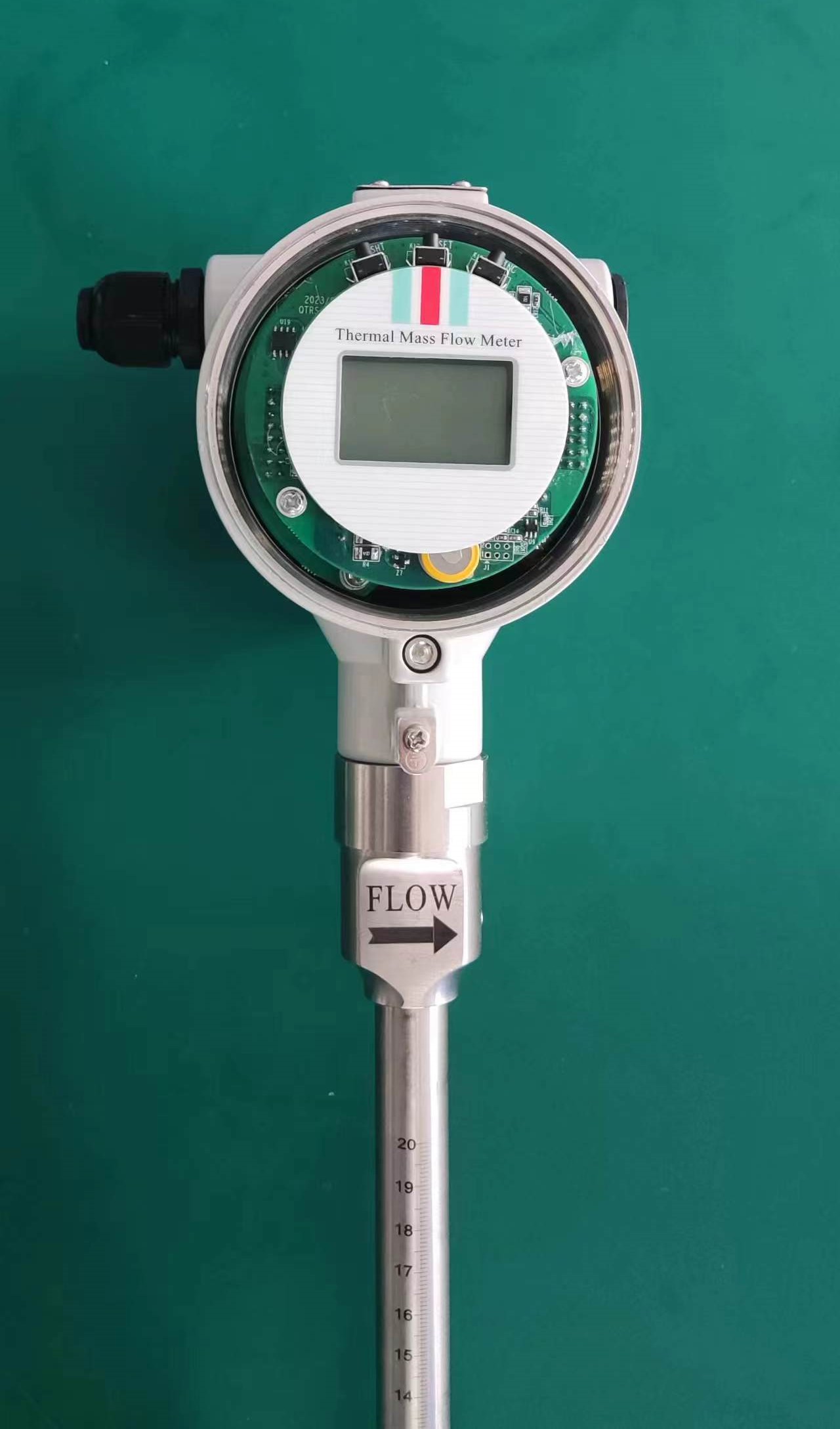
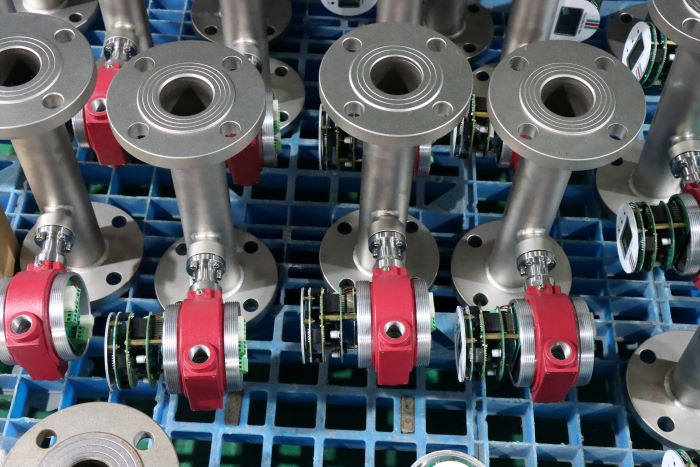
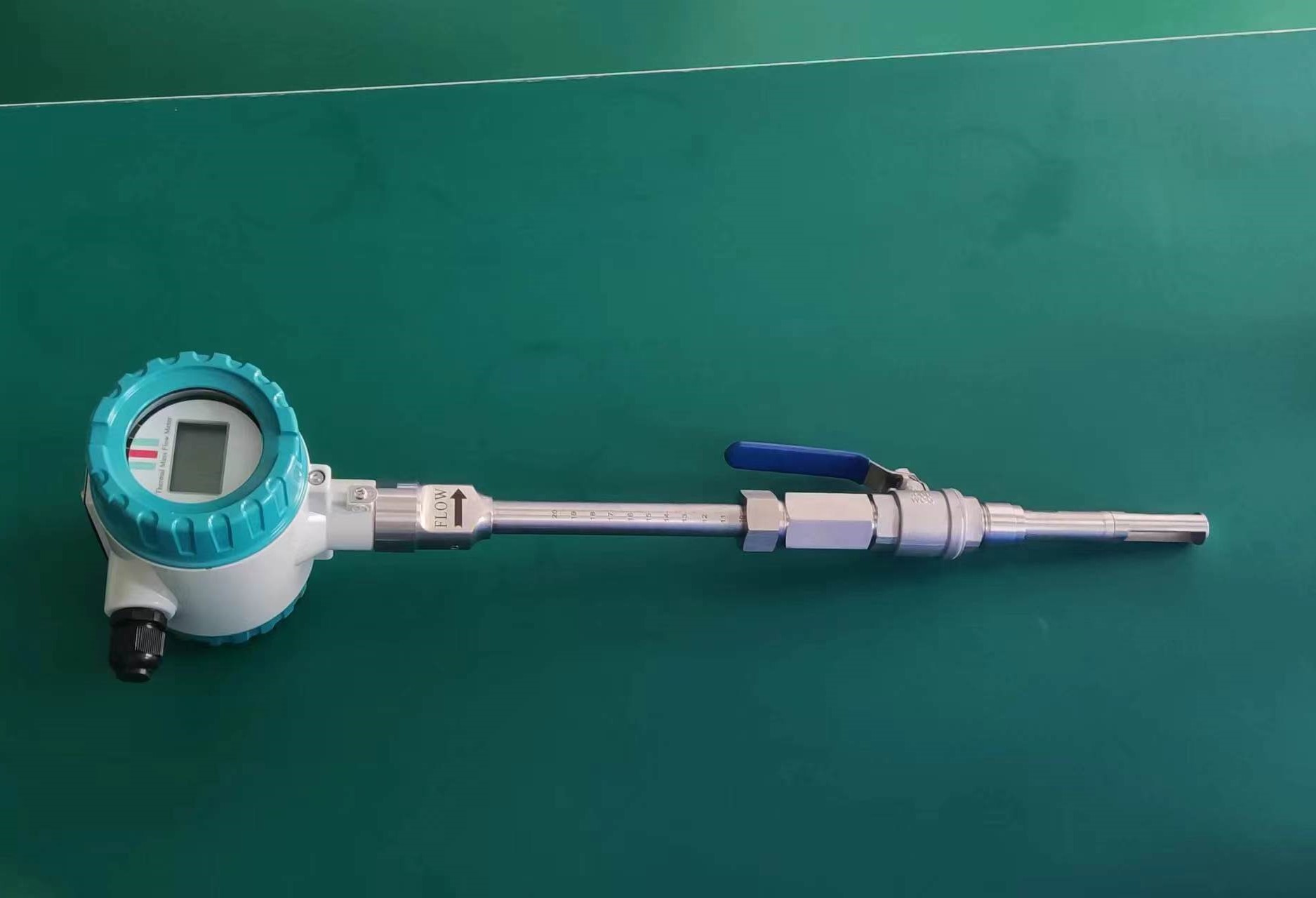
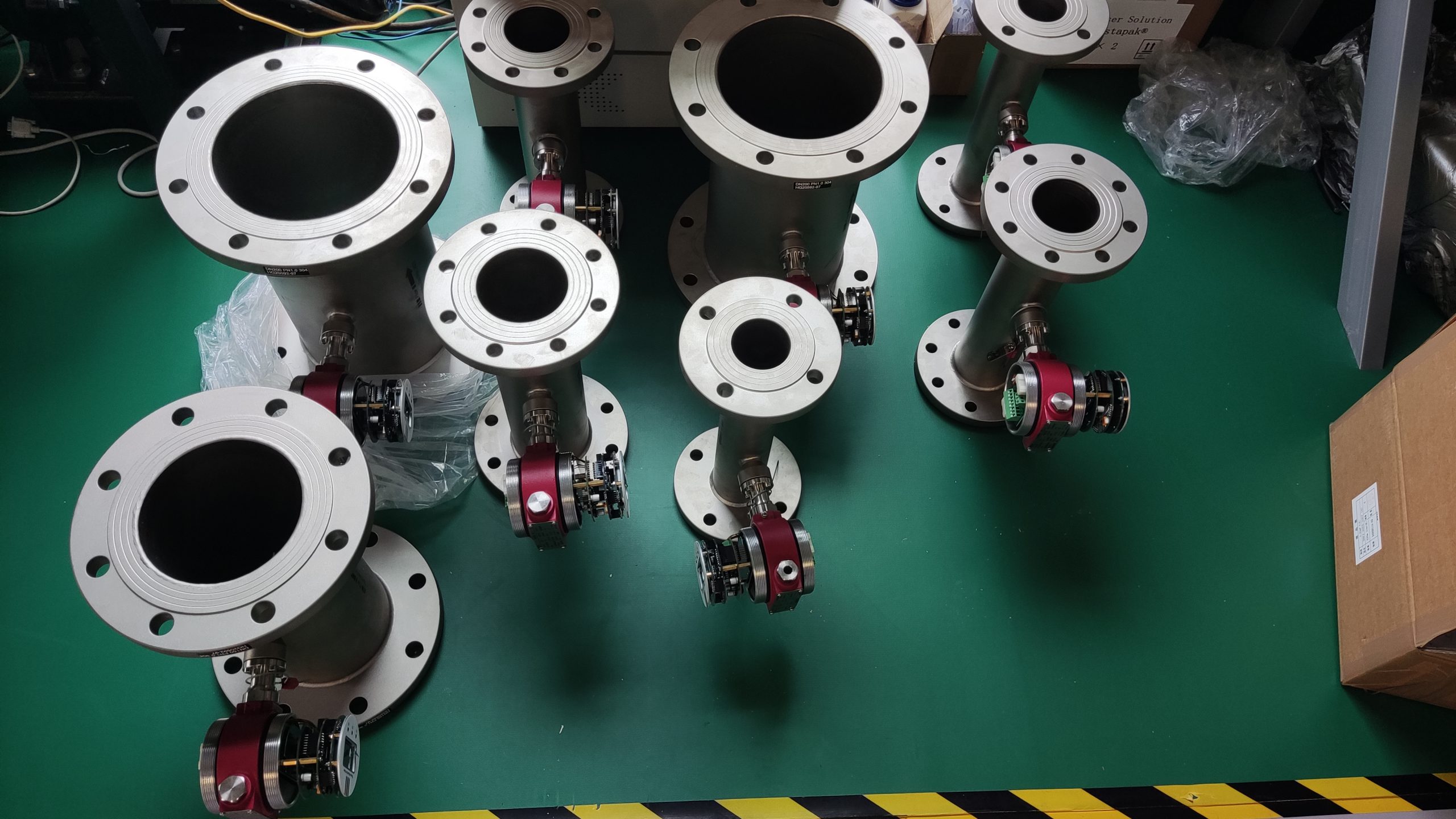
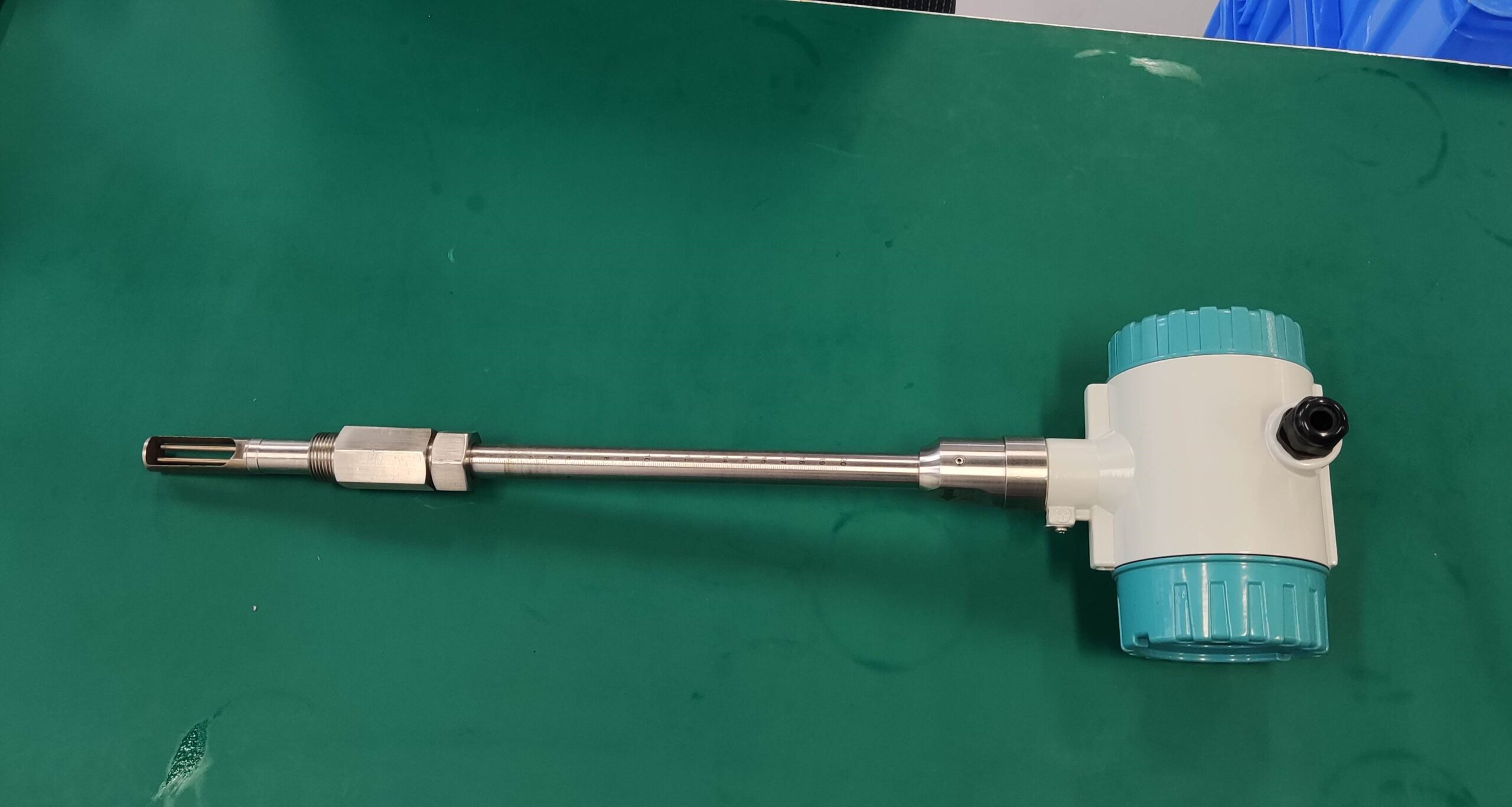
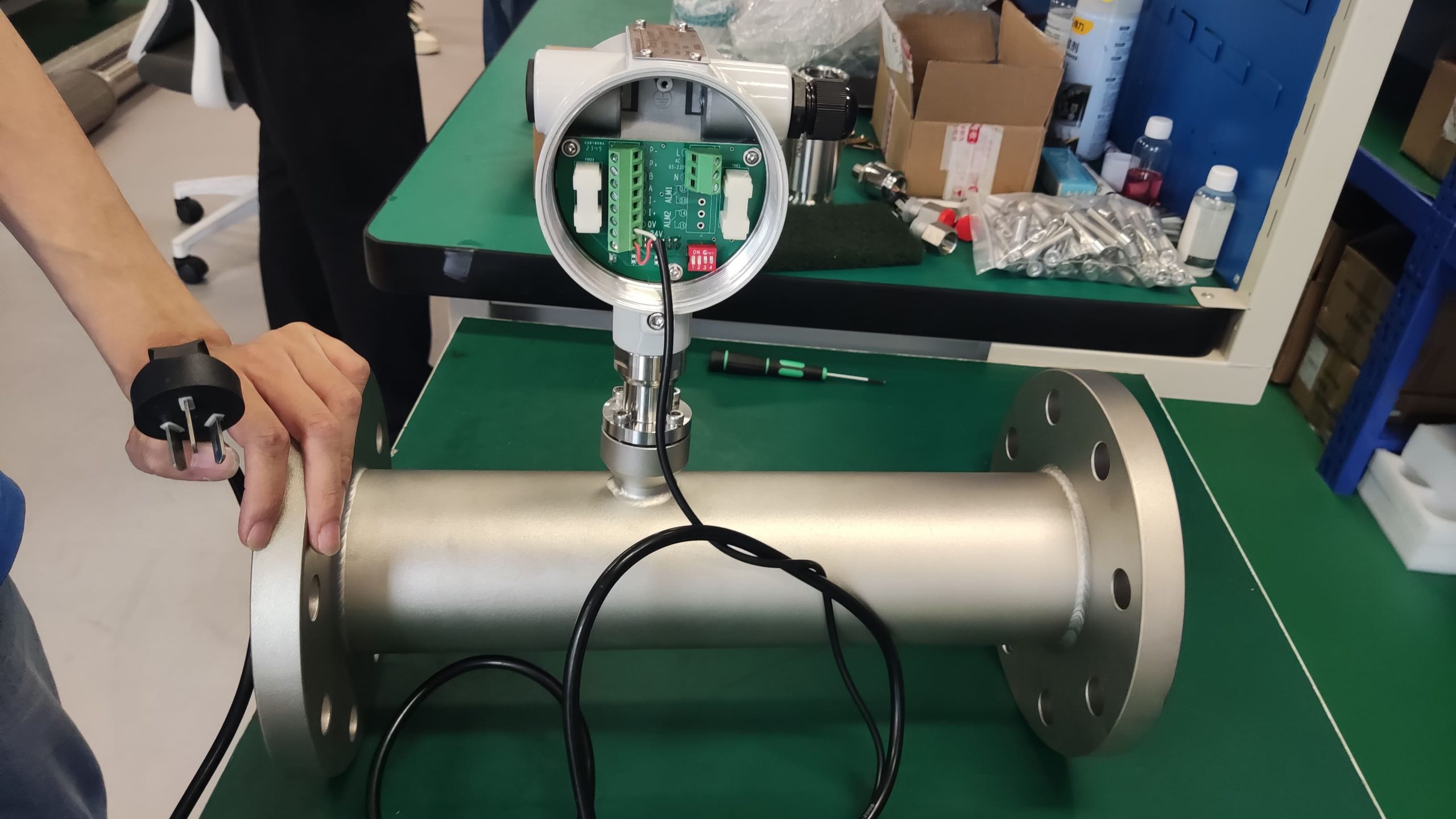
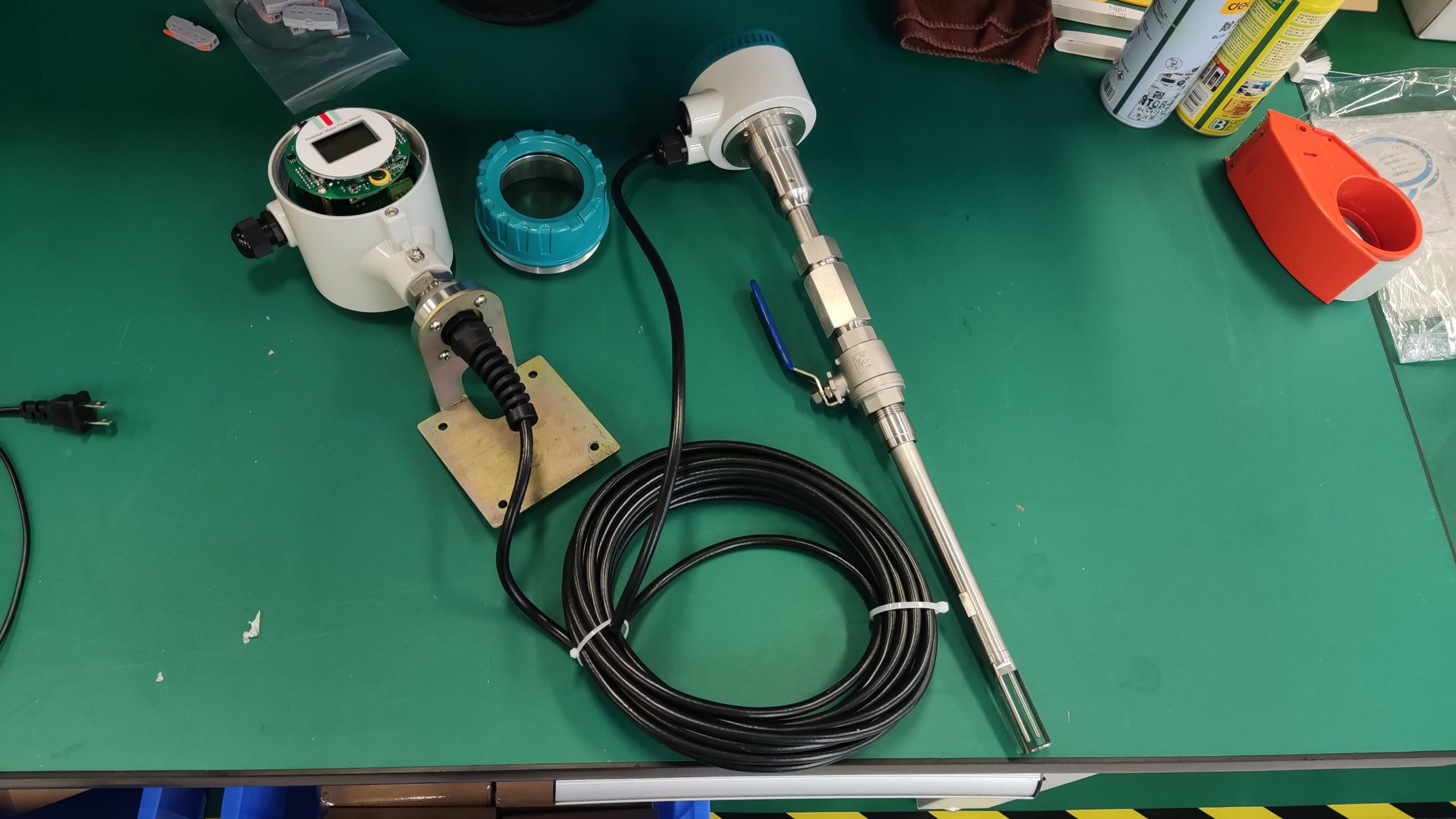
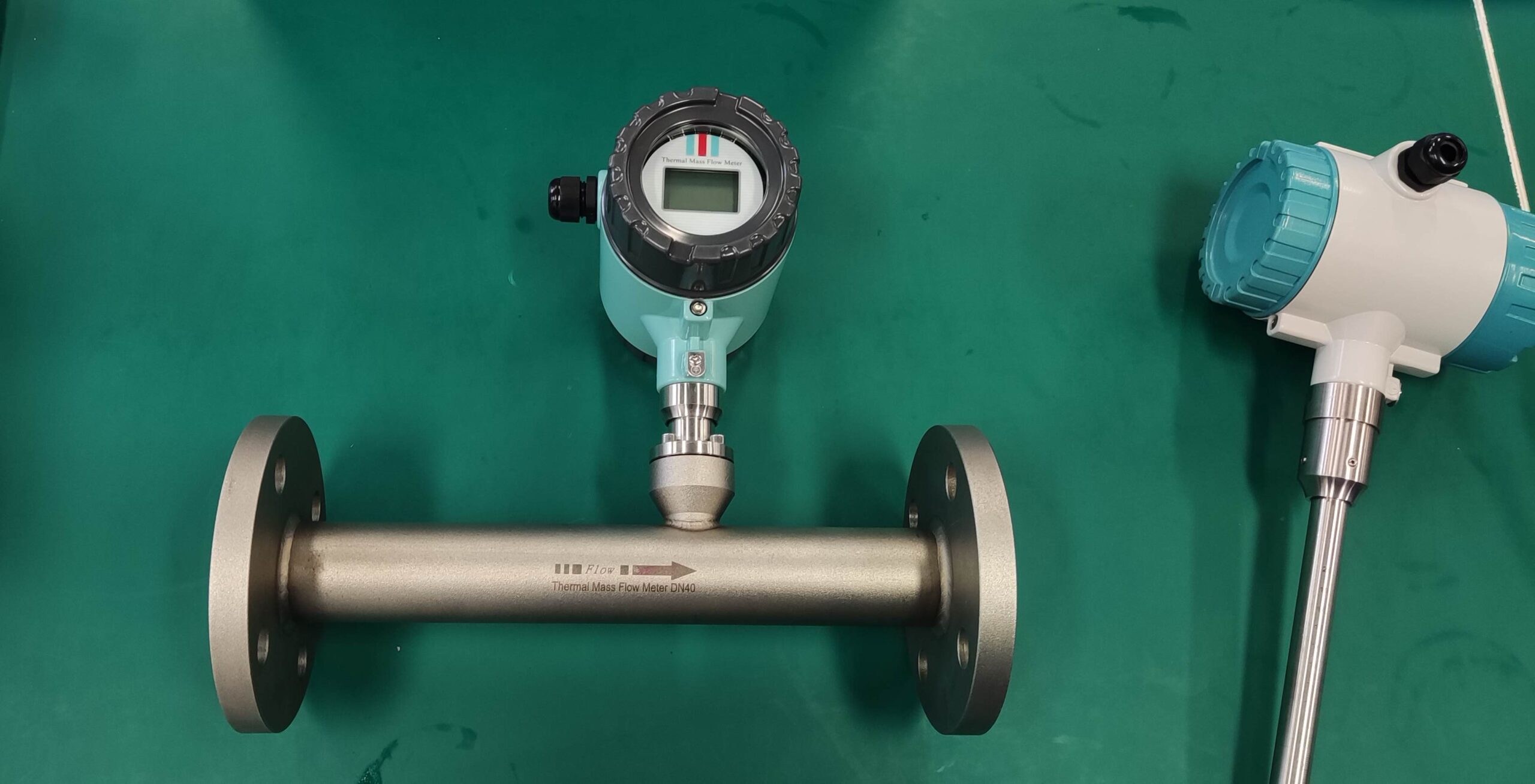
