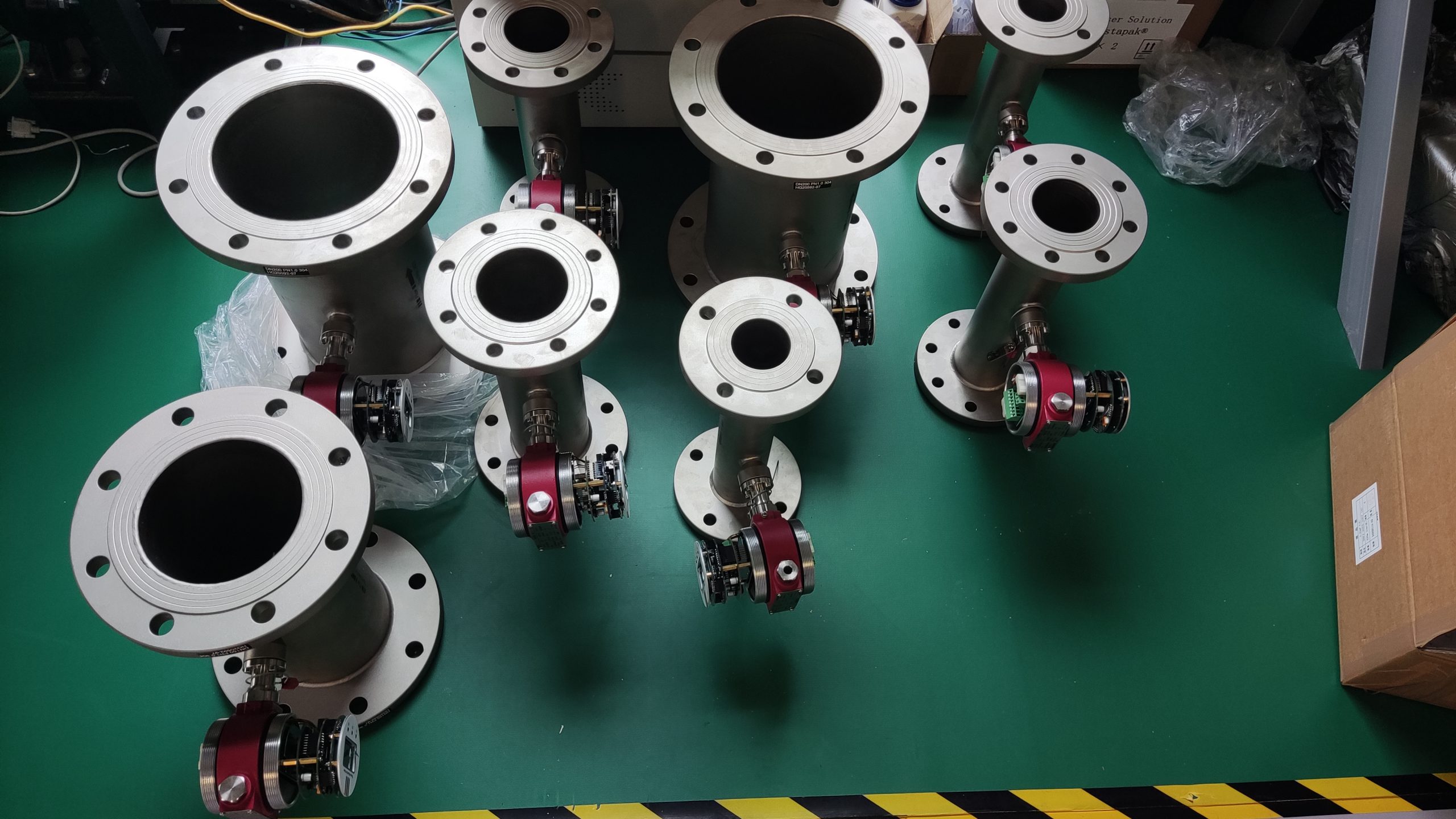
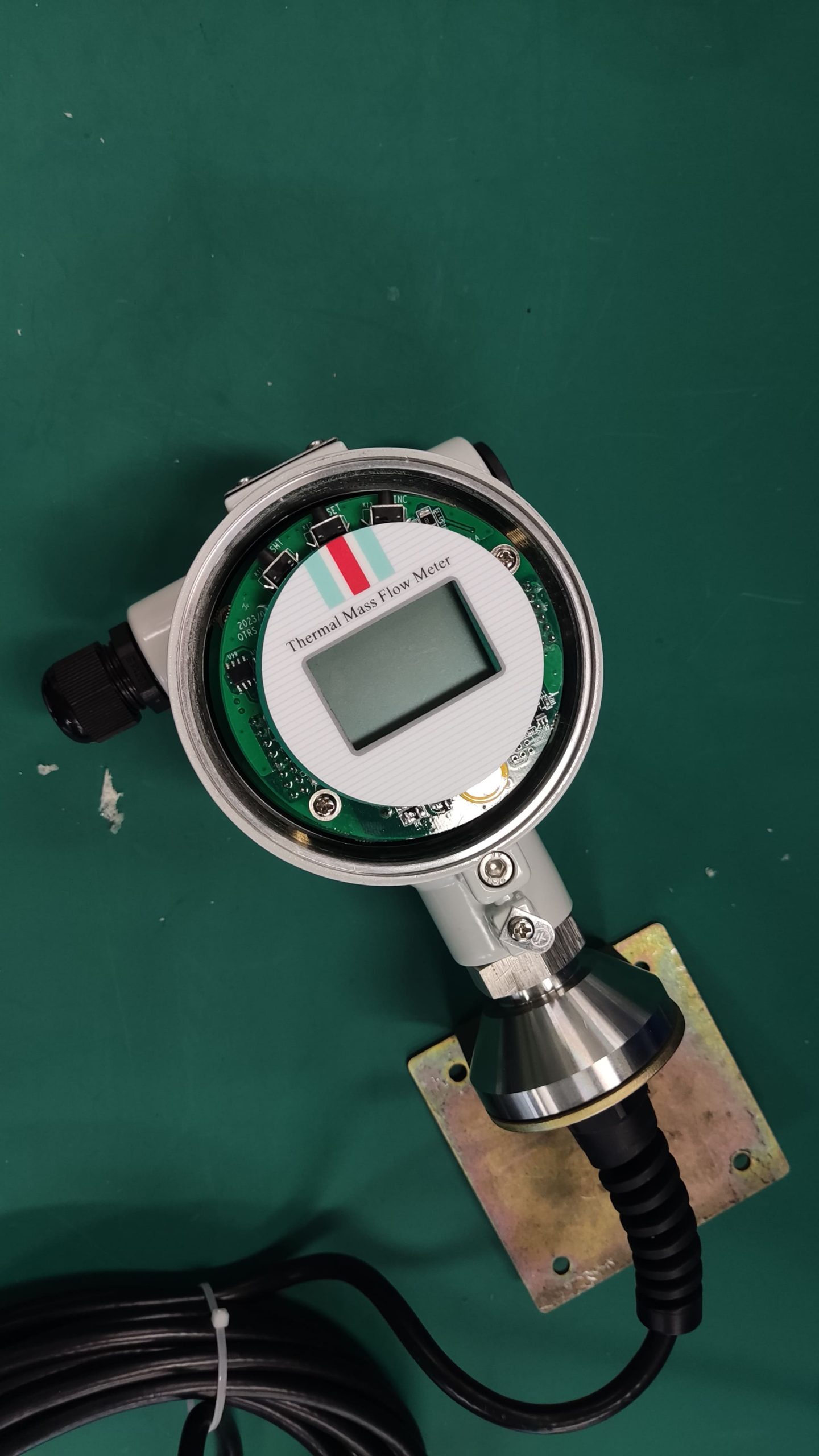
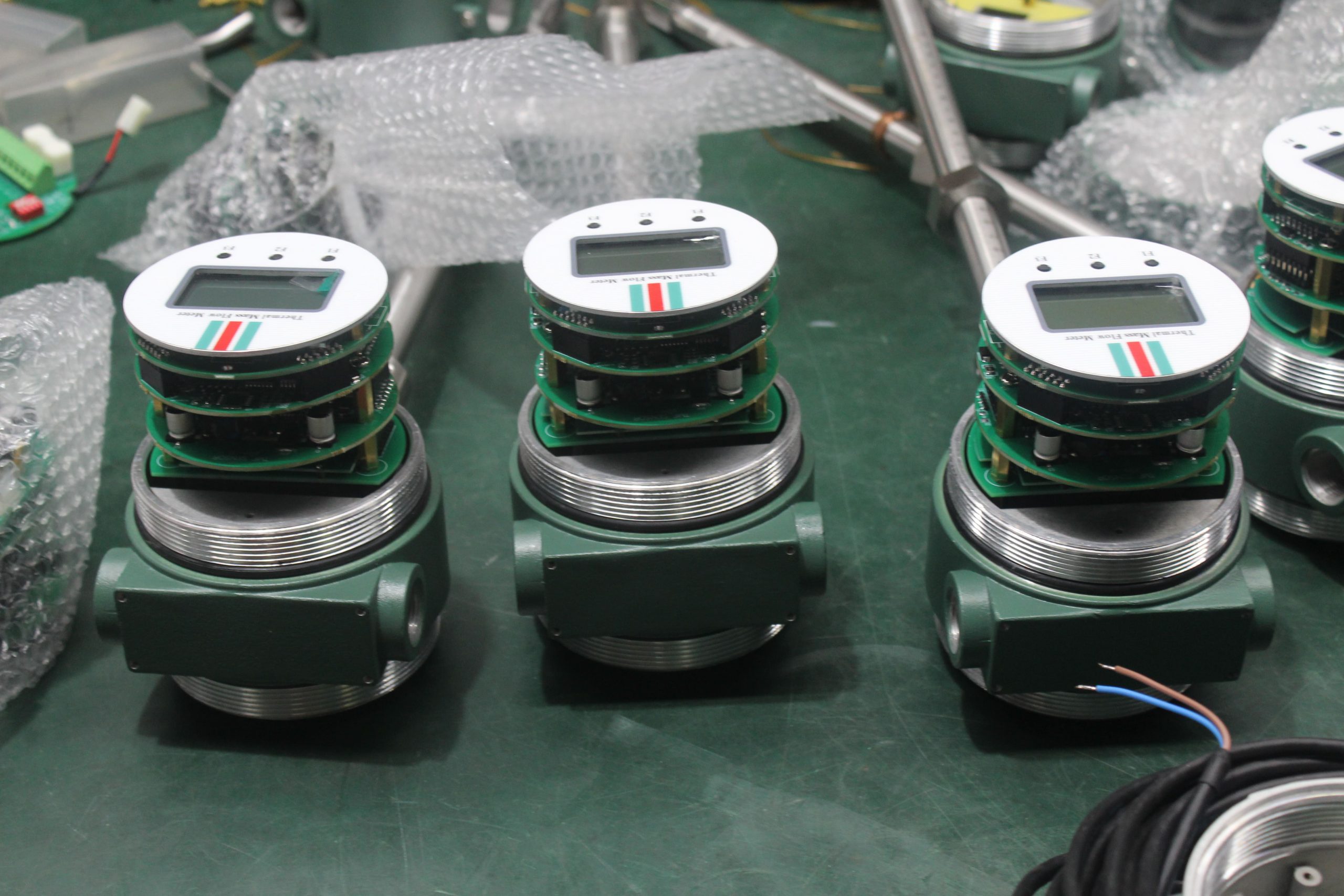
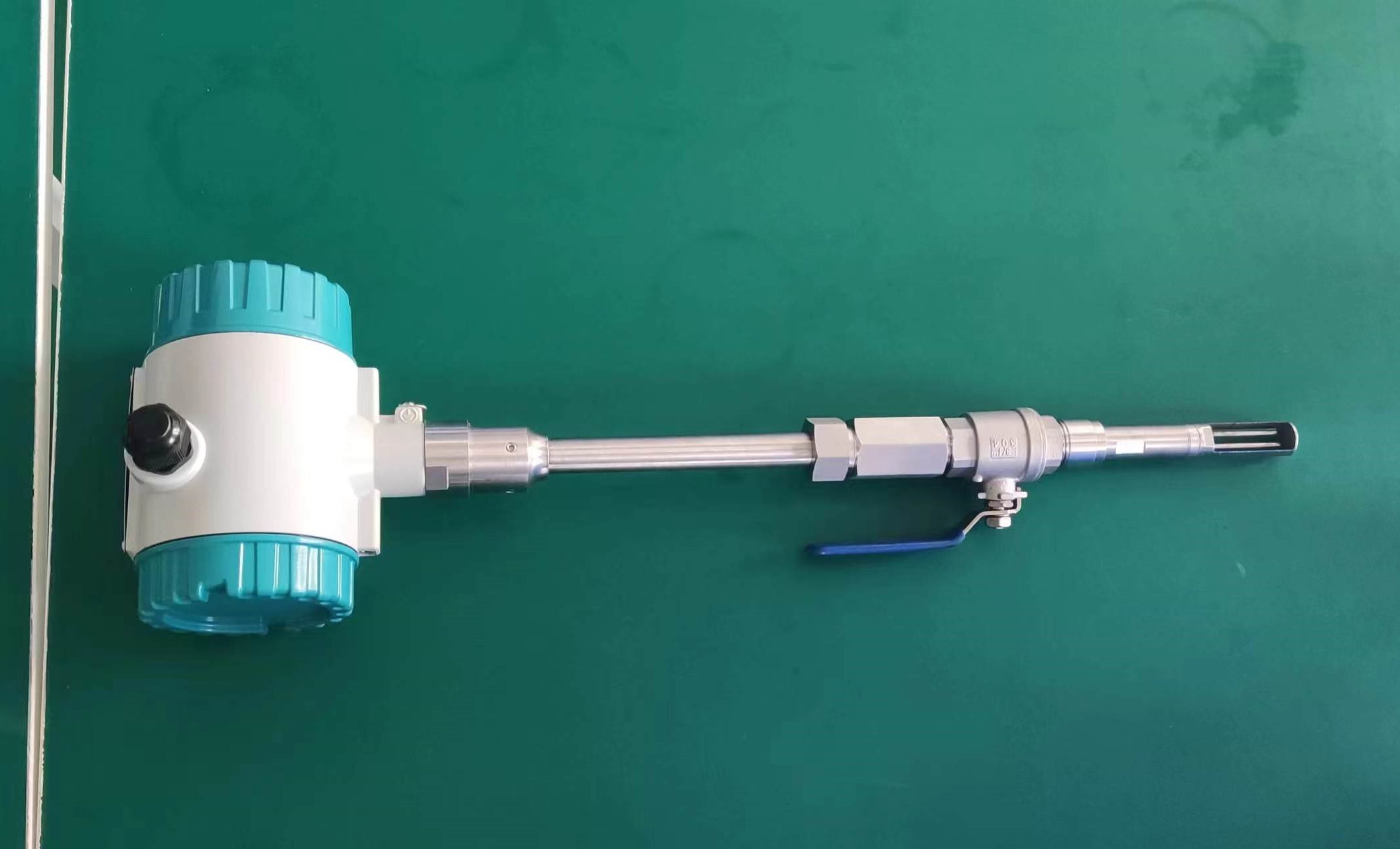
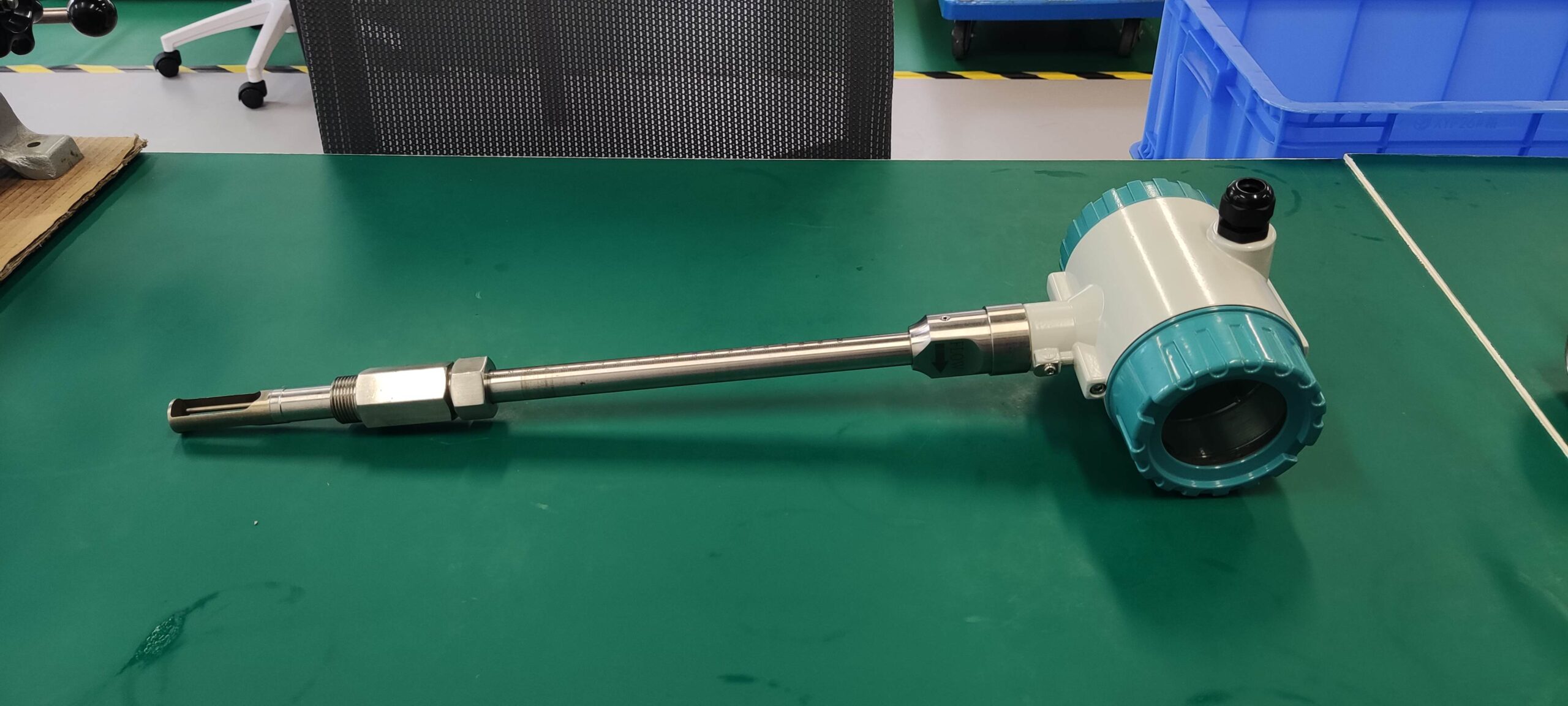
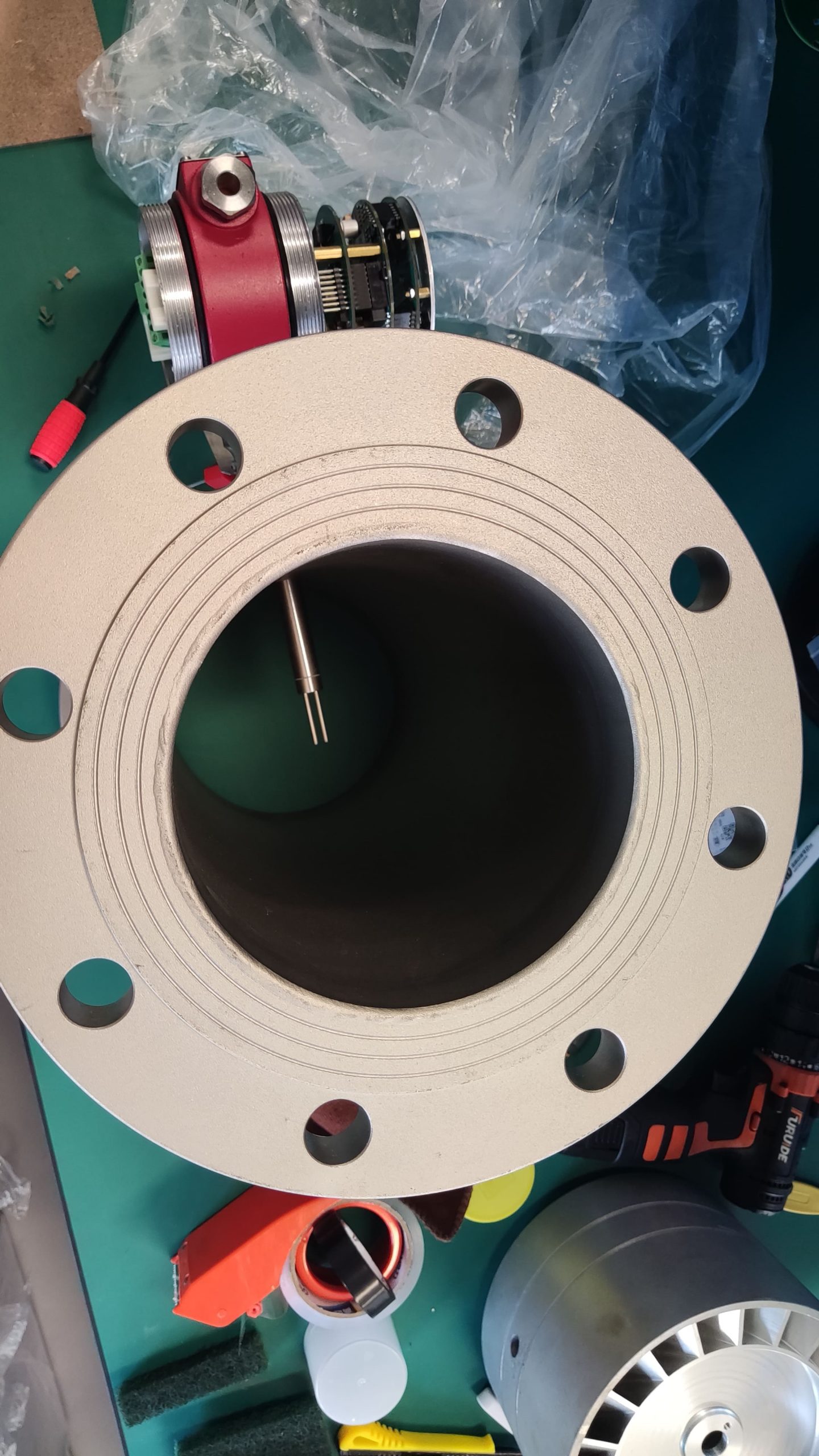
A detailed description of the thermal gas mass flowmeter
1. Principle of thermal gas mass flowmeter
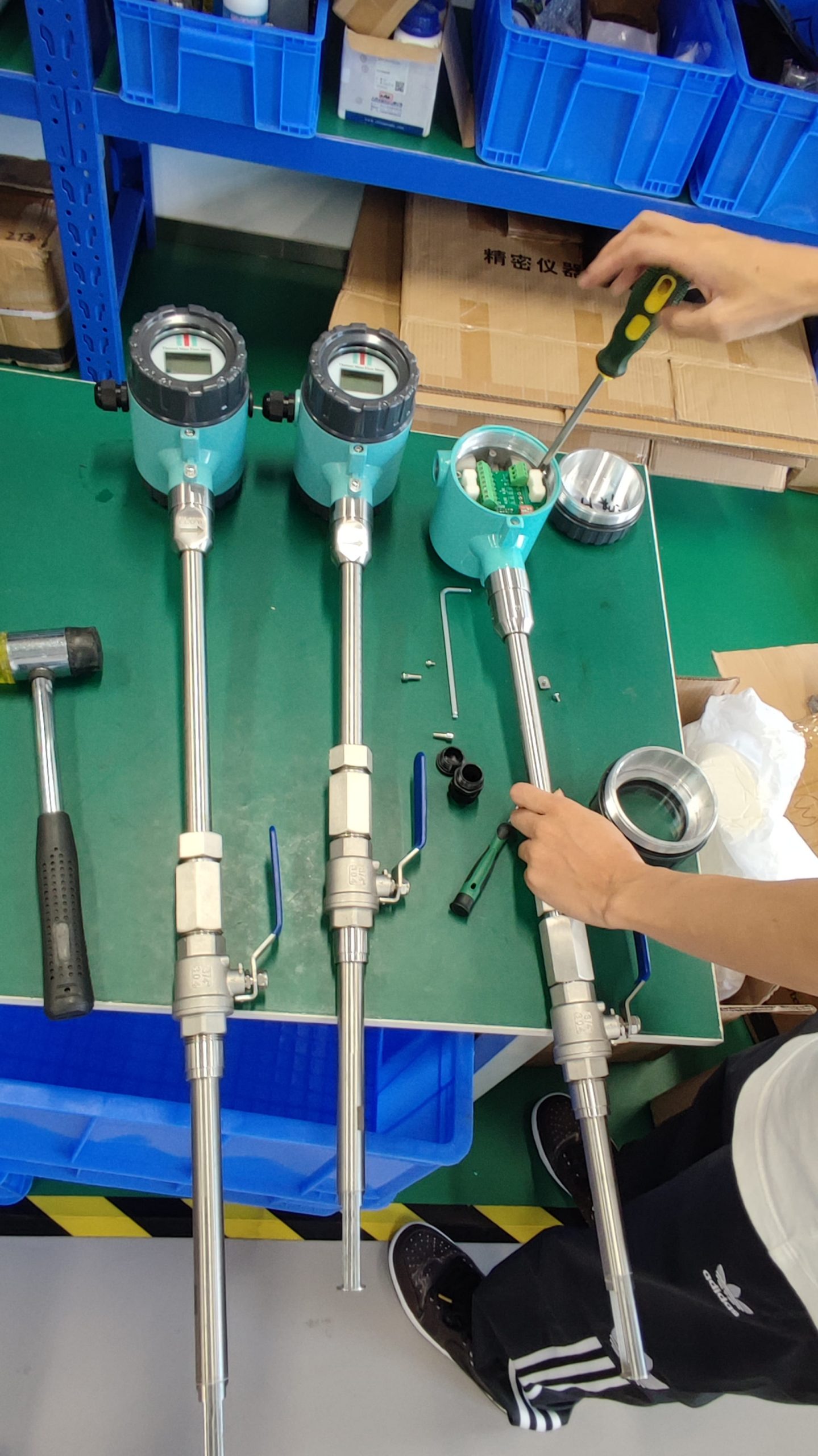
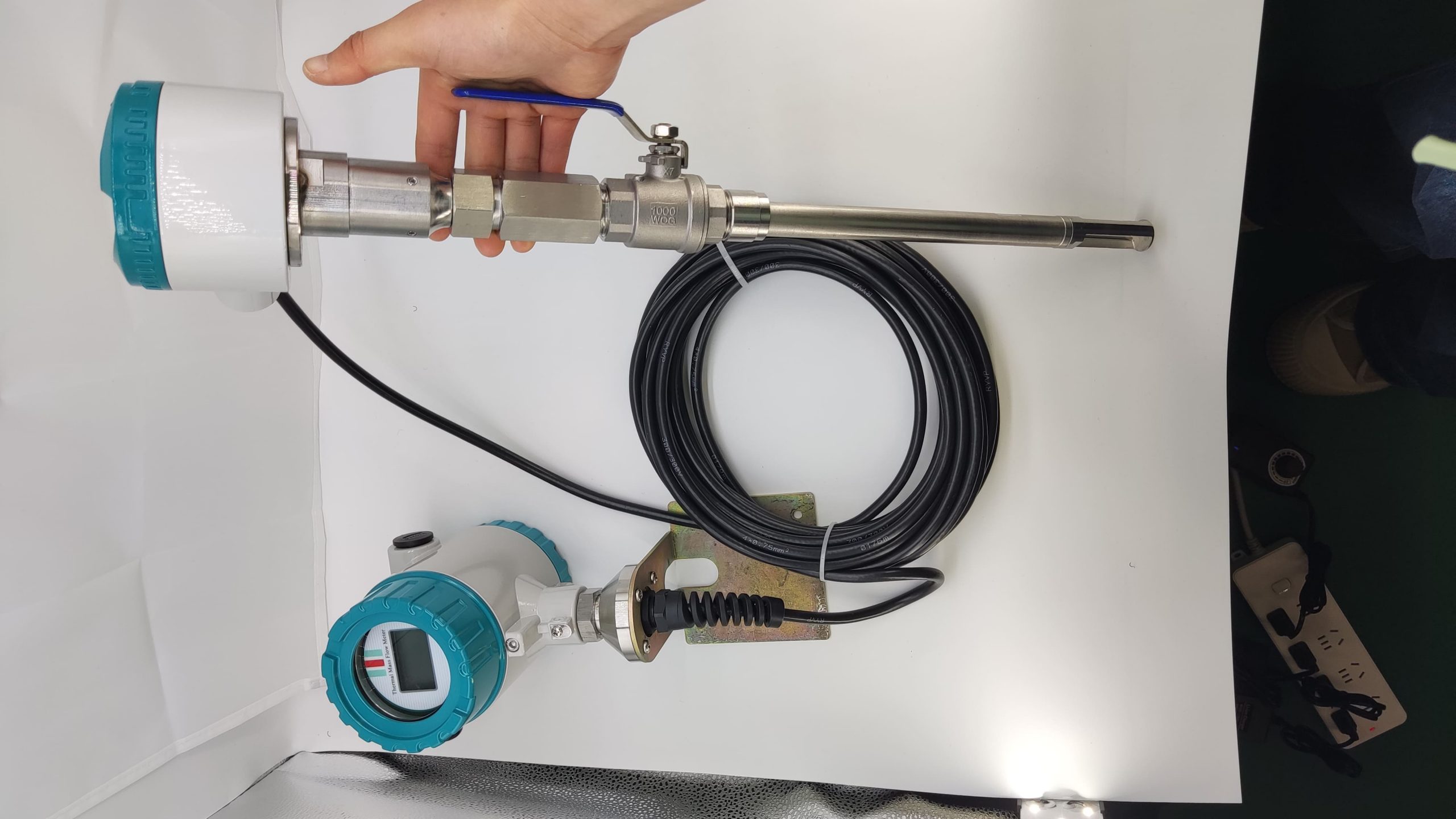
