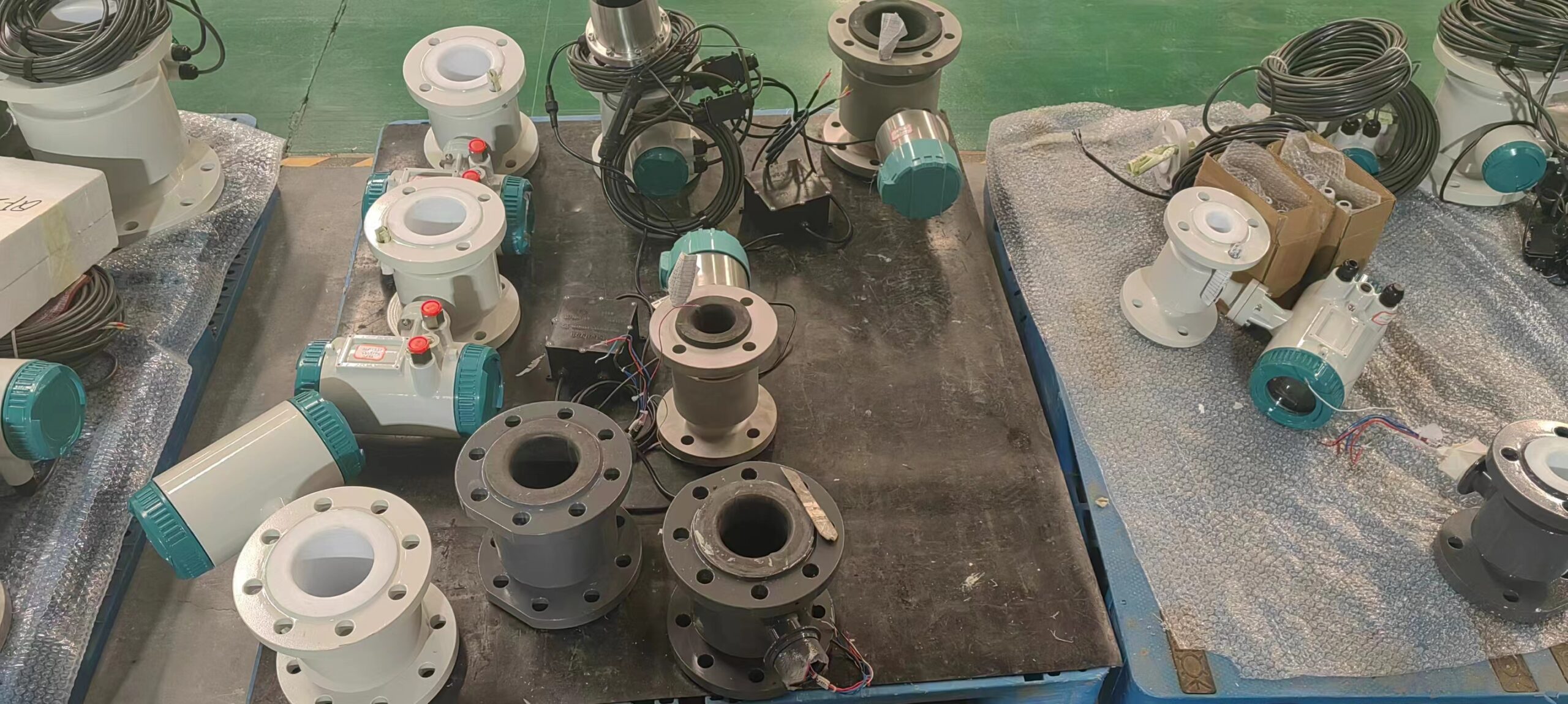
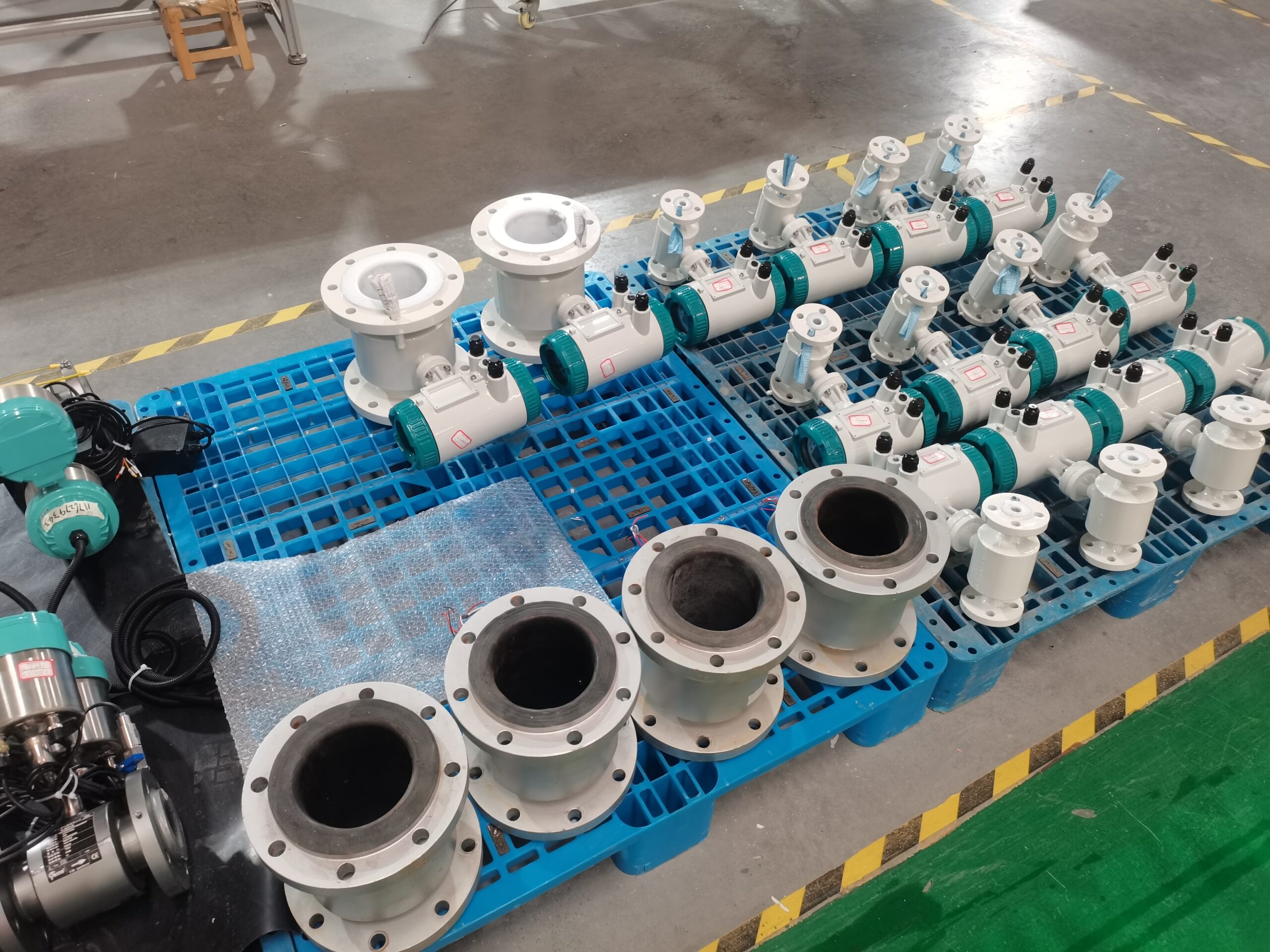
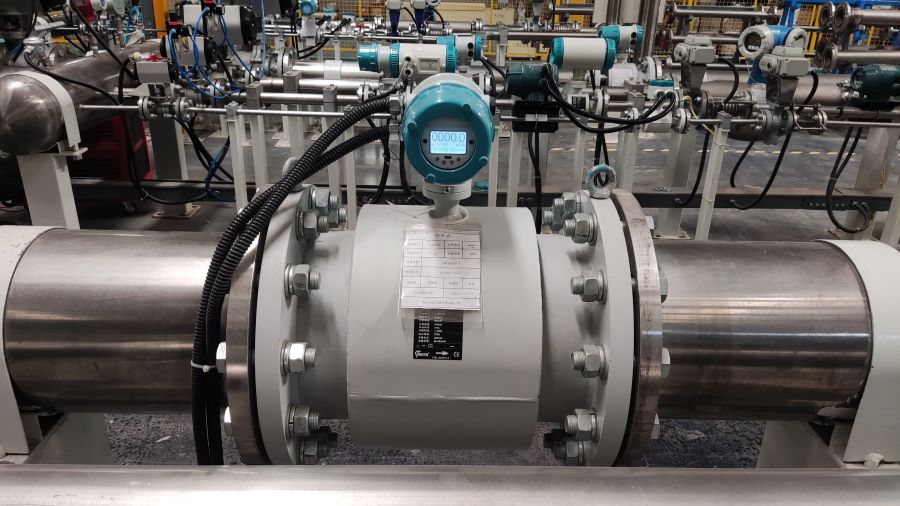
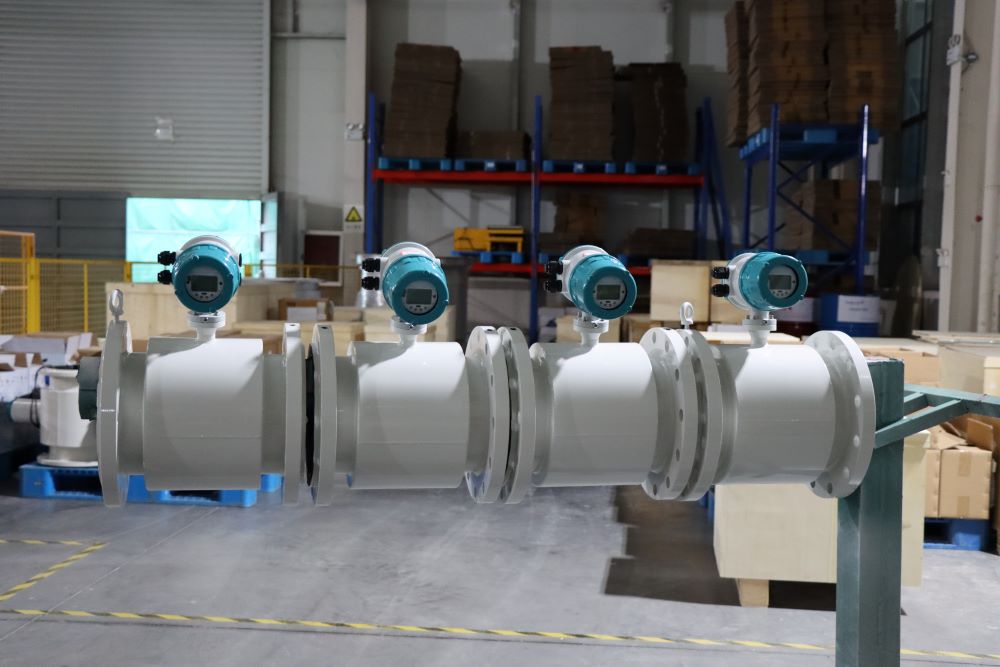
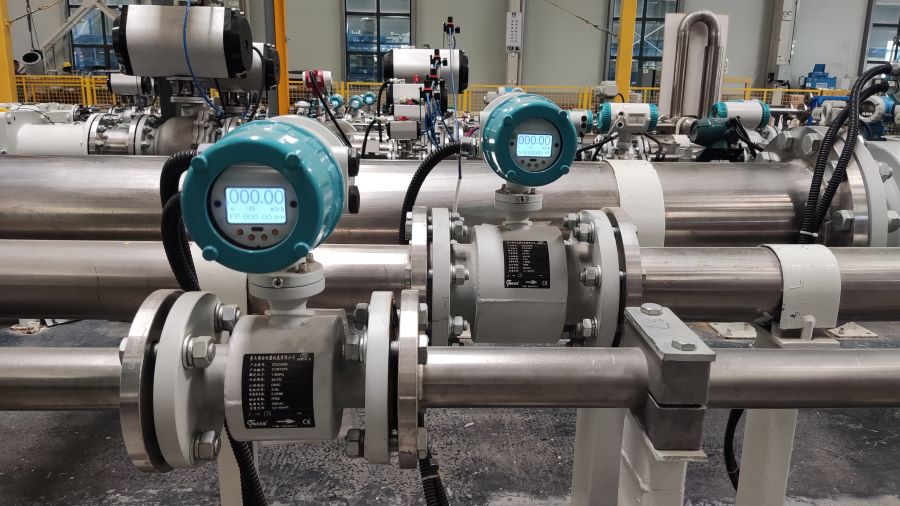
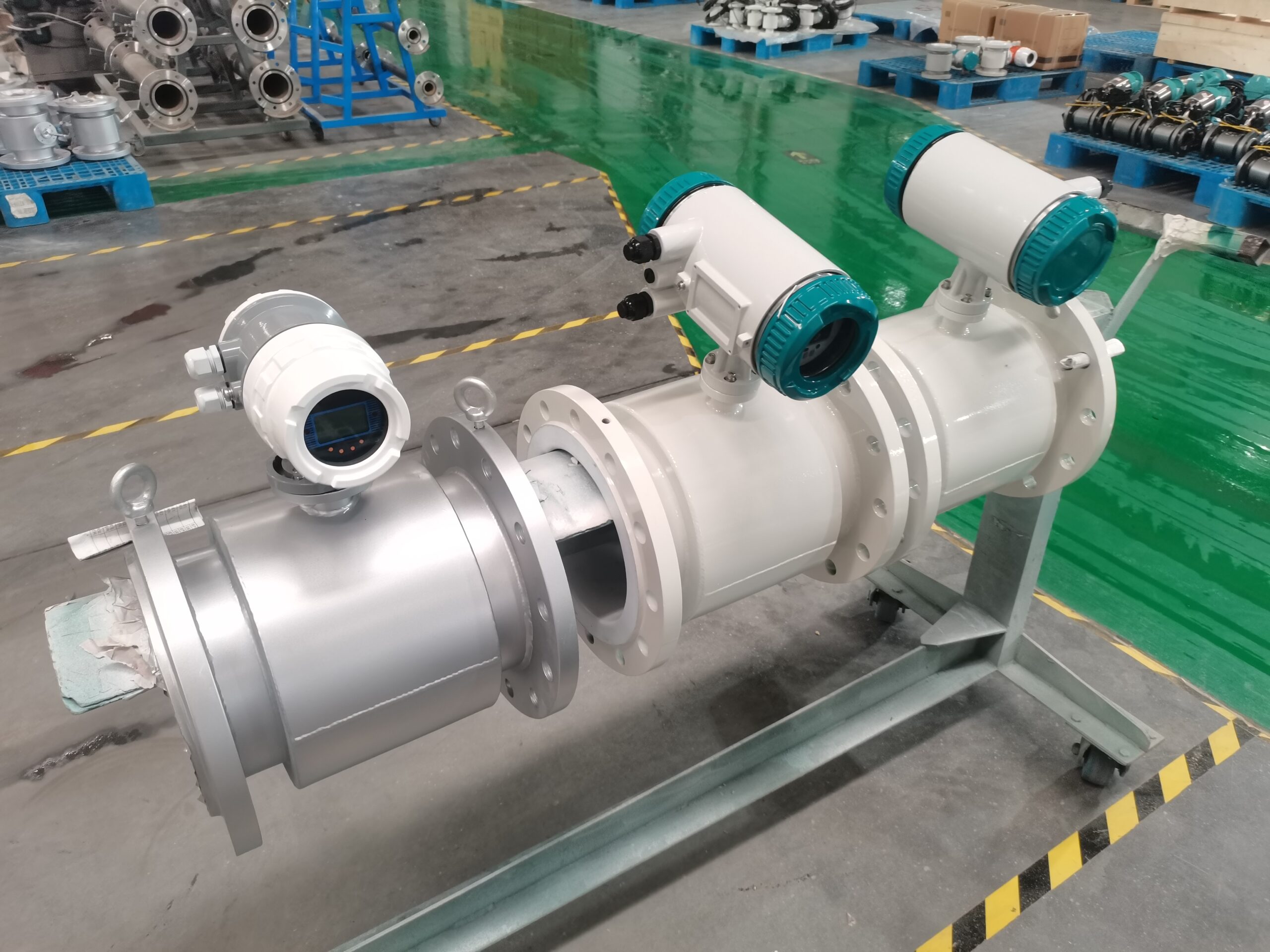
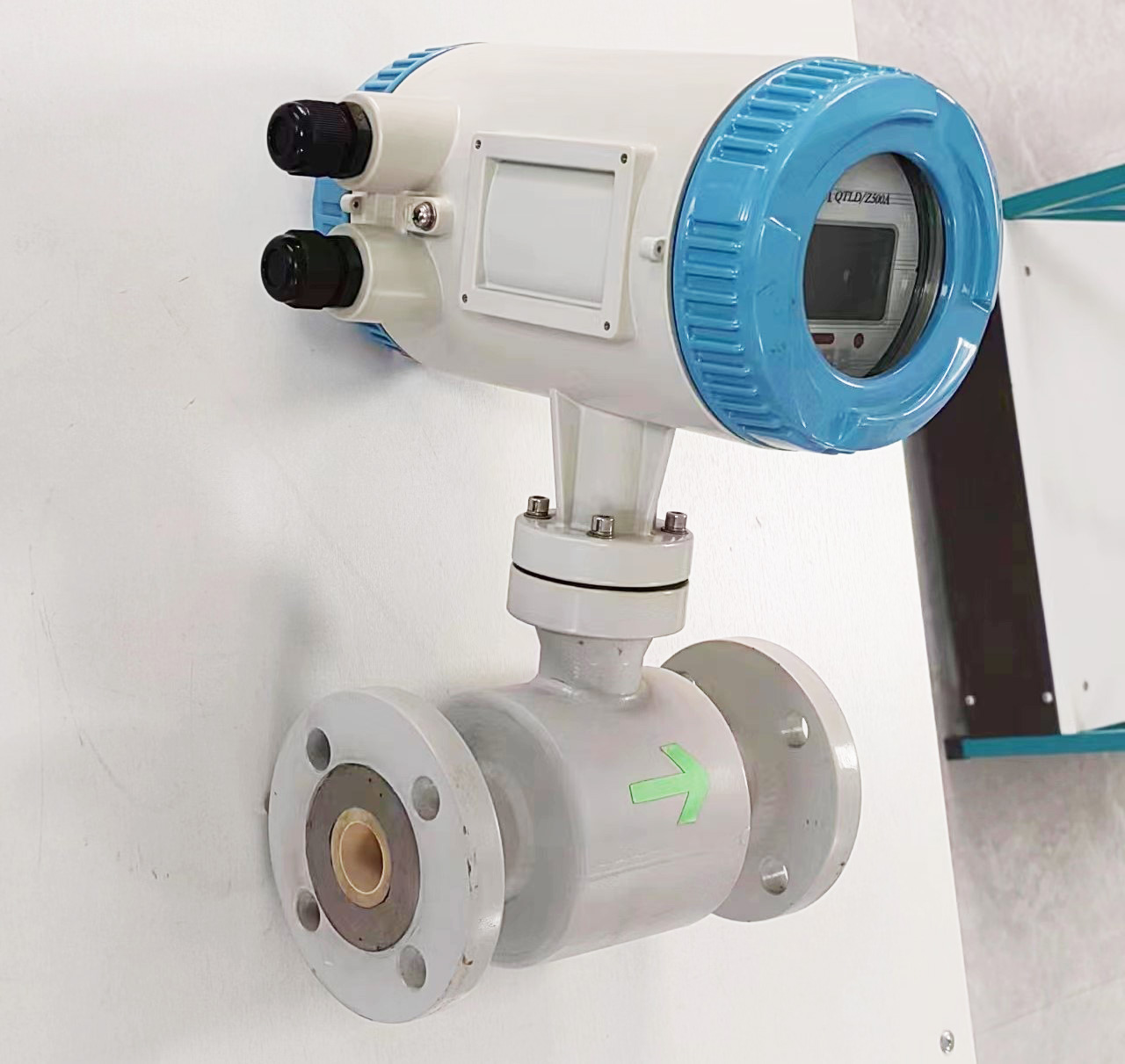
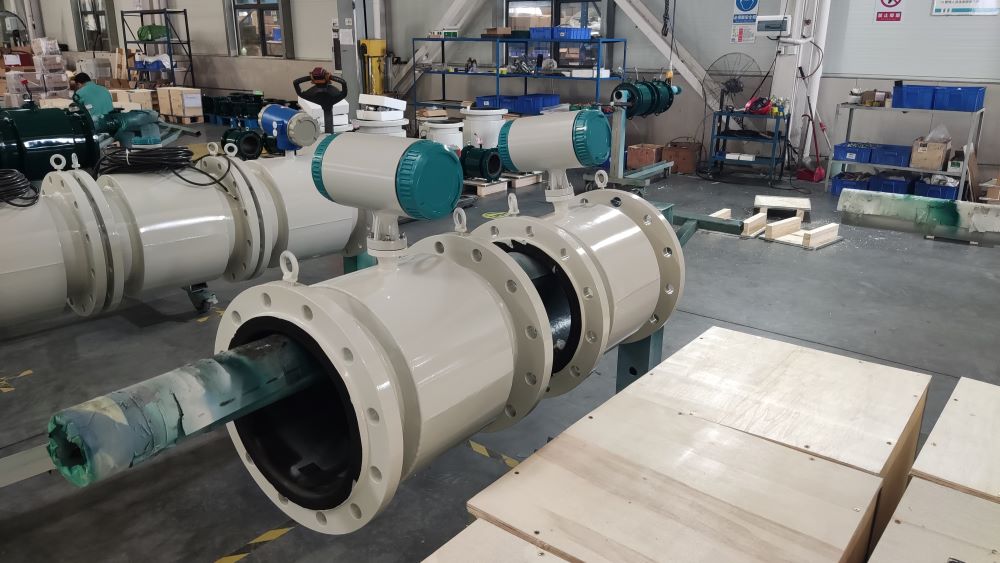
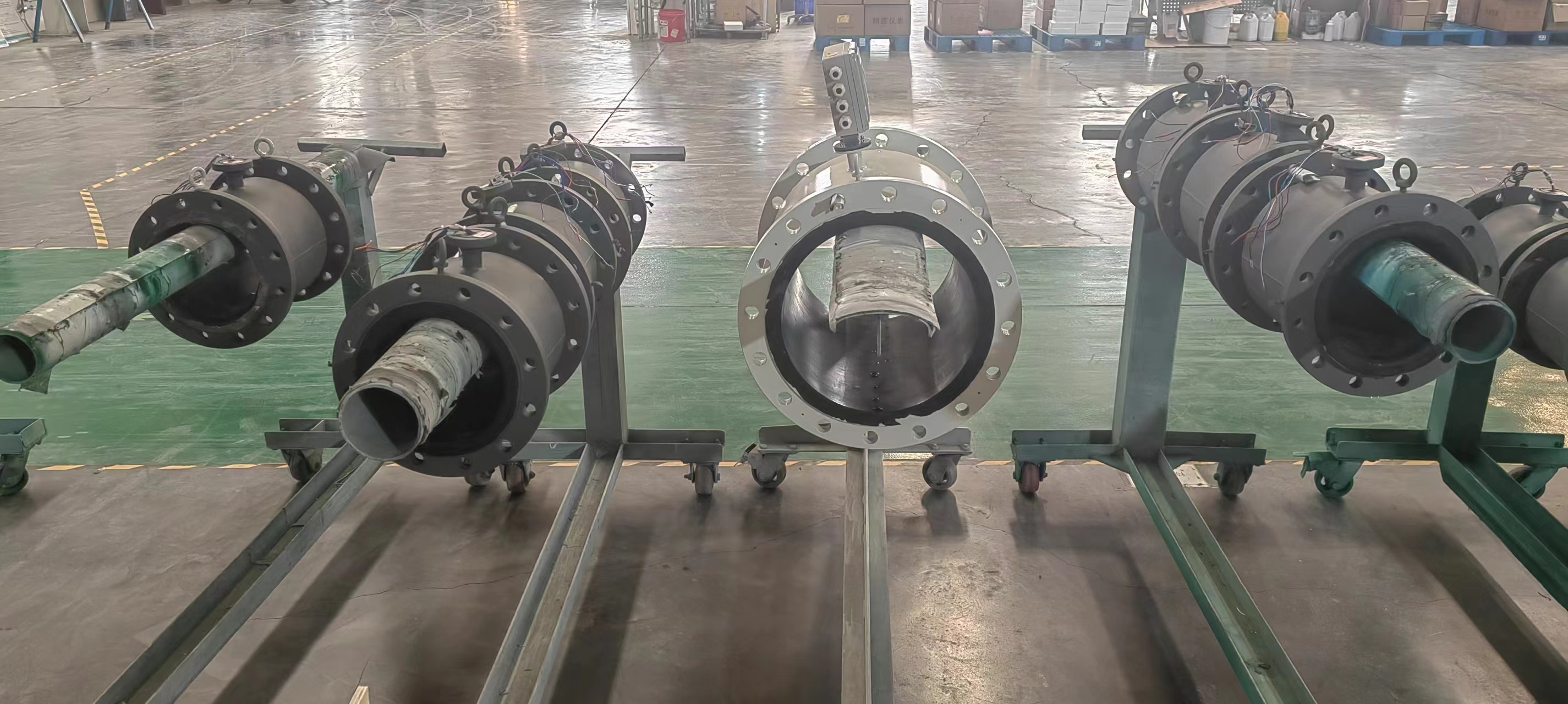
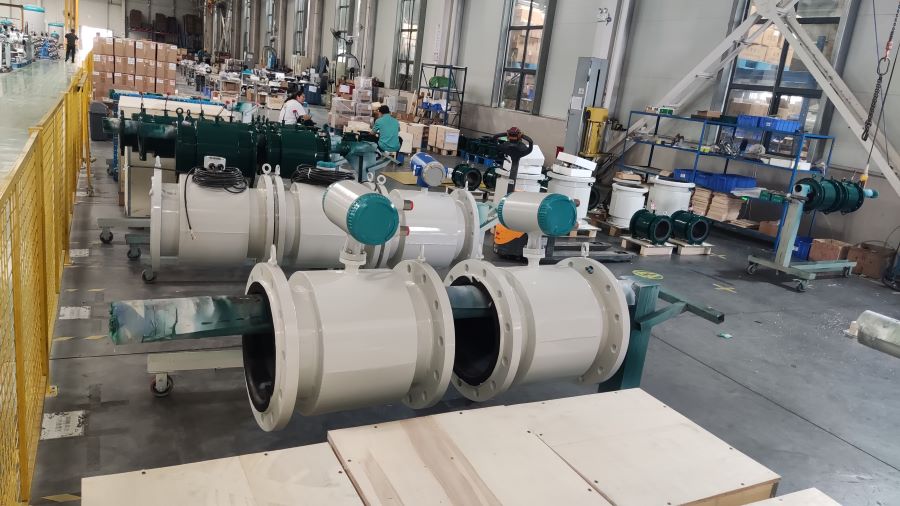
Digital Display Water Flow Meter Pipeline Water Pump Liquid Electromagnetic Magnetic Flowmeter