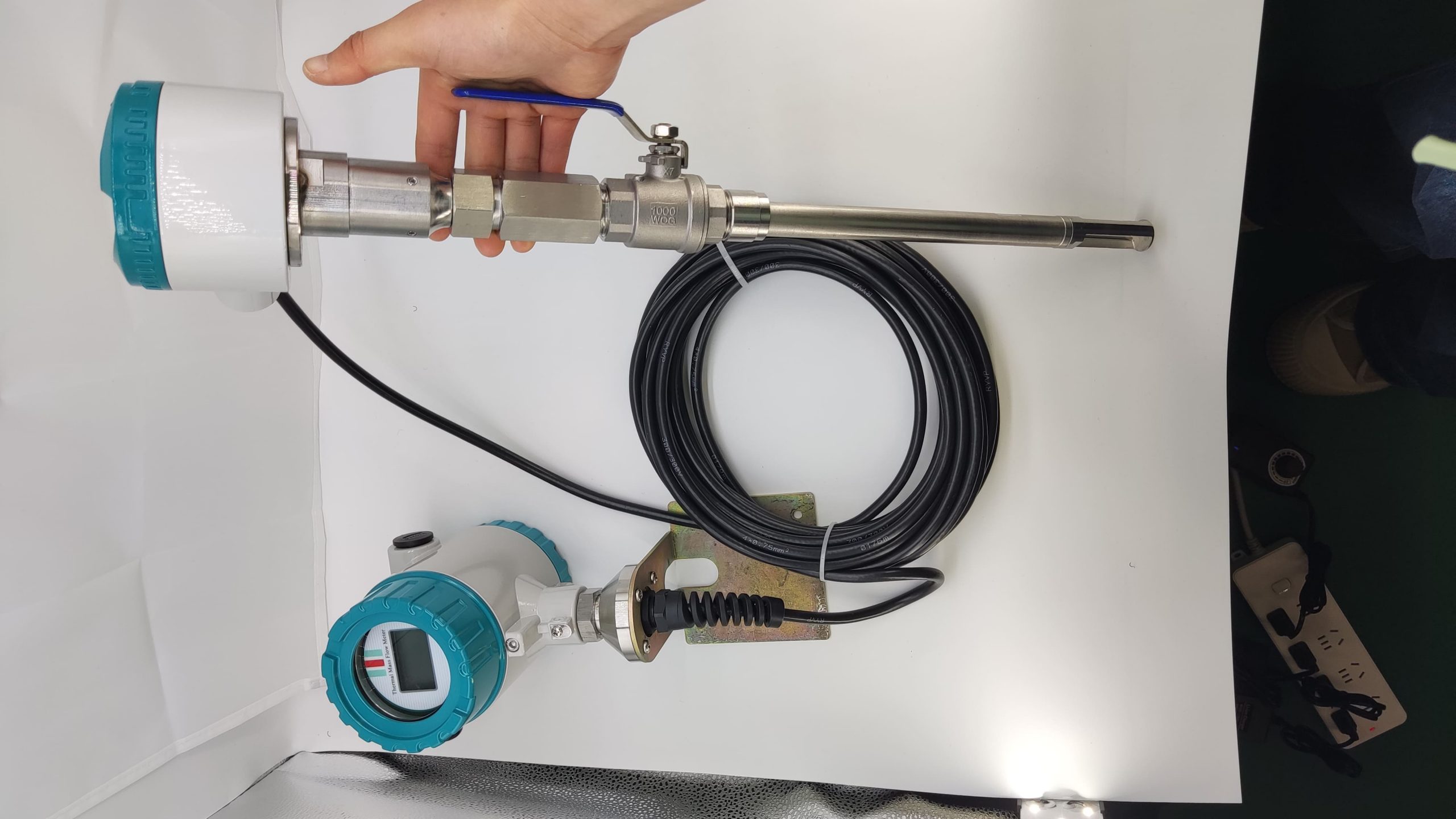
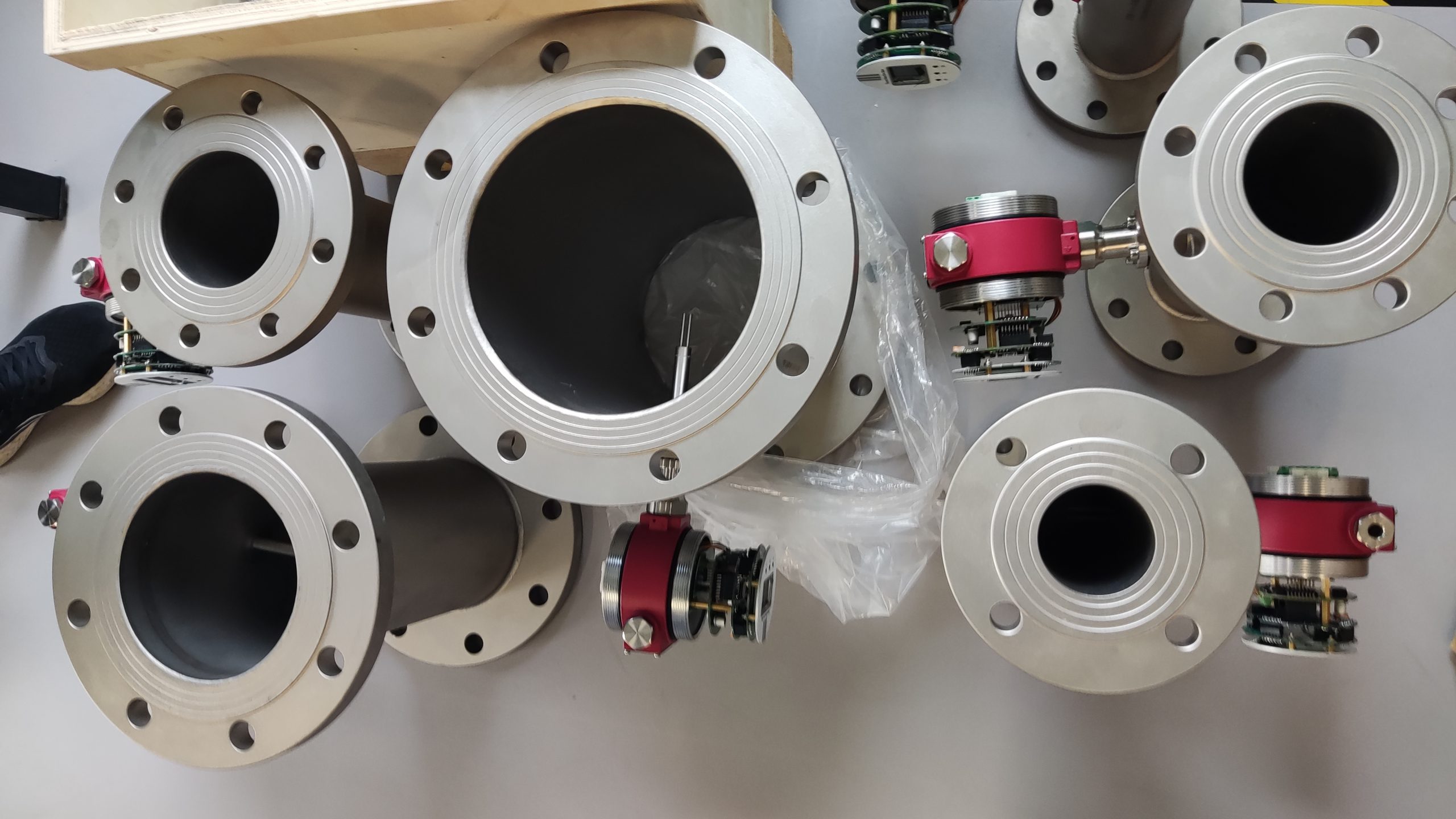
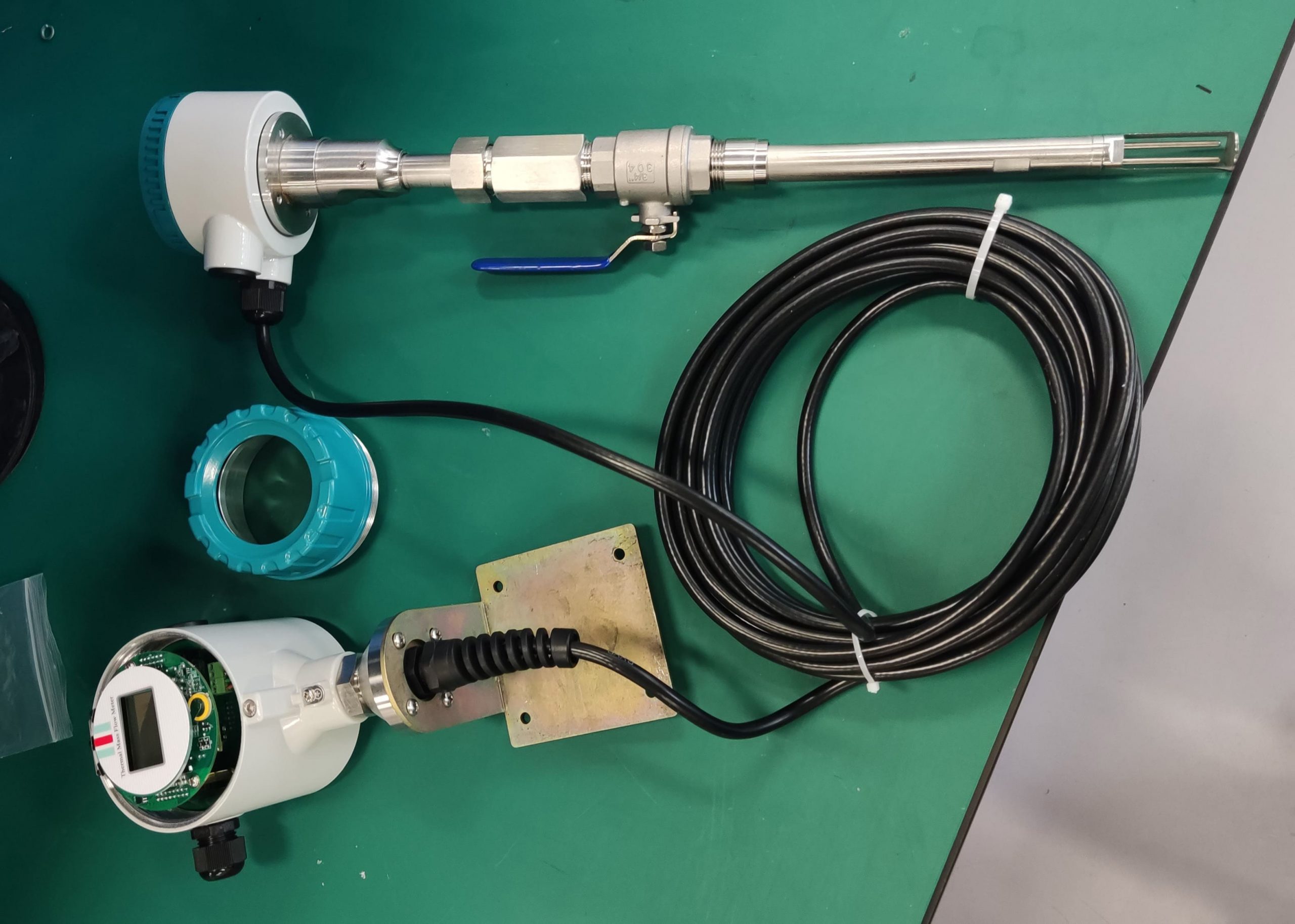
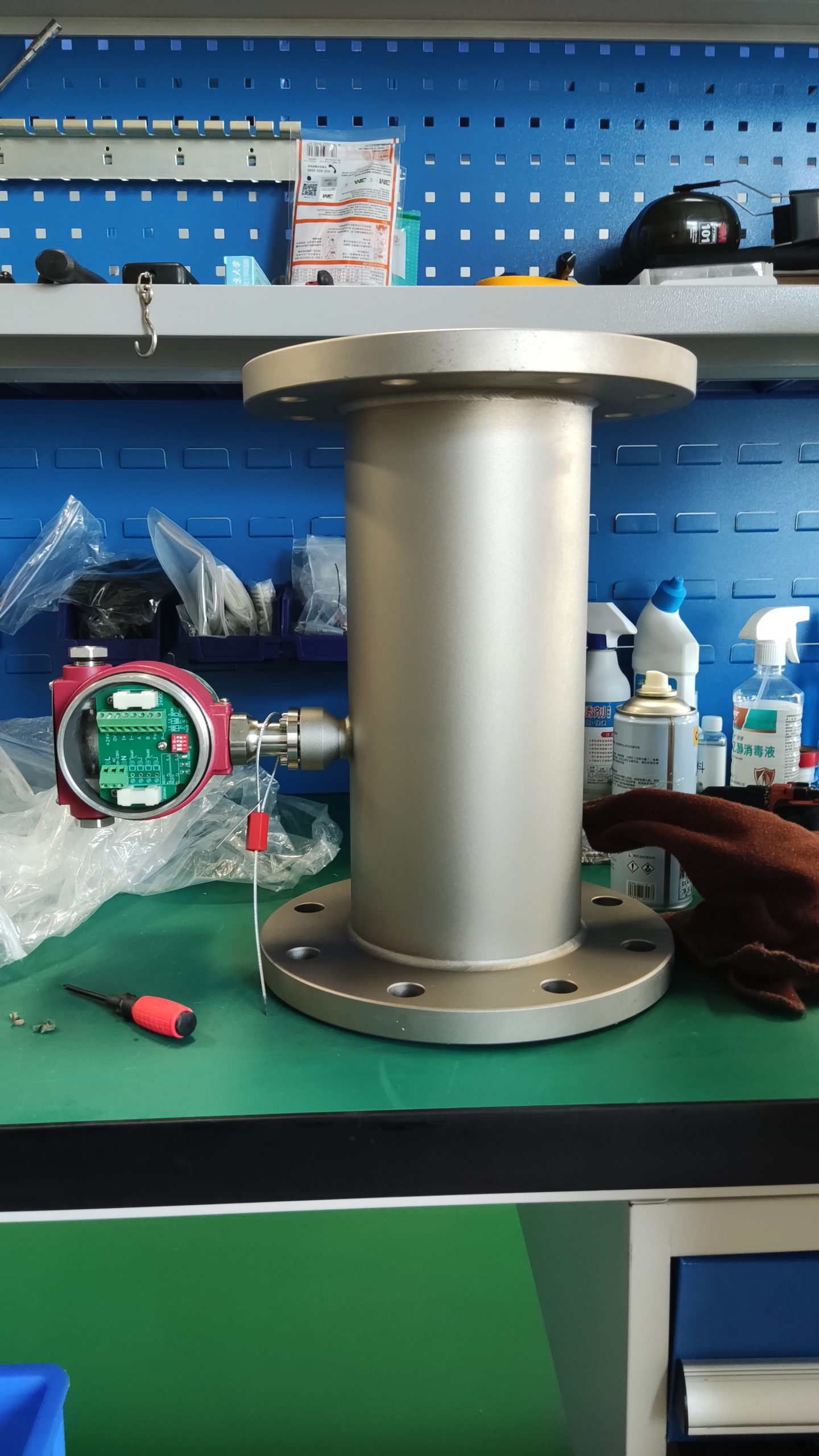
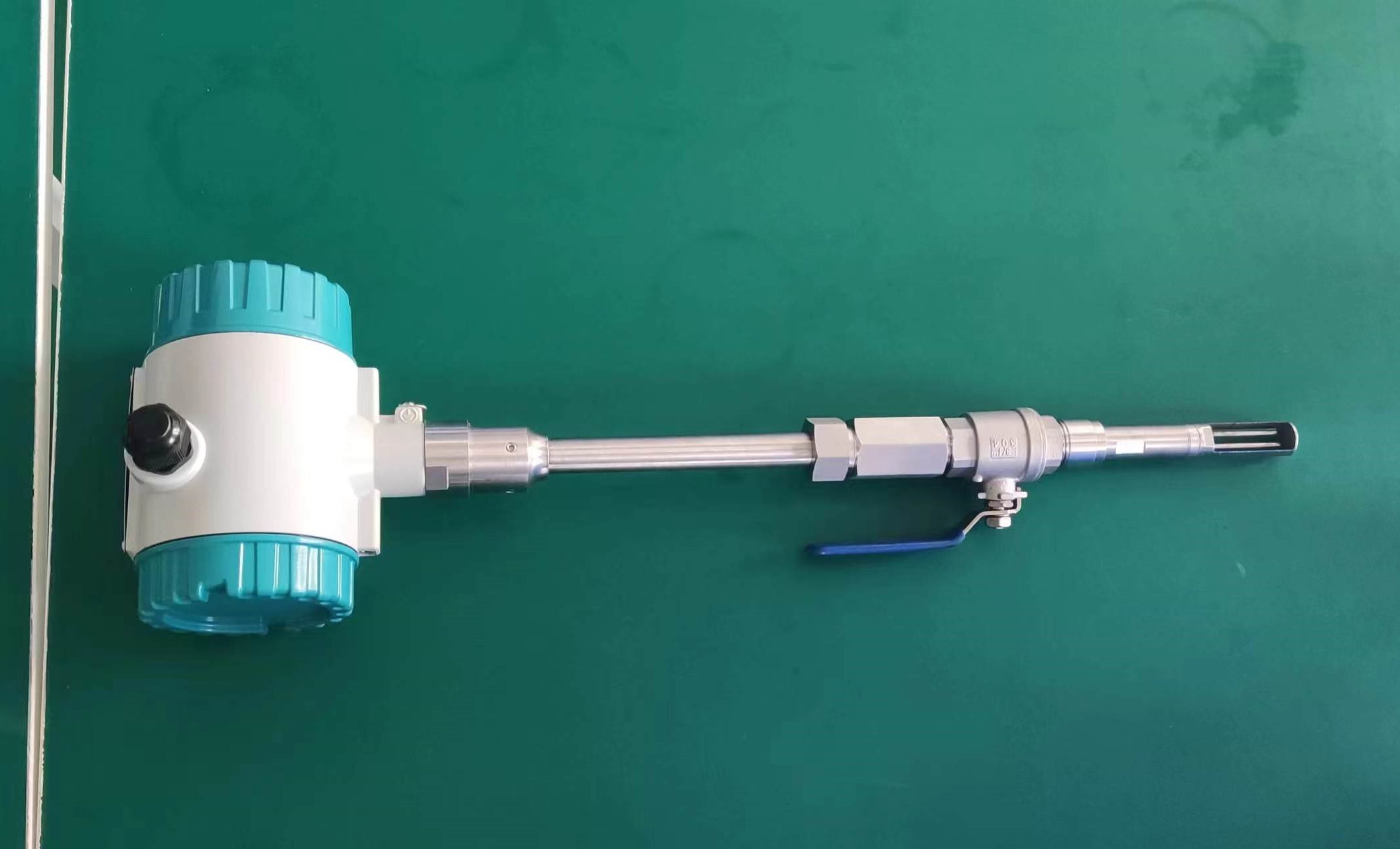
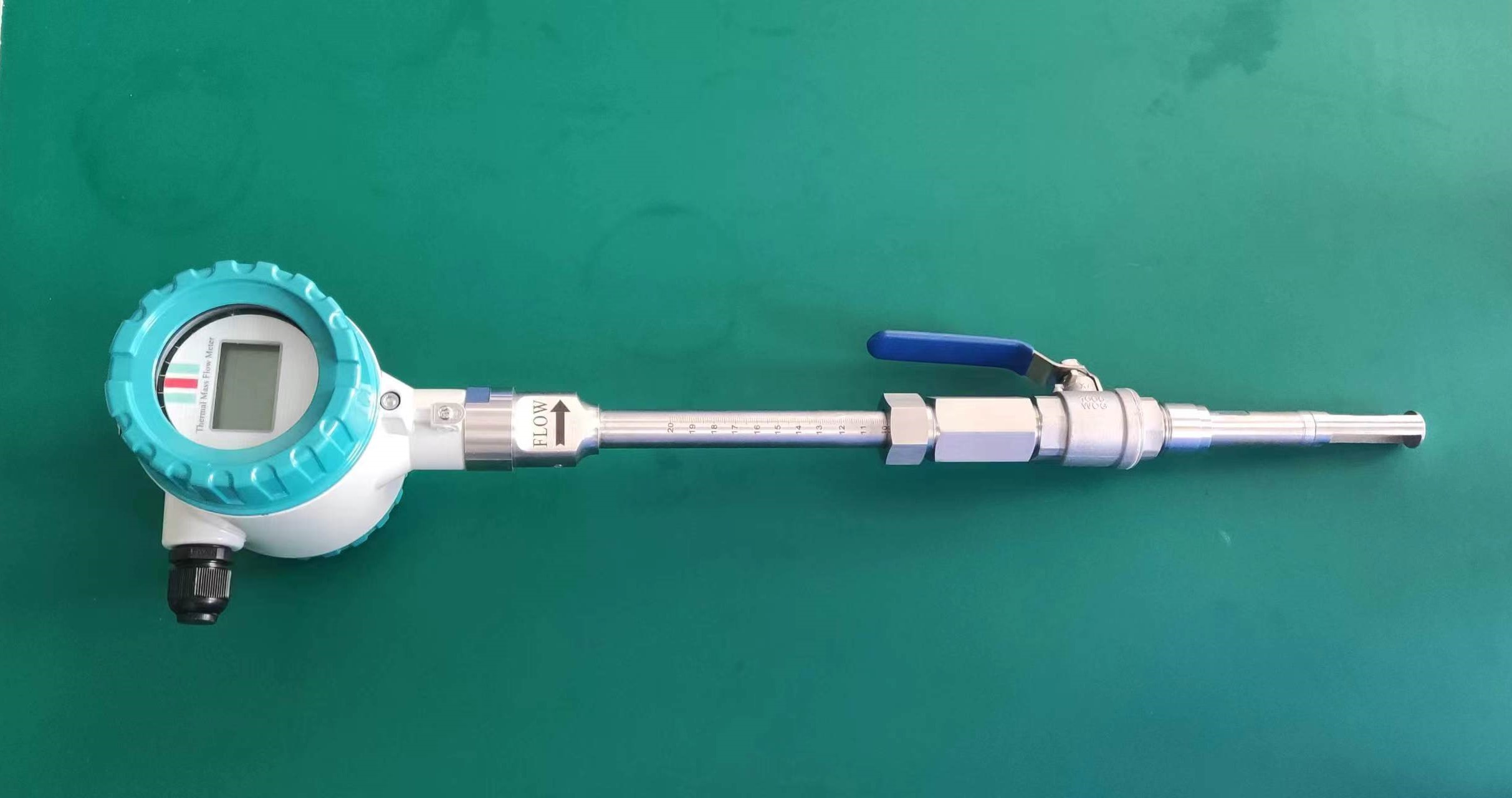
Good Quality Large Diameter Insert Thermal Gas Mass Flowmeter/LPG Flow Meter