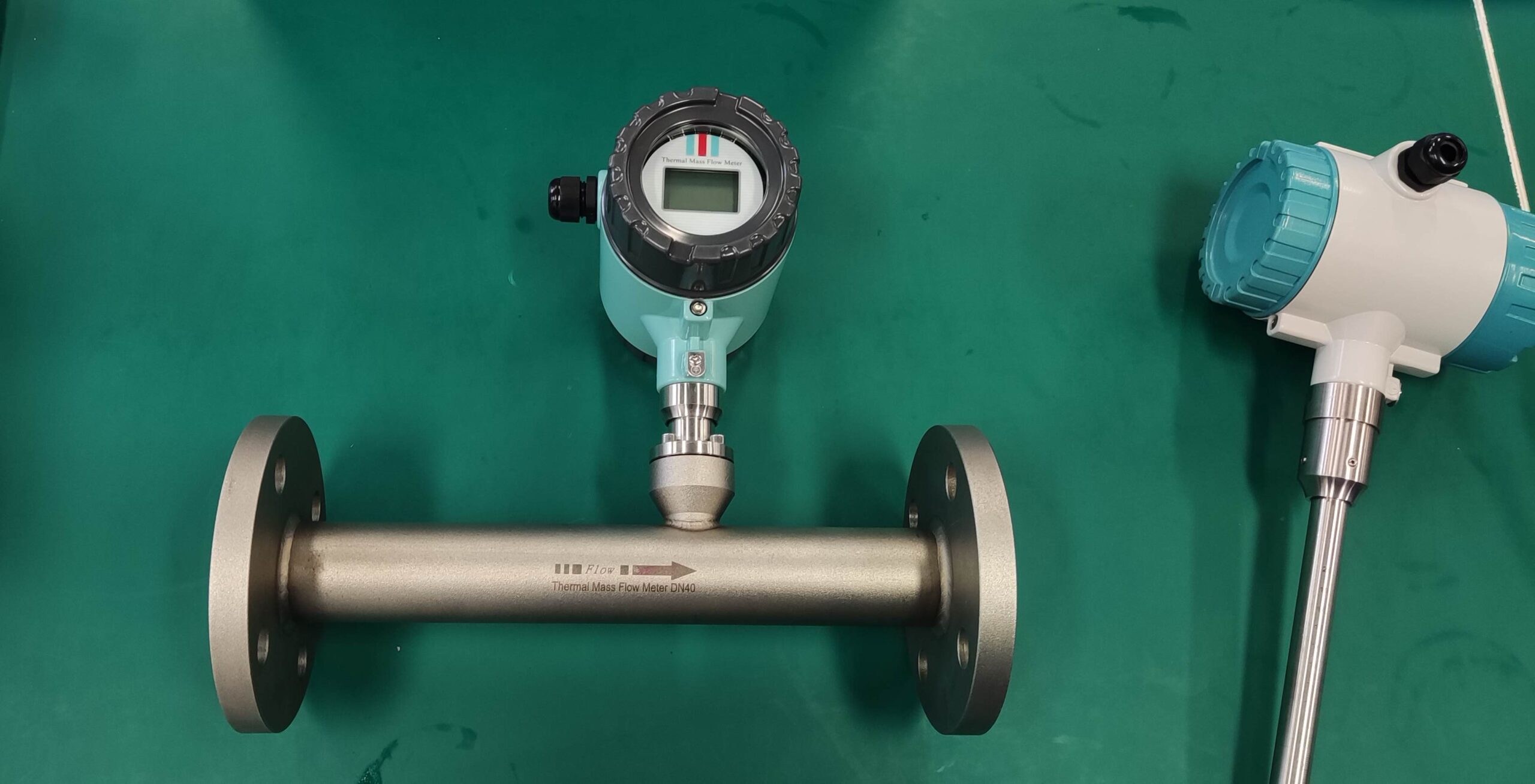
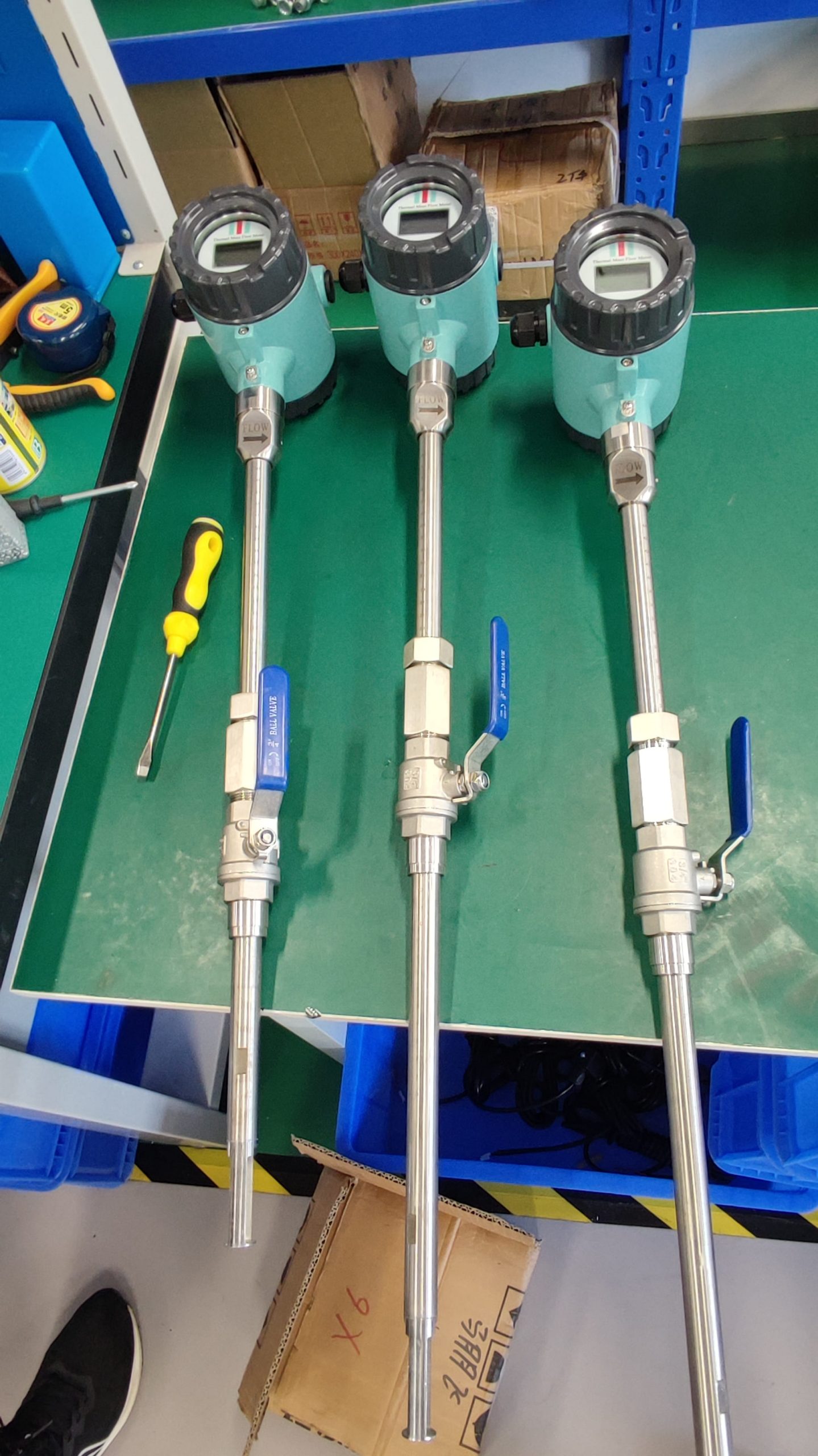
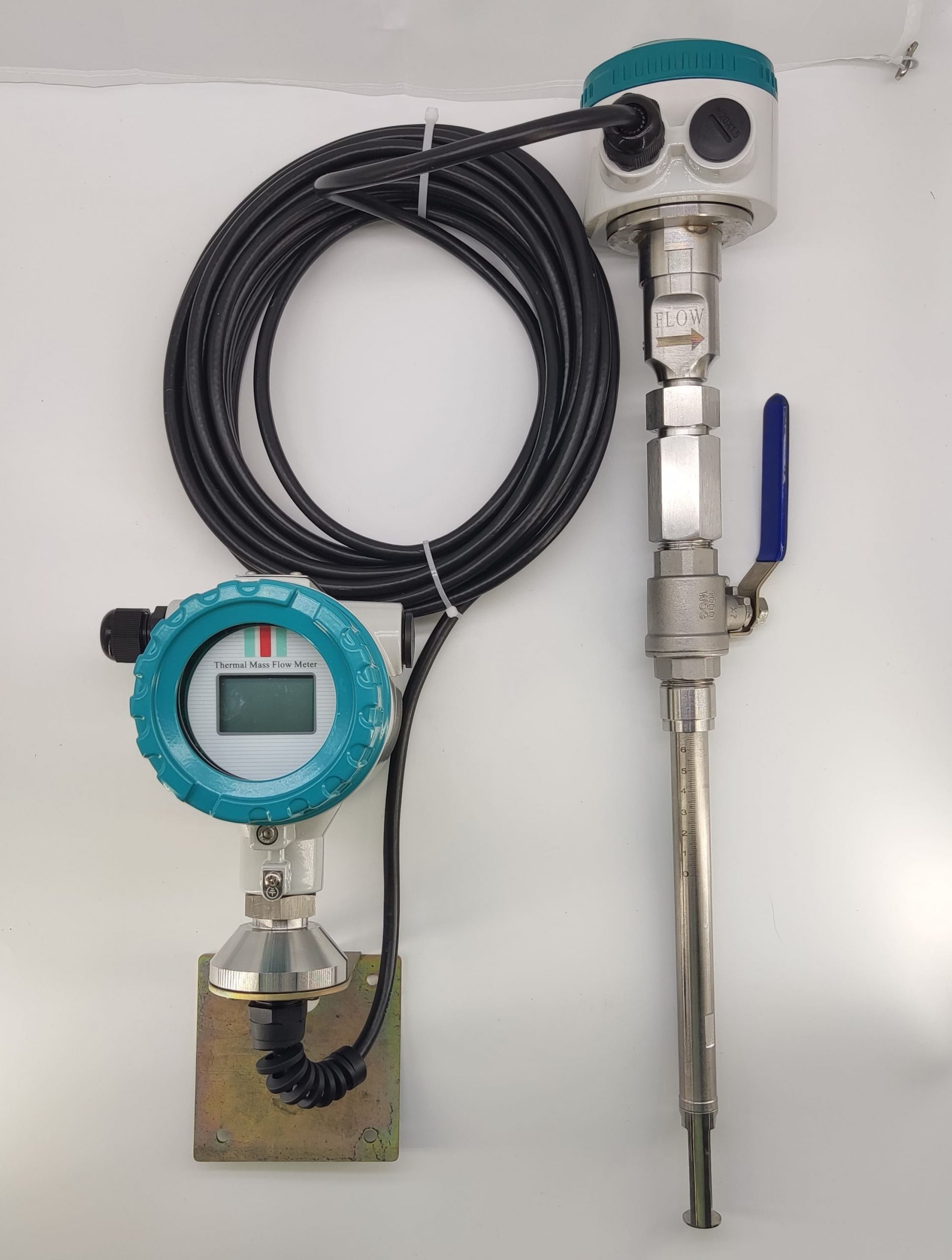
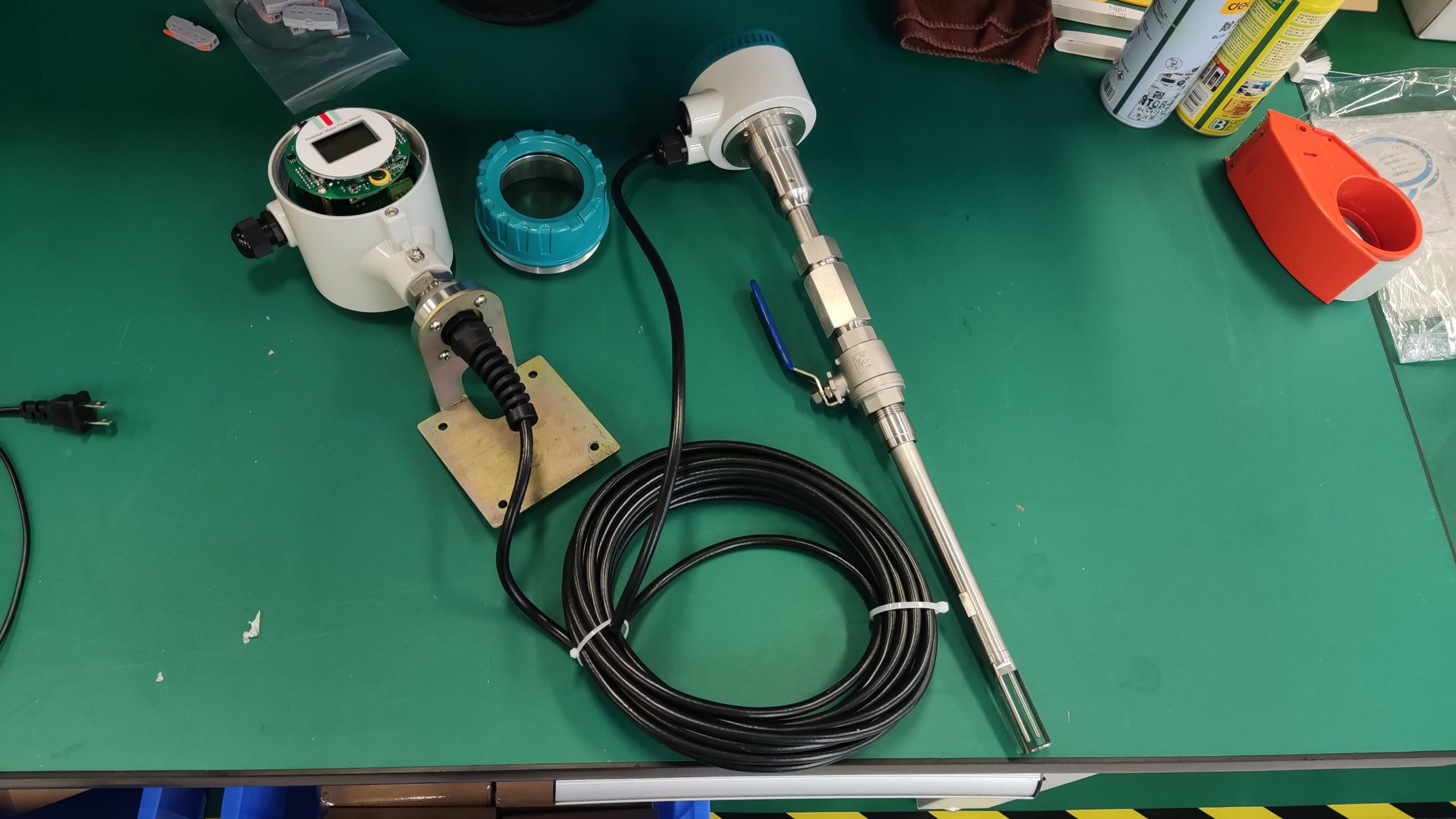
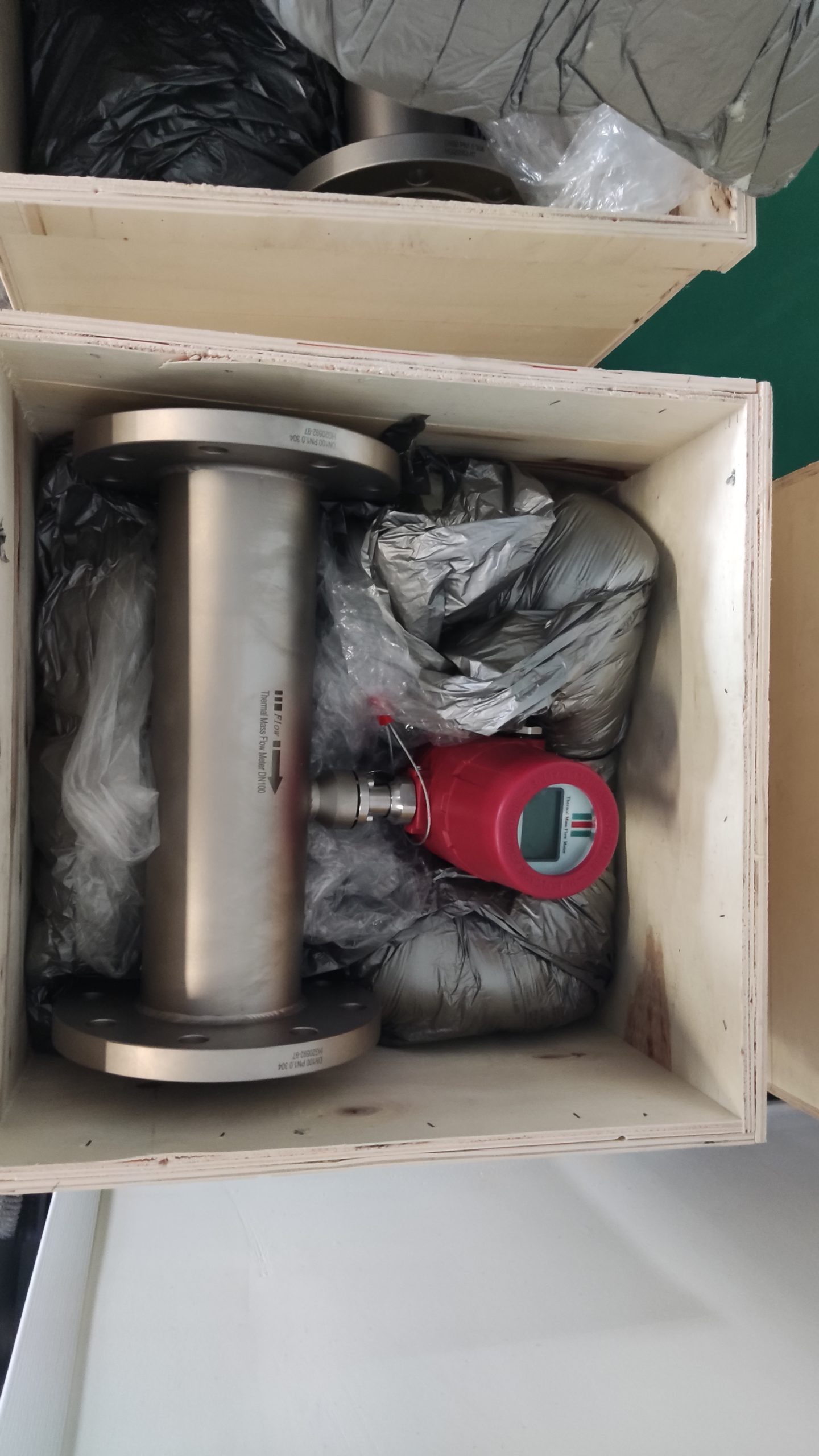
Thermal gas mass flowmeter The thermal distributed flowmeter uses the flow fluid to transfer heat to change the heat conduction distribution effect of measuring the temperature distribution of the tube