Electromagnetic flowmeters, also known as magmeters or magnetic flowmeters, typically generate electrical output signals proportional to the flow rate of a conductive fluid passing through a pipe. The most common output signals from electromagnetic flowmeters include:
Analog Output (4-20 mA or 0-10 V):
Analog output signals are widely used in process control systems. The most common analog signals are 4-20 mA (milliamps) or 0-10 V (volts). The output signal is proportional to the flow rate, with 4 mA or 0 V representing the minimum flow rate, and 20 mA or 10 V representing the maximum flow rate. The choice between 4-20 mA and 0-10 V depends on the requirements of the control system.
Frequency/Pulse Output:
Electromagnetic flowmeters can also provide a frequency or pulse output signal, where the frequency or number of pulses per unit of flow is proportional to the flow rate. This type of output is often used for applications where the receiving device can process digital signals. Pulse signals are easier to transmit over long distances without signal degradation.
Digital Communication Protocols:
Many modern electromagnetic flowmeters feature digital communication protocols, allowing them to communicate directly with control systems, data loggers, or other devices. Common digital protocols include:
HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer): Combines analog and digital communication on the same signal, allowing for additional information to be transmitted over the 4-20 mA analog loop.
FOUNDATION Fieldbus: A digital communication protocol used in process automation.
Modbus: A widely used serial communication protocol for industrial applications.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM):
Some electromagnetic flowmeters provide a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal. In PWM, the width of the pulse is varied proportionally to the flow rate. PWM signals can be suitable for certain control applications.
Status/Alarm Outputs:
Electromagnetic flowmeters may have additional outputs to indicate device status or trigger alarms. These outputs can be used to signal conditions such as low flow, sensor fault, or other diagnostic information.
The choice of output signal depends on the requirements of the specific application and the compatibility with the receiving device or control system. Before selecting an electromagnetic flowmeter, it’s crucial to understand the communication options and choose the one that best suits the needs of the overall system. Additionally, adherence to industry standards and communication protocols ensures seamless integration with other components in the industrial process.



-.jpg)























-.jpg)