In practical applications, thermal mass flowmeters require careful attention to various factors to ensure accurate and reliable measurement of fluid flow rates. Here are some key considerations for the practical application of thermal mass flowmeters:
Fluid Properties: Understand the properties of the fluid being measured, including temperature, pressure, density, viscosity, and composition. Thermal mass flowmeters are typically suitable for measuring clean, dry gases, but certain factors like moisture content and impurities can affect performance. Ensure that the fluid properties are within the specified range for accurate measurement.
Flow Range: Select a thermal mass flowmeter with a measurement range that covers the anticipated flow rates in your application. Ensure that the flowmeter is capable of accurately measuring both low and high flow rates within the specified range.
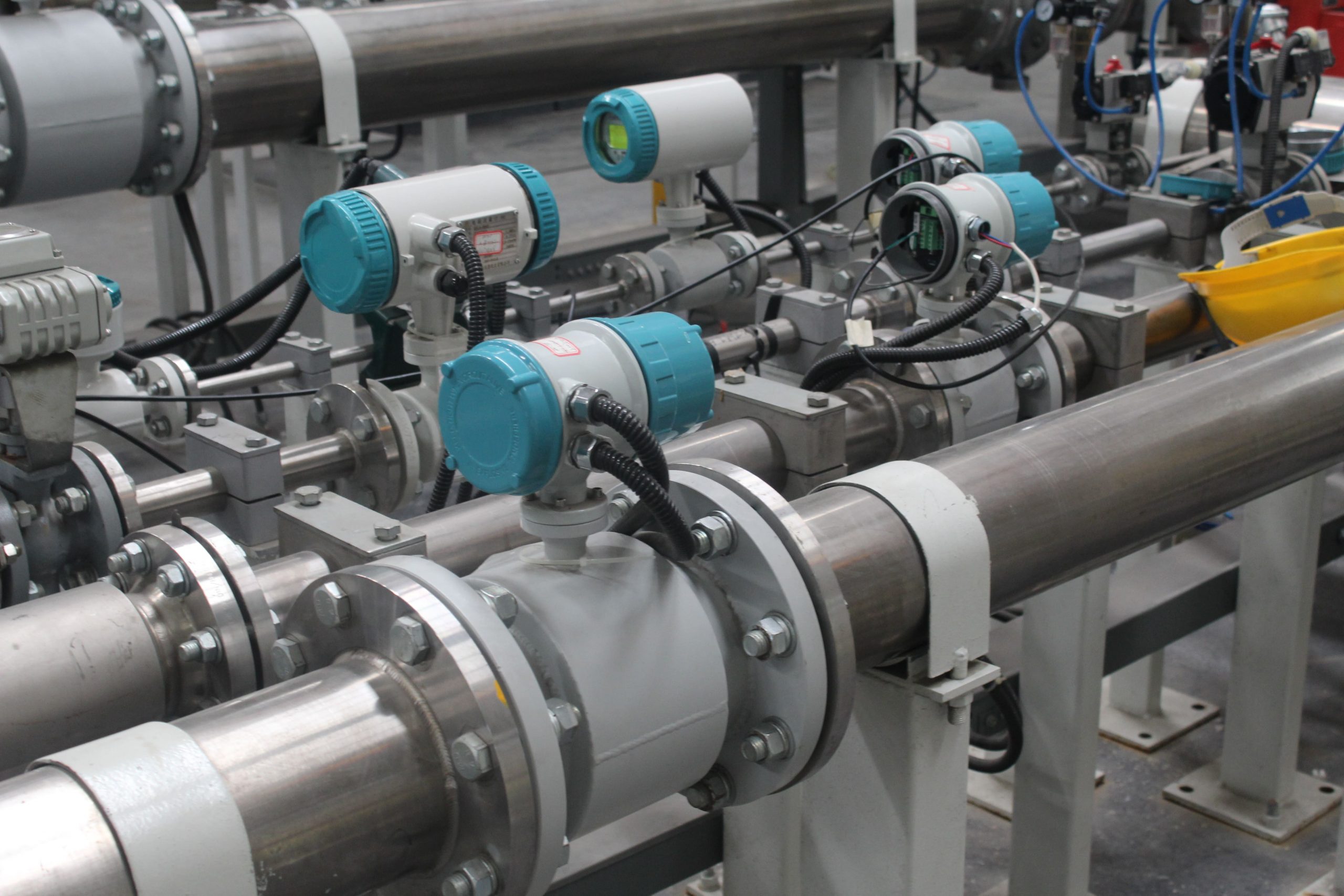
Installation Location: Choose an appropriate location for installing the flowmeter within the pipeline. Consider factors such as straight run requirements, flow profile, and avoidance of flow disturbances. Follow manufacturer recommendations for orientation and positioning of the flowmeter to ensure optimal performance.
Straight Run Requirements: Provide sufficient straight pipe lengths upstream and downstream of the flowmeter to ensure a fully developed flow profile. Follow manufacturer guidelines for the minimum straight run requirements to minimize flow disturbances and turbulence.
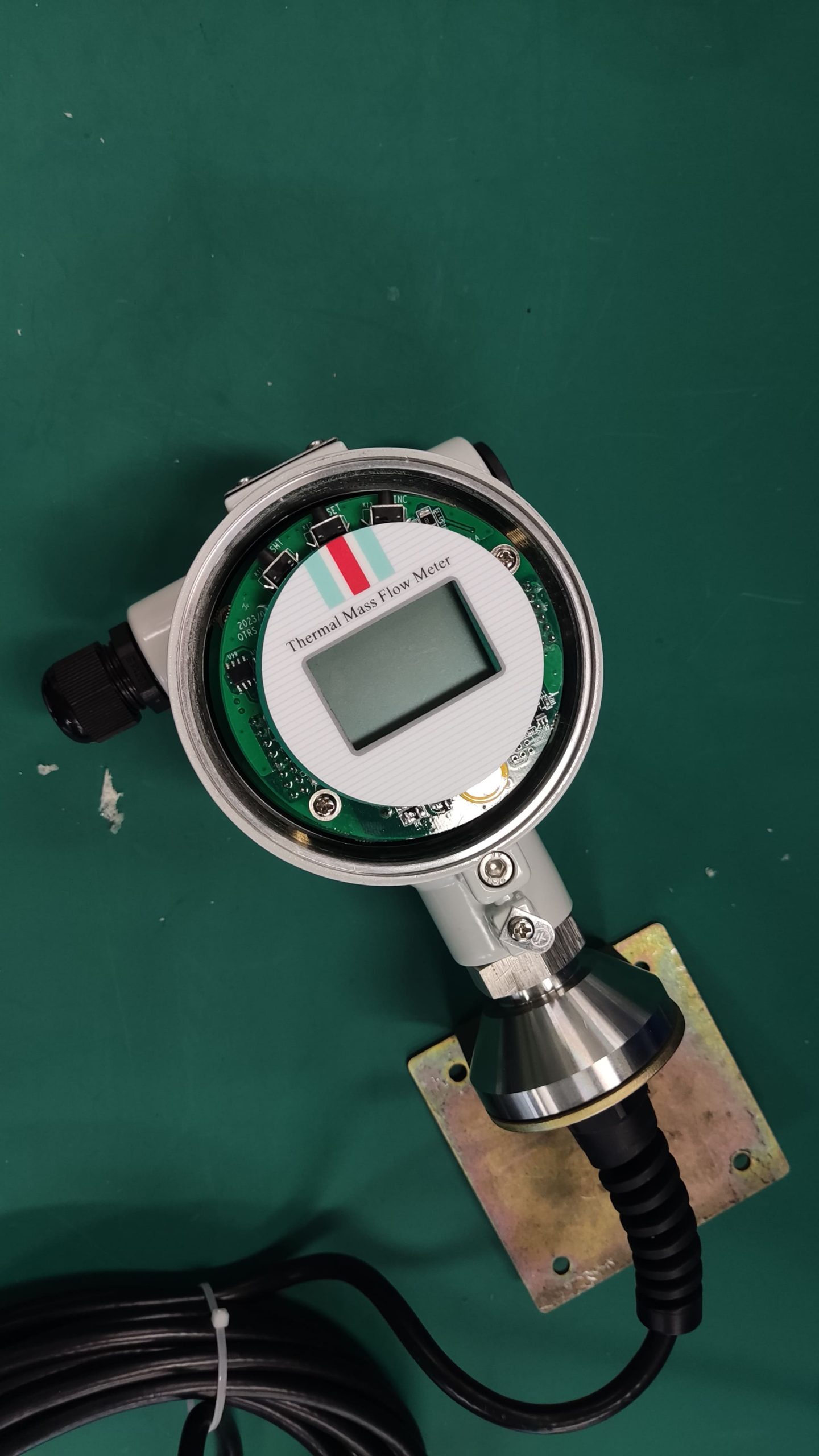
Calibration and Verification: Regularly calibrate the flowmeter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or industry standards. Verify the accuracy of the flowmeter periodically using calibrated reference instruments or methods. Calibration ensures that the flowmeter maintains accurate measurement over time.
Environmental Conditions: Consider the ambient conditions surrounding the flowmeter, such as temperature, humidity, and vibration. Ensure that the flowmeter is installed in a suitable environment and protected from extreme conditions that could affect performance.
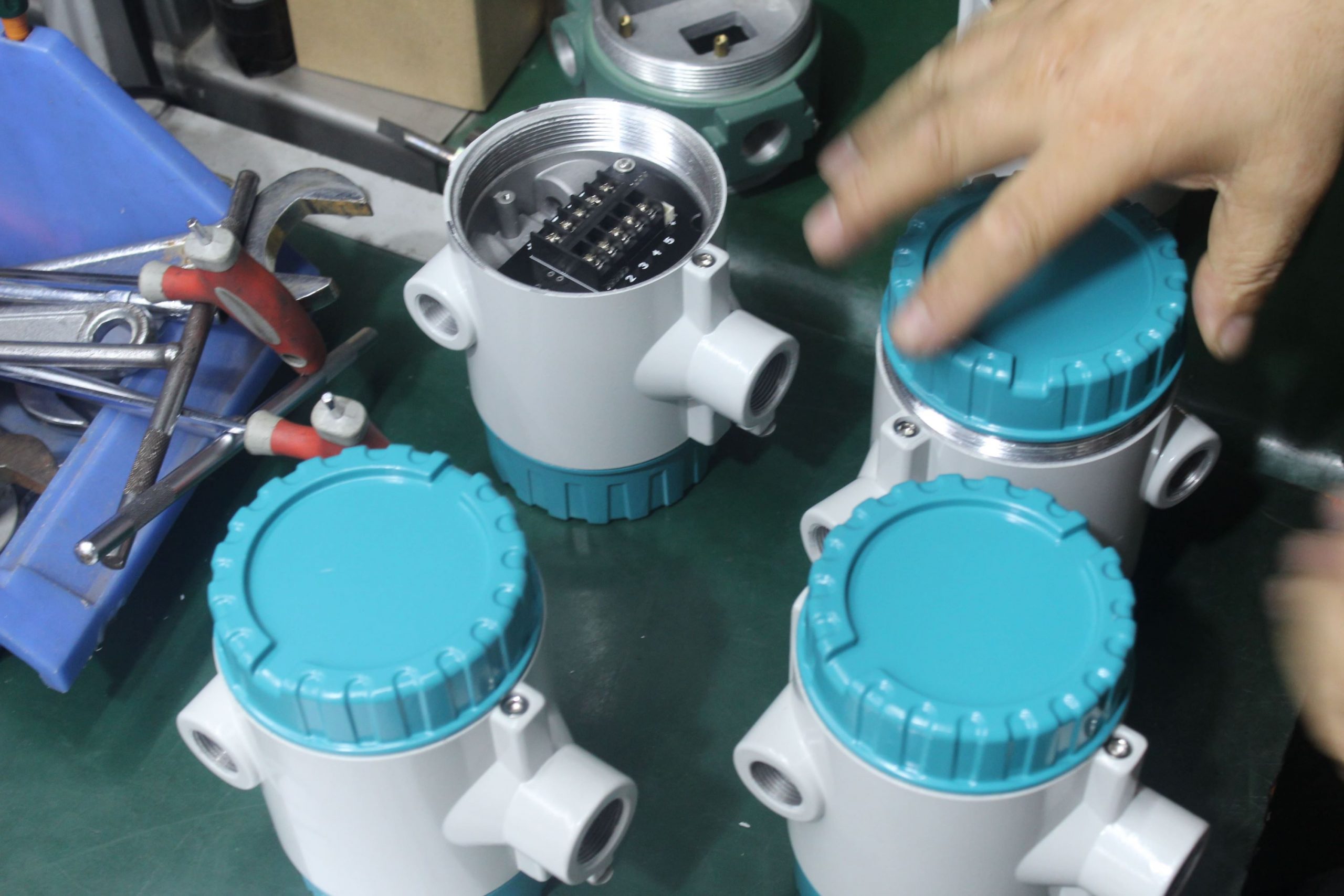
Maintenance and Cleaning: Establish a regular maintenance schedule for the flowmeter, including inspection, cleaning, and servicing. Keep the sensor elements clean and free from any contaminants that could affect measurement accuracy. Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance procedures.
Data Logging and Monitoring: Implement data logging and monitoring systems to track the performance of the flowmeter in real-time. Monitor key parameters such as flow rates, temperatures, and pressure readings to detect any anomalies or issues.
Safety Considerations: Adhere to safety protocols during installation, operation, and maintenance of the flowmeter to prevent accidents or damage to equipment. Follow industry standards and guidelines for handling gases and operating equipment in hazardous environments.
Training and Familiarization: Ensure that personnel responsible for operating and maintaining the flowmeter are properly trained and familiar with its operation. Provide training on calibration procedures, troubleshooting techniques, and safety protocols to ensure effective use of the flowmeter.
By paying attention to these practical considerations, you can optimize the performance of thermal mass flowmeters in your application and ensure accurate measurement of fluid flow rates over time. Regular maintenance, calibration, and adherence to best practices are essential for maximizing the reliability and longevity of the flowmeter.