wall. 2) King’s Law using the heat dissipation (cooling) effect. And because the structure of the detection element extends into the measuring tube, also known as immersion or intrusion type. Some instruments that are inserted from outside the tube into the process tube when in use are called plug-in.
2, thermal gas mass flowmeter advantages
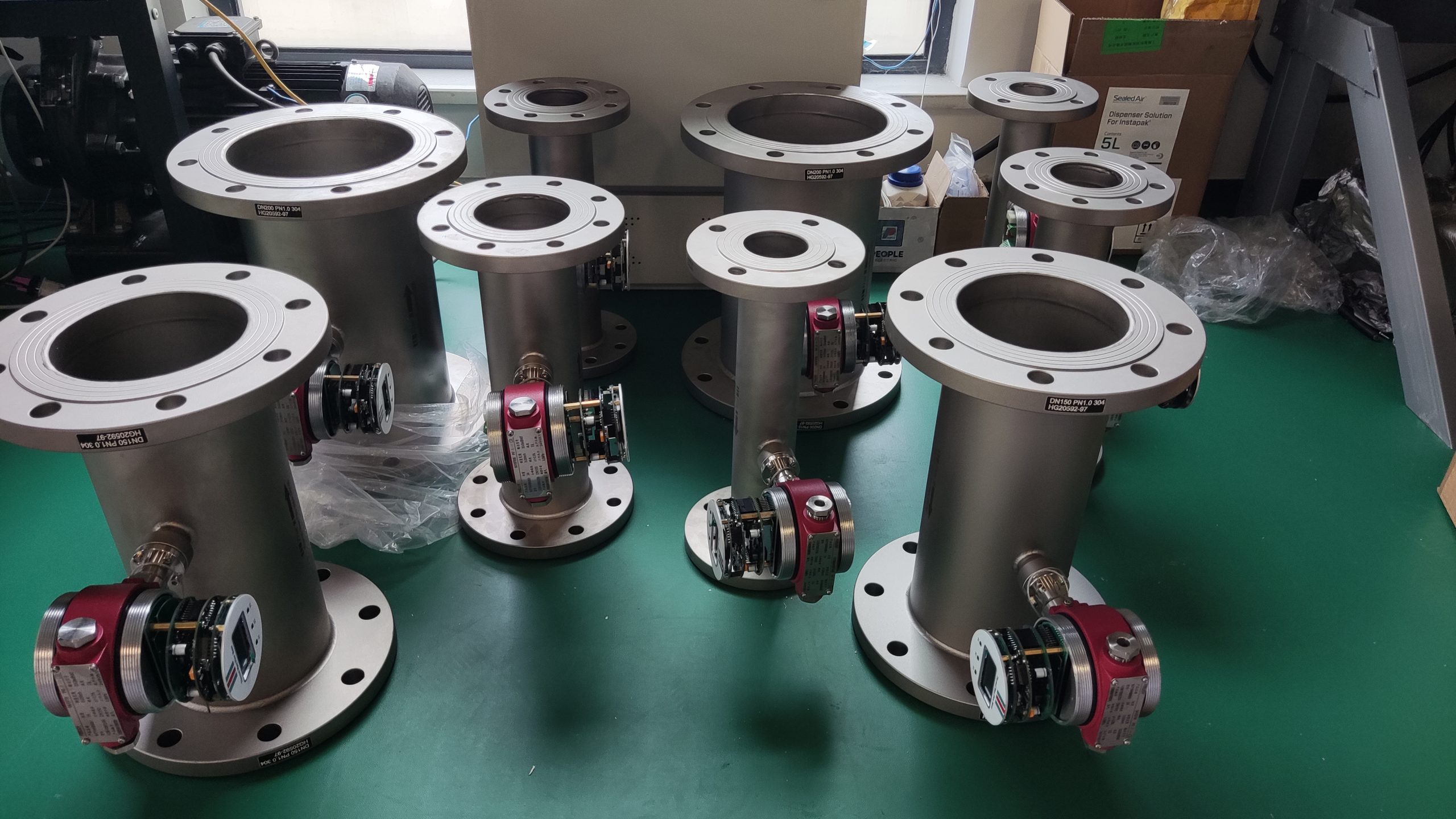
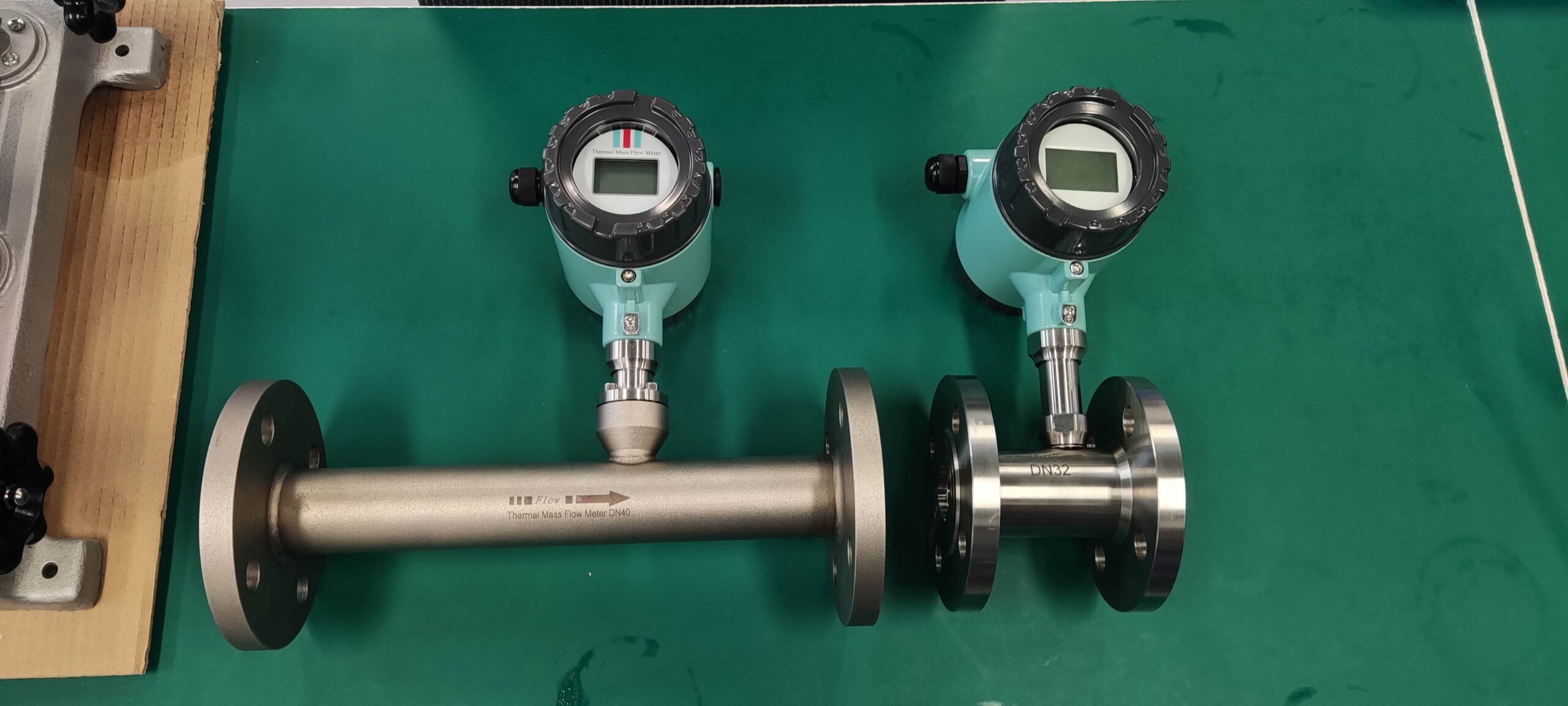
Thermal distributed flowmeter can measure low flow rate (gas 0.02~2m/s) small flow; The immersion type can measure the flow rate of low to medium to high (gas 2 to 60m/s), and the plug-in flowmeter is more suitable for large pipe diameters.
Flowmeter has no moving parts, no shunt pipe heat distributed instrument unimpeded flow parts, pressure loss is small; The heat distribution instrument and immersion instrument with shunt pipe have little pressure loss although there is a choke in the measuring pipe.
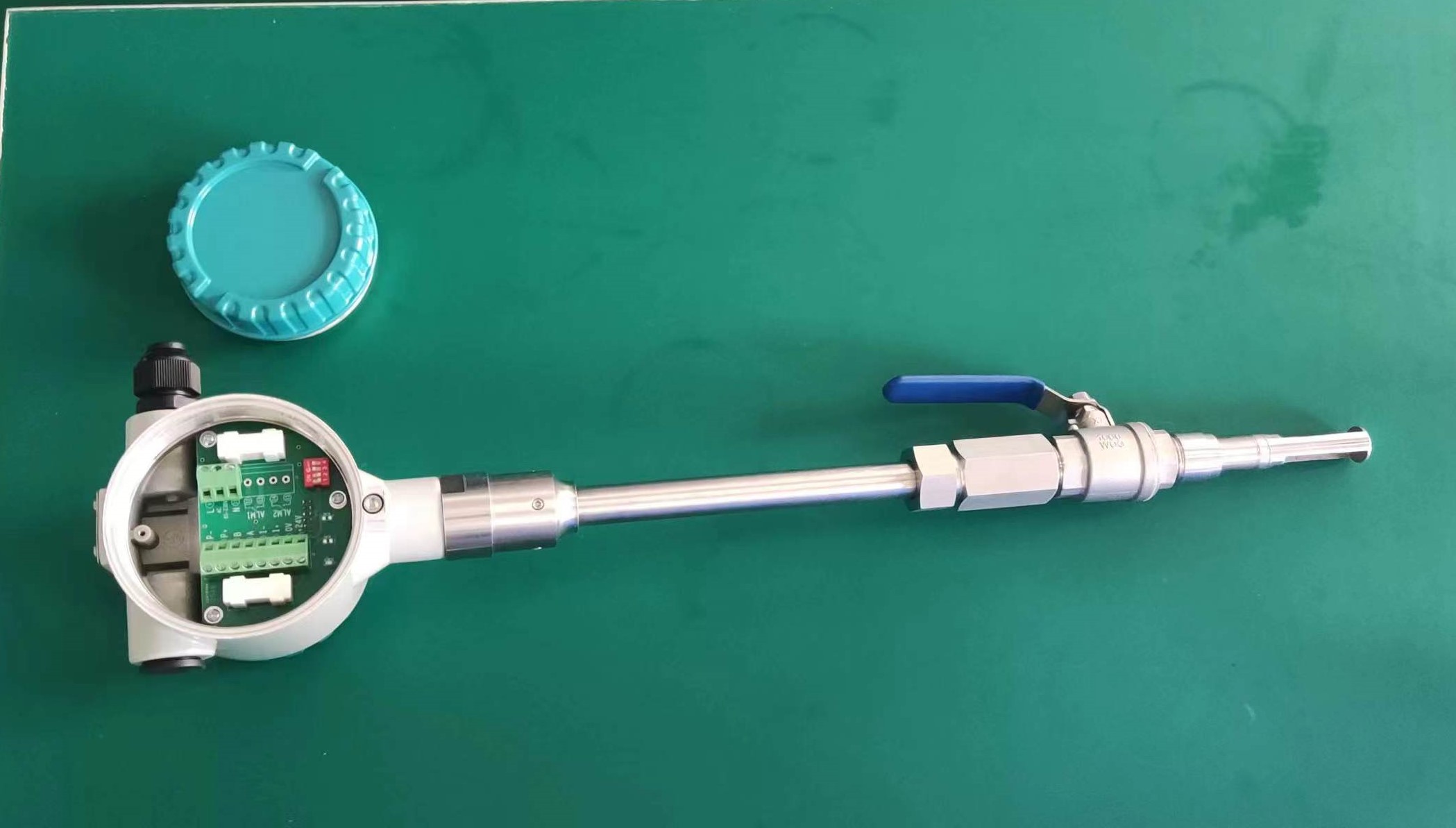
Flowmeter performance is relatively improved. Compared with the derived mass flow meter, there is no need for temperature sensor, pressure sensor and calculation unit, only flow sensor, simple composition, low probability of failure.
The thermal distributed instrument is used for H2, N2, O2, CO, NO and other diatomic gases that are close to ideal gases. It is not necessary to use these gases for special calibration, and the instrument is directly calibrated with air. The experiment shows that the difference is only about 2%. For Ar, He and other monatomic gases, the multiplication factor is 1.4; For other gases, the specific heat capacity can be converted, but the deviation may be slightly larger.
The specific heat capacity of a gas varies with the pressure temperature, but small changes around the temperature and pressure used can be considered constant.
3, thermal gas mass flowmeter shortcomings
Thermal mass flowmeters are slow to respond.
In the place where the composition of the measured gas varies greatly, the measured value will vary greatly due to the change of cp value and thermal conductivity.
For small flow rates, the instrument will introduce considerable heat to the measured gas.
For the thermal distributed flow meter, if the measured gas deposits scale layer on the pipe wall affect the measured value, it must be cleaned regularly; The thin tube type instrument has the disadvantage of easy blockage, and can not be used under normal circumstances.
The use of pulsating flows will be